Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
Rendering Options gibt Ihnen zusätzliche Kontrolle über das Rendering-Gerät. Jedes Rendering-Gerät – PdfDevice, XpsDevice, DocDevice, und ImageDevice – verfügt über einen eigenen Satz von Optionen, die in den Klassen PdfRenderingOptions, XpsRenderingOptions, DocRenderingOptions bzw. ImageRenderingOptions implementiert sind. Sie können die Seitengröße ändern, Ränder und Farben konfigurieren, ein Sicherheitskennwort für ein PDF-Gerät festlegen usw. Die Anpassung der Rendering-Optionen ist wichtig, um das gewünschte Ausgabedokument zu erhalten. So können Sie beispielsweise die Dateigröße verringern, indem Sie die Bildqualität und -auflösung anpassen, oder die Lesbarkeit verbessern, indem Sie Seitenränder und Textformatierung einstellen.
In diesem Artikel wird anhand von C#-Beispielen beschrieben, wie Rendering-Optionen verwendet werden können, um den Rendering-Prozess von HTML zu PDF, XPS, DOCX und Bildern anzupassen. Ein Renderer-Gerät nimmt ein Options-Objekt als Parameter und stellt ein Ausgabedokument dar. Um mehr zu erfahren, lesen Sie bitte den Artikel Rendering Device.
Im Folgenden wird gezeigt, wie Sie mit PdfRenderingOptions die Seitengröße beim Rendern von HTML in PDF anpassen können:
1// Render HTML to PDF in C# with custom page size
2
3string code = @"<span>Hello, World!!</span>";
4
5// Initialize an HTML document from HTML code
6using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(code, ".");
7
8// Create an instance of PdfRenderingOptions and set a custom page size
9PdfRenderingOptions options = new PdfRenderingOptions()
10{
11 PageSetup =
12 {
13 AnyPage = new Page(new Size(Length.FromInches(4),Length.FromInches(2)))
14 }
15};
16
17// Prepare a path to save the converted file
18string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "file-with-custom-page-size.pdf");
19
20// Create an instance of the PdfDevice and specify the options and output file to render
21using PdfDevice device = new PdfDevice(options, savePath);
22
23// Render HTML to PDF
24document.RenderTo(device);Der Namensraum Aspose.Html.Rendering besteht aus zahlreichen Renderer-Objekten und entsprechenden Low-Level-Optionen-Klassen, die für das Rendering von Dokumenten in der IDevice Implementierung verantwortlich sind. Die Klassen RenderingOptions und CssOptions repräsentieren Rendering-Optionen, oder mit anderen Worten, allgemeine Rendering-Optionen. Diese Optionen gelten für alle Rendering-Geräte und alle Rendering-Verfahren von HTML bis PDF, XPS, DOCX und Images:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| PageSetup | This property gets a page setup object and uses it for configuration output page-set. |
| Css | Gets a CssOptions object which is used for configuration of CSS properties processing. |
| BackgroundColor | This property sets the color that will fill the background of every page. By default, this property is Transparent. |
| HorizontalResolution | Sets horizontal resolution for output images in pixels per inch. The default value is 300 dpi. |
| VerticalResolution | Sets vertical resolution for output images in pixels per inch. The default value is 300 dpi. |
| MediaType | Sets MediaType which will be used for media queries resolution during rendering. Default value is Print. |
Im folgenden Beispiel zeigen wir, wie wir die Auflösung der resultierenden Bilddatei steuern können, was sich letztlich auf ihre Größe und Qualität auswirkt:
1// Render HTML to PNG with custom resolution using C#
2
3// Prepare a path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "spring.html");
5
6// Create an instance of HTML document
7using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
8
9// Prepare path to save output file
