什么是XPS文件? |知识库
介绍
从有关 页面描述语言的文章中,您发现XPS是静态PDL之一。这里的文章将为您提供有关XPS格式和XPS文件的更多信息,它们的特殊性,结构和用法。
什么是XPS格式?
XPS或缩写的XML纸张规范文件表示ZIP压缩的资源包(图像,字体等)和基于XML的文件,可以引用这些资源。基于XML的文件存储了包装的各个部分之间的文档和页面的内容以及关系。 XPS格式的重要特征是,所有必要的文档资源都存储在与文档本身同一包中。
XPS格式文件的典型结构
如果我们打开任何带有ZIP实用程序的XPS文件,我们可以查看以下结构:
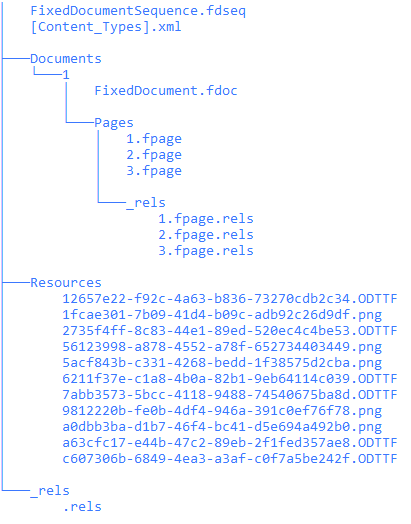
“固定文档序列.fdseq”是包装树的根。它包含包装中的文档列表。
<FixedDocumentSequence xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/xps/2005/06">
<DocumentReference Source="Documents/1/FixedDocument.fdoc" />
</FixedDocumentSequence>
在上面的示例中,固定文档序列仅包含一个文档,但可以包含更多文档。
“ [content_type] .xml”包含在相应XML模式中描述的软件包零件的扩展和内容类型之间的映射:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Types xmlns="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/package/2006/content-types">
<Default Extension="fdseq" ContentType="application/vnd.ms-package.xps-fixeddocumentsequence+xml" />
<Default Extension="rels" ContentType="application/vnd.openxmlformats-package.relationships+xml" />
<Default Extension="fdoc" ContentType="application/vnd.ms-package.xps-fixeddocument+xml" />
<Default Extension="fpage" ContentType="application/vnd.ms-package.xps-fixedpage+xml" />
<Default Extension="ODTTF" ContentType="application/vnd.ms-package.obfuscated-opentype" />
<Default Extension="png" ContentType="image/png" />
</Types>
“文档”零件位于“文档”文件夹中,也位于其自己的文件夹中,其名称是“固定文档序列”部分中文档的索引。
Document的文件夹还包含“ fpage”或“固定页面”零件和具有页面关系的文件夹。
“ fixeDocument.fdoc”包含“固定页面”部分和“链接目标”列表上的引用。
<FixedDocument xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/xps/2005/06">
<PageContent Source="Pages/1.fpage">
<PageContent.LinkTargets>
<LinkTarget Name="Page1" />
<LinkTarget Name="Conditions" />
<LinkTarget Name="Rfd_Conditions" />
<LinkTarget Name="Label2" />
......................................
<PageContent.LinkTargets>
</PageContent>
<PageContent Source="Pages/2.fpage">
<PageContent.LinkTargets>
<LinkTarget Name="Page2" />
<LinkTarget Name="Rectangle" />
<LinkTarget Name="peQ5" />
......................................
<PageContent.LinkTargets>
</PageContent>
<PageContent Source="Pages/3.fpage">
<PageContent.LinkTargets>
<LinkTarget Name="Page3" />
<LinkTarget Name="Followup" />
<LinkTarget Name="Rfd_Followup" />
<LinkTarget Name="Label41" />
......................................