10string savePath1 = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "output_resolution_50.png");
11string savePath2 = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "output_resolution_300.png");
12
13// Create options for low-resolution screens
14 ImageRenderingOptions options1 = new ImageRenderingOptions()
15 {
16 HorizontalResolution = 50,
17 VerticalResolution = 50
18 };
19
20// Create an instance of Image device
21using ImageDevice device1 = new ImageDevice(options1, savePath1);
22
23// Render HTML to PNG
24document.RenderTo(device1);
25
26
27// Create options for high-resolution screens
28ImageRenderingOptions options2 = new ImageRenderingOptions()
29{
30 HorizontalResolution = 300,
31 VerticalResolution = 300
32};
33
34// Create an instance of Image device
35using ImageDevice device2 = new ImageDevice(options2, savePath2);
36
37// Render HTML to PNG
38document.RenderTo(device2);Das nächste Bild zeigt das Ergebnis des Renderings der Datei spring.html mit 50 dpi und 300 dpi Auflösung:

CSS der Medientyp ist ein wichtiges Merkmal, das angibt, wie ein Dokument auf verschiedenen Medien dargestellt werden soll: auf dem Bildschirm, auf Papier, mit einer Blindenschriftvorrichtung, usw. Es gibt mehrere Möglichkeiten, den Medientyp für eine Formatvorlage anzugeben: über verknüpfte Formatvorlagen oder durch Inlining:
Linked Style Sheet
1 <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" media="print" href="style.css">Inline Style Sheet
1<style type="text/css">
2@media print {
3 body{ color: #000000; }
4}
5</style>Aspose.HTML API unterstützt diese Funktion, so dass Sie HTML-Dokumente so konvertieren können, wie sie auf dem Bildschirm oder im Druck aussehen, indem Sie die entsprechenden Medientypen und Stilvorlagen anwenden. Das folgende Beispiel zeigt, wie man den Medientyp einrichtet:
1// Create an option class
2var options = new PdfRenderingOptions();
3
4// Set the 'screen' media-type
5options.Css.MediaType = MediaType.Screen;Bitte beachten Sie, dass der Standardwert von CssOptions.MediaType Print ist. Das bedeutet, dass das Dokument durch Anwendung von Stilvorlagen für das Druckgerät konvertiert wird und wie auf Papier aussieht (Sie können die Druckvorschau Ihres Browsers verwenden, um den Unterschied zu sehen). Wenn Sie also möchten, dass das Dokument so aussieht, wie es auf dem Bildschirm dargestellt wird, sollten Sie MediaType.Screen. verwenden
Die Eigenschaft BackgroundColor wird verwendet, um die Hintergrundfarbe des Ausgabedokuments festzulegen, wenn HTML-basierte Dateien in PDF-, XPS-, DOCX- oder Bildformate gerendert werden. Standardmäßig ist die Hintergrundfarbe transparent. Sie können diese Eigenschaft jedoch mit der Klasse RenderingOptions auf eine bestimmte Farbe einstellen.
1// Render HTML to PDF with custom background color using C#
2
3// Prepare path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "spring.html");
5
6// Prepare a path to save the converted file
7string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "spring.pdf");
8
9// Create an instance of HTML document
10using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
11
12// Initialize options with 'Azure' as a background-color
13PdfRenderingOptions options = new PdfRenderingOptions()
14{
15 BackgroundColor = System.Drawing.Color.Azure
16};
17
18// Create an instance of PDF device
19using PdfDevice device = new PdfDevice(options, savePath);
20
21// Render HTML to PDF
22document.RenderTo(device);Die Seiteneinrichtung ist eine Reihe von Parametern, die das Layout einer gedruckten Seite bestimmen. Diese Parameter umfassen alles von der Seitengröße, den Rändern und der automatischen Größenanpassung bis hin zu den @Seitenprioritätsregeln. Mit diesen Parametern können Sie ganz einfach ein individuelles Layout für jede Seite einrichten.
Das nächste Beispiel zeigt, wie man ein PDF-Dokument mit unterschiedlichen Seitengrößen für die linke und rechte Seite erstellt (siehe die Ergebnisvisualisierung in Abbildung (a) unten):
1// Render HTML to PDF with custom page size using C#
2
3// Prepare HTML code
4string code = @"<style>div { page-break-after: always; }</style>
5<div>First Page</div>
6<div>Second Page</div>
7<div>Third Page</div>
8<div>Fourth Page</div>";
9
10// Initialize an HTML document from the HTML code
11using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(code, ".");
12
13// Create the instance of Rendering Options and set a custom page size
14PdfRenderingOptions options = new PdfRenderingOptions();
15options.PageSetup.SetLeftRightPage(
16 new Page(new Size(400, 150)),
17 new Page(new Size(400, 50))
18);
19
20// Prepare a path to save the converted file
21string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "output-custom-page-size.pdf");
22
23// Create the PDF Device and specify options and output file
24using PdfDevice device = new PdfDevice(options, savePath);
25
26// Render HTML to PDF
27document.RenderTo(device);In einigen Fällen kann der Inhalt der HTML-Seite breiter sein als die mit den Optionen festgelegte Seitengröße. Wenn Sie den Seiteninhalt nicht abschneiden möchten, können Sie die Eigenschaft AdjustToWidestPage der Klasse PageSetup verwenden. Das folgende Beispiel zeigt, wie man die Seitengröße an den Inhalt anpasst (siehe die Ergebnisvisualisierung in Abbildung (b) unten):
1// Render HTML to PDF and adjust to the widest page with C#
2
3// Prepare HTML code
4string code = @"<style>
5 div { page-break-after: always; }
6</style>
7<div style='border: 1px solid red; width: 300px'>First Page</div>
8<div style='border: 1px solid red; width: 500px'>Second Page</div>";
9
10// Initialize an HTML document from the HTML code
11using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(code, ".");
12
13// Create the instance of Rendering Options and set a custom page-size
14PdfRenderingOptions options = new PdfRenderingOptions();
15options.PageSetup.AnyPage = new Page(new Size(400, 200));
16
17// Enable auto-adjusting for the page size
18options.PageSetup.AdjustToWidestPage = true;
19
20// Prepare a path to save the converted file
21string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "output-widest-page-size.pdf");
22
23// Create the PdfDevice and specify options and output file
24using PdfDevice device = new PdfDevice(options, savePath);
25
26// Render HTML to PDF
27document.RenderTo(device);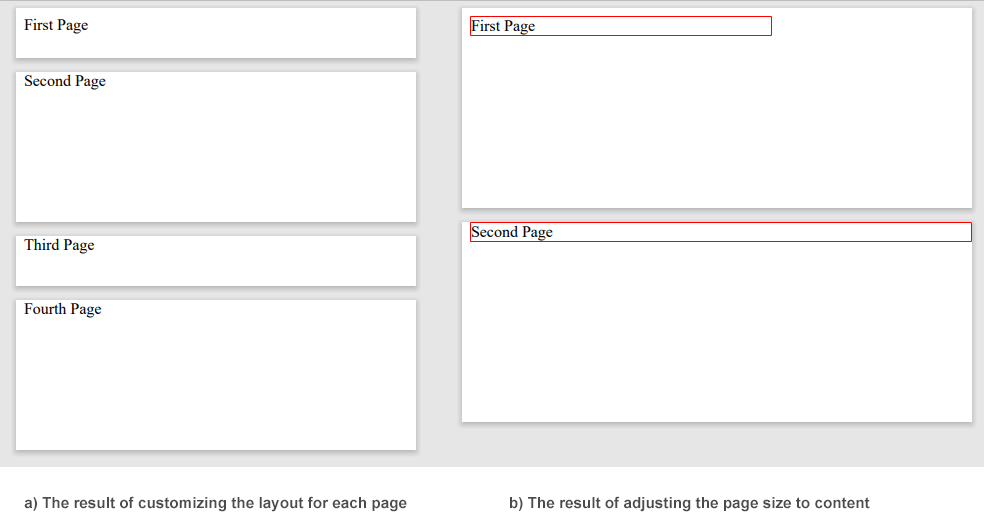
Um mehr über den Rendering-Prozess zu erfahren, lesen Sie bitte den Artikel Rendering Device.