</PageContent.LinkTargets>
</PageContent>
</FixedDocument>
linktarget元素定义了可以通过超链接解决的指定页面描述元素。
“固定页面”包含一个静态页面描述,其中任何图形元素都由XML元素表示,并具有所有必要的属性。 以下是索引1的固定页面的减少内容。
<FixedPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/xps/2005/06" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/xps/2005/06/resourcedictionary-key" xml:lang="en-us" Width="784" Height="1024">
<FixedPage.Resources>
<ResourceDictionary>
<ImageBrush x:Key="b0" ViewportUnits="Absolute" TileMode="None" ViewboxUnits="Absolute" Viewbox="0,0,150,84" Viewport="0,0,150,84" ImageSource="/Resources/5acf843b-c331-4268-bedd-1f38575d2cba.png" />
<ImageBrush x:Key="b1" ViewportUnits="Absolute" TileMode="None" ViewboxUnits="Absolute" Viewbox="0,0,308,222" Viewport="0,0,306.612612612613,221" ImageSource="/Resources/56123998-a878-4552-a78f-652734403449.png" />
<LinearGradientBrush x:Key="b2" StartPoint="1,1" EndPoint="1,29" ColorInterpolationMode="SRgbLinearInterpolation" MappingMode="Absolute" SpreadMethod="Pad">
<LinearGradientBrush.GradientStops>
<GradientStop Color="sc#0.980392158, 1, 1, 1" Offset="0" />
<GradientStop Color="sc#0.521568656, 1, 1, 1" Offset="1" />
</LinearGradientBrush.GradientStops>
</LinearGradientBrush>
<ImageBrush x:Key="b3" ViewportUnits="Absolute" TileMode="None" ViewboxUnits="Absolute" Viewbox="-1.77635683940025E-15,0,30.004187214593,28.0039080669535" Viewport="0,0,34,31.7333333333333" ImageSource="/Resources/1fcae301-7b09-41d4-b09c-adb92c26d9df.png" />
<ImageBrush x:Key="b4" ViewportUnits="Absolute" TileMode="None" ViewboxUnits="Absolute" Viewbox="0,0,33.92,42.24" Viewport="0,0,33.92,42.24" ImageSource="/Resources/9812220b-fe0b-4df4-946a-391c0ef76f78.png" />
</ResourceDictionary>
</FixedPage.Resources>
<Canvas RenderTransform="0.96150234741784,0,0,0.96150234741784,0,0">
<Canvas Name="Page1" RenderTransform="1.0400390625,0,0,1.0400390625,0,0">
<Path Fill="#FFFFFFFF" Data="M0,0L784,0 784,1024 0,1024Z" />
<Canvas Clip="M0,0L784,0 784,1024 0,1024Z">
<Canvas Name="Rfd_Conditions" RenderTransform="1,0,0,1,51,712" />
<Glyphs Name="Label2" OriginX="517.83" OriginY="22.0533333333333" FontRenderingEmSize="10" FontUri="/Resources/6211f37e-c1a8-4b0a-82b1-9eb64114c039.ODTTF" UnicodeString="Patient Name:" Fill="#FF404040" />
<Glyphs Name="Label3" OriginX="556.08" OriginY="42.0533333333333" FontRenderingEmSize="10" FontUri="/Resources/6211f37e-c1a8-4b0a-82b1-9eb64114c039.ODTTF" UnicodeString="Acct#:" Fill="#FF404040" />
<Path Name="Line" Stroke="#FF00529B" StrokeThickness="1" StrokeMiterLimit="10" Fill="#00FFFFFF" RenderTransform="1,0,0,1,41,206" Data="M0,0.5L680,0.5" />
<Path Name="Image" Fill="{StaticResource b0}" RenderTransform="1,0,0,1,15,7" Data="M0,0L150,0 150,84 0,84Z" />
<Canvas Name="HxConditionsDissatisfiedPatients" RenderTransform="1,0,0,1,53,714">
<Path Stroke="#FF000000" StrokeThickness="1" StrokeMiterLimit="10" RenderTransform="0.8,0,0,0.8,2.4,2.4" Data="M0.5,0.5L23.5,0.5 23.5,23.5 0.5,23.5Z" />
<Glyphs OriginX="33" OriginY="16.16" FontRenderingEmSize="12" FontUri="/Resources/2735f4ff-8c83-44e1-89ed-520ec4c4be53.ODTTF" UnicodeString="Dissatisfied patients" Fill="#FF404040" />
</Canvas>
<Path Name="Rectangle3" Stroke="#FF808080" StrokeThickness="1" StrokeMiterLimit="10" Fill="#00FFFFFF" RenderTransform="1,0,0,1,74,951" Data="M0.5,0.5L329.5,0.5 329.5,44.5 0.5,44.5Z" />