Wenn Sie wissen möchten, wie Sie die Rendering-Optionen nutzen können, um die Größe der Dokumentseiten an die Größe des Inhalts anzupassen und umgekehrt, lesen Sie bitte den Artikel Wie kann ich die Größe des Dokuments während der Konvertierung von HTML ändern?
Die Klasse
PdfRenderingOptions unterstützt neben allgemeinen Optionen auch einige spezifische Parameter wie JpegQuality, DocumentInfo, Encryption und FormFieldBehaviour.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| JpegQuality | Specifies the quality of JPEG compression for images. The default value is 95. |
| DocumentInfo | This property contains information about the output PDF document. |
| Encryption | This property gets or sets encryption details. If it is not set, then no encryption will be performed. |
| FormFieldBehaviour | This property specifies the behavior of form fields in the output PDF document. |
Die Eigenschaft FormFieldBehaviour wird verwendet, um das Verhalten von Formularfeldern in einem PDF-Dokument festzulegen. Was es bedeutet, eine PDF-Datei zu reduzieren und wie man dies mit der Aspose.HTML for .NET-Bibliothek macht, erfahren Sie im Artikel
PDF reduzieren.
Der folgende C#-Code zeigt, wie eine PDF-Ausgabedatei mit Hilfe der Klasse “PdfRenderingOptions” verschlüsselt werden kann:
1// Render HTML to PDF with password protection using C#
2
3// Prepare a path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "document.html");
5
6// Initialize the HTML document from the file
7using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
8
9// Create the instance of Rendering Options
10PdfRenderingOptions options = new PdfRenderingOptions();
11
12// Set the permissions to the file
13options.Encryption = new PdfEncryptionInfo(
14 "user_pwd",
15 "owner_pwd",
16 PdfPermissions.PrintDocument,
17 PdfEncryptionAlgorithm.RC4_128);
18
19// Prepare a path to save the converted file
20string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "output-options.pdf");
21
22// Create an instance of the PdfDevice and specify options and output file
23using PdfDevice device = new PdfDevice(options, savePath);
24
25// Render HTML to PDF
26document.RenderTo(device);Das obige Beispiel zeigt, wie man eine neue
PdfRenderingOptions Instanz erstellt und Verschlüsselungsoptionen für eine PDF-Ausgabedatei festlegt. Dazu sollten Sie den
PdfEncryptionInfo(userPassword, ownerPassword, permissions, encryptionAlgorithm) Konstruktor verwenden, um ein PdfEncryptionInfo Objekt zu erstellen, das die Verschlüsselungseinstellungen für die PDF-Datei definiert. Der Konstruktor benötigt vier Parameter:
– userPassword und ownerPassword, die zum Öffnen und Arbeiten mit der PDF-Datei erforderlich sind;
permissions - eine Reihe von erlaubten Berechtigungen für eine PDF-Datei. In diesem Fall ist PdfPermissions.PrintDocument angegeben, wodurch der Benutzer das Dokument drucken kann;encryptionAlgorithm - der Verschlüsselungsalgorithmus, mit dem die PDF-Datei gesichert wird. In diesem Fall wird PdfEncryptionAlgorithm.RC4_128 verwendet, ein 128-Bit-RC4-Verschlüsselungsalgorithmus.Die Klasse ImageRenderingOptions unterstützt alle allgemeinen Optionen und ermöglicht die Konfiguration spezifischer Optionen wie Anti-Aliasing, Text-Rendering-Konfiguration, Bildformatauswahl und Bildkomprimierung.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Compression | Sets Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) Compression. By default, this property is LZW. |
| Format | Sets the ImageFormat (JPG, PNG, BMP, TIFF, or GIF). By default, this property is PNG. |
| UseAntialiasing | This property sets the rendering quality for the image. |
| Text | Gets a TextOptions object which is used for configuration of text rendering. |
Betrachten wir, wie man ein spezielles ImageRenderingOptions-Objekt verwendet, um die Rendering-Qualität für das Bild zu konfigurieren. Das folgende Beispiel zeigt, wie man die Auflösung und das Antialiasing für das resultierende Bild ändern kann.