<Canvas Name="Conditions" RenderTransform="1,0,0,1,51,712" />
<Path Fill="#FF0066CC" Data="M0,12.77L330.4,12.77 330.4,13.47 0,13.47Z" />
</Canvas>
<PathGeometry x:Key="all">
<PathFigure StartPoint="20,70" IsClosed="true">
<PolyLineSegment Points="250,70 250,300 20,300" />
</PathFigure>
<PathFigure StartPoint="135,70">
<ArcSegment Size="115,115" IsLargeArc="true" RotationAngle="0" SweepDirection="Counterclockwise" Point="135,300" />
<ArcSegment Size="115,115" IsLargeArc="true" RotationAngle="0" SweepDirection="Counterclockwise" Point="135,70" />
</PathFigure>
<PathFigure StartPoint="135,70">
<PolyQuadraticBezierSegment Points="270,185 135,300" />
<PolyQuadraticBezierSegment Points="0,185 135,70" />
</PathFigure>
<PathFigure StartPoint="250,185">
<PolyBezierSegment Points="173.34,85 96.67,285 20,185" />
<PolyBezierSegment Points="96.67,85 173.34,285 250,185" />
</PathFigure>
</PathGeometry>
</Canvas>
</Canvas>
</Canvas>
</Canvas>
<Path FixedPage.NavigateUri="http://www.bottomline.com" Fill="#00000000" Data="F1M170,77L500.4,77 500.4,91.58 170,91.58Z" />
</FixedPage>
如我们所见,有几个图形元素:“路径”,“ pategemetry”和“ glyphs”以及将其他图形元素分组为相同的转换和剪辑,“ canvas”的元素。 “路径”和“ pategemetry”可以包含触发的矢量图形形状或/并填充纯色或复杂刷,例如梯度或图像刷。梯度刷可以是线性的,也可以是径向,图像刷总是在“资源”文件夹中的图像上包含引用。现在有一个单独的图形元素用于栅格图像。填充“ ImageBrush”的“路径”元素用于此目的。
在该页面描述片段中,我们还能发现另一个值得注意的地方:文本仅作为属性“unicodeString”包含在“Glyphs”元素中,而不是像 XML 或 HTML 那样作为该元素的子元素。因此,内容与标记并未分离。这就是为什么 XPS 不能被称为标记语言的原因。
XPS 文件和 XML 的语法均采用增强巴科斯范式 (ABNF)。
页面使用的资源位于单独的元素“ fixepage.resources”中。
那些在远程(此页面的远程不适合此页面)文件的页面资源,例如,字体或图像,也具有关系文件中的“*.fpage.rels”中的相应说明。
资源存储在具有“资源”名称的文件夹中。这样的文件夹可以位于不同级别的包装结构上。通常,字体和图像包含在那里。所有字体均具有trueType字体的 *.ttf扩展名,也具有 *.odttf扩展名,用于混淆的truetype字体。通过未经许可在其他地方抑制字体提取并在其他地方使用该字体的混淆。此外,TrueType字体的XPS仅支持 *.odttc扩展名的TrueType字体集合。不支持其他字体类型。图像可以以PNG,JPEG,TIFF或WDP(Windows Media Photo Images)格式使用。 有时在其他资源中 .DIC文件被满足。这是词典部分。它包含不需要单独文件的所谓“远程资源”的文档或页面。从某种意义上说,远程将它们存储在“文档”部分中,而是在外部文件夹中。在这些资源中,可以是刷子,pathgeemetry,matrixTransform元素等。文档中使用的ICC颜色也将“.ICC”文件放在“资源”文件夹中。
XPS文件的可选零件。
XPS文件可以包含其他用于导航,打印和签名的零件。
XPS文档结构。
文档零件的导航是通过“文档”部分及其子元素“记录线”,“故事”,“故事段”, “段落”,“表”和“名字元素”。文档结构与页面一起存储在文档文件夹中。
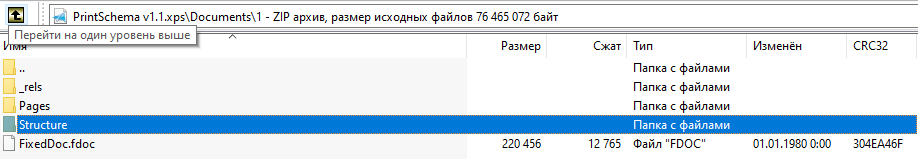
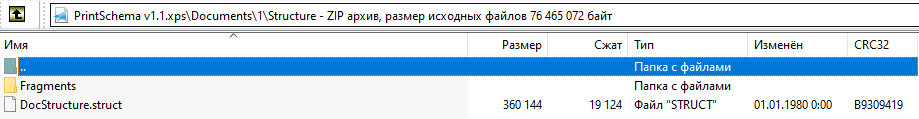
“ docstructure.structure”文件包含带有故事范围的引用的记录输出线。
<DocumentStructure xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/xps/2005/06/documentstructure">
<DocumentStructure.Outline>
<DocumentOutline xml:lang="en-US">
<OutlineEntry OutlineLevel="1" Description="Print Schema Specification" OutlineTarget="../FixedDoc.fdoc#PG_1_LNK_1069"/>
<OutlineEntry OutlineLevel="1" Description="Contents" OutlineTarget="../FixedDoc.fdoc#PG_8_LNK_1070"/>
<OutlineEntry OutlineLevel="2" Description="About This Specification" OutlineTarget="../FixedDoc.fdoc#PG_24_LNK_1074"/>
<OutlineEntry OutlineLevel="2" Description="How This Specification Is Organized" OutlineTarget="../FixedDoc.fdoc#PG_24_LNK_1075"/>
<OutlineEntry OutlineLevel="3" Description="2.1.4.1 <psf:Property>" OutlineTarget="../FixedDoc.fdoc#PG_49_LNK_1124"/>
<OutlineEntry OutlineLevel="4" Description="Example 2.1-6. Property syntax example" OutlineTarget="../FixedDoc.fdoc#PG_50_LNK_1125"/>
.....................................................................................................................................
</DocumentOutline>
</DocumentStructure.Outline>
<Story StoryName="MainStory">
<StoryFragmentReference Page="1"/>
<StoryFragmentReference Page="2"/>
<StoryFragmentReference Page="3"/>
.....................................
</Story>
<Story StoryName="s1">
<StoryFragmentReference Page="1"/>
</Story>
<Story StoryName="s2">
<StoryFragmentReference Page="2"/>
</Story>
<Story StoryName="s3">
<StoryFragmentReference Page="3"/>
</Story>
......................................
</DocumentStructure>
在“片段”中,文件夹故事片段存储了。
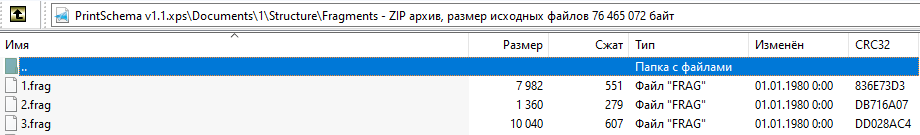
每个“片段”包含带有“命名元素”和“表”元素的“段落”。
<StoryFragments xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/xps/2005/06/documentstructure">
<StoryFragment FragmentType="Content" StoryName="MainStory">
<ParagraphStructure>
<NamedElement NameReference="a5"/>
<NamedElement NameReference="a6"/>
<NamedElement NameReference="a7"/>
</ParagraphStructure>
<ParagraphStructure>
<NamedElement NameReference="a8"/>
</ParagraphStructure>
<TableStructure>
<TableRowGroupStructure>
<TableRowStructure>
<TableCellStructure>
<ParagraphStructure>
<NamedElement NameReference="a28"/>
<NamedElement NameReference="a29"/>
</ParagraphStructure>
</TableCellStructure>
<TableCellStructure>
<ParagraphStructure>
<NamedElement NameReference="a30"/>
<NamedElement NameReference="a31"/>
<NamedElement NameReference="a32"/>
</ParagraphStructure>
</TableCellStructure>
</TableRowStructure>
<TableRowStructure>
<TableCellStructure>
<ParagraphStructure>
<NamedElement NameReference="a33"/>
<NamedElement NameReference="a34"/>
</ParagraphStructure>
</TableCellStructure>
<TableCellStructure>
<ParagraphStructure>
<NamedElement NameReference="a35"/>
<NamedElement NameReference="a36"/>
</ParagraphStructure>
</TableCellStructure>
</TableRowStructure>
</TableRowGroupStructure>
</TableStructure>
<ParagraphStructure>
<NamedElement NameReference="a9"/>
<NamedElement NameReference="a10"/>
</ParagraphStructure>
...................................................................
</StoryFragment>
</StoryFragments>
在XPS文件中打印门票。
打印功能是通过“打印票”零件实现的。它包含可以连接到文档序列,一个文档或页面的打印设置。 “ printTicket”零件存储在用“*_pt.xml”掩码的文件中,其中“ pt”为printTicket。 PrintTicket文件位于“元数据”文件夹中。
printTicket的示例。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<psf:PrintTicket xmlns:psf="http://schemas.microsoft.com/windows/2003/08/printing/printschemaframework"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
version="1"
xmlns:ns0000="http://schemas.microsoft.com/windows/2006/06/printing/printschemakeywords/microsoftxpsdocumentwriter"
xmlns:psk="http://schemas.microsoft.com/windows/2003/08/printing/printschemakeywords">
<psf:ParameterInit name="ns0000:PageDevmodeSnapshot">
<psf:Value xsi:type="xsd:string">
TQBpAGMAcgBvAHMAbwBmAHQAIABYAFAAUwAgAEQAb........=
</psf:Value>
</psf:ParameterInit>
<psf:ParameterInit name="psk:JobCopiesAllDocuments">
<psf:Value xsi:type="xsd:integer">1</psf:Value>
</psf:ParameterInit>
<psf:Feature name="psk:PageMediaSize">
<psf:Option name="psk:ISOA4">
<psf:ScoredProperty name="psk:MediaSizeWidth">
<psf