1// Render HTML to JPG with custom resolution and antialiasing settings with C#
2
3// Prepare a path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "color.html");
5
6// Initialize the HTML document from the file
7using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
8
9// Create an instance of Rendering Options
10ImageRenderingOptions options = new ImageRenderingOptions(ImageFormat.Jpeg)
11{
12 // Disable smoothing mode
13 UseAntialiasing = false,
14
15 // Set the image resolution as 75 dpi
16 VerticalResolution = Resolution.FromDotsPerInch(75),
17 HorizontalResolution = Resolution.FromDotsPerInch(75),
18};
19
20// Prepare a path to save the converted file
21string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "color-options.jpg");
22
23// Create an instance of the ImageDevice and specify options and output file
24using ImageDevice device = new ImageDevice(options, savePath);
25
26// Render HTML to JPG
27document.RenderTo(device);Die von unserer Bibliothek erzeugten XPS-Dateien haben keine spezifischen Parameter. Alle Parameter von XpsRenderingOptions werden von der Basisklasse RenderingOptions geerbt und hier beschrieben
1// Render HTML to XPS with custom page size using C#
2
3// Prepare a path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "document.html");
5
6// Initialize the HTML document from the file
7using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
8
9// Create an instance of Rendering Options
10XpsRenderingOptions options = new XpsRenderingOptions();
11options.PageSetup.AnyPage = new Page(new Size(Length.FromInches(5), Length.FromInches(2)));
12
13// Prepare a path to save the converted file
14string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "document-options.xps");
15
16// Create an instance of the XpsDevice and specify options and output file
17using XpsDevice device = new XpsDevice(options, savePath);
18
19// Render HTML to XPS
20document.RenderTo(device);Die Klasse
DocRenderingOptions unterstützt alle allgemeinen Optionen und ermöglicht es Ihnen, die Eigenschaften FontEmbeddingRule und DocumentFormat für die Ausgabedatei anzupassen.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| FontEmbeddingRule | This property gets or sets the font embedding rule. Available values are Full and None. The default value is None. |
| DocumentFormat | This property gets or sets the file format of the output document. The default value is DOCX. |
Das folgende Beispiel zeigt, wie Sie die Rendering-Optionen für Ausgabedokumente anpassen können, indem Sie die Regel für die Seitengröße und die Schrifteinbettung festlegen:
1// Render HTML to DOCX in C# with custom page settings
2
3// Prepare a path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "nature.html");
5
6// Initialize the HTML document from the file
7using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
8
9// Create an instance of Rendering Options and set a custom page size
10DocRenderingOptions options = new DocRenderingOptions();
11options.PageSetup.AnyPage = new Page(new Size(Length.FromInches(8), Length.FromInches(10)));
12options.FontEmbeddingRule = (FontEmbeddingRule.Full);
13
14// Prepare a path to save the converted file
15string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "nature-options.docx");
16
17// Create an instance of the DocDevice and specify options and output file
18using DocDevice device = new DocDevice(options, savePath);
19
20// Render HTML to DOCX
21document.RenderTo(device);Sie können die vollständigen C#-Beispiele und Datendateien von GitHub herunterladen.
Aspose.HTML bietet kostenlose Online- Konverter, die HTML-, XHTML-, MHTML-, EPUB-, XML- und Markdown-Dateien in eine Reihe von gängigen Formaten konvertieren können. Sie können Ihre HTML-basierten Dokumente ganz einfach in PDF, XPS, DOCX, JPG, PNG, GIF, TIFF und andere konvertieren. Wählen Sie einfach eine Datei aus, wählen Sie das zu konvertierende Format, und schon sind Sie fertig. Und das Beste daran: Es ist völlig kostenlos!
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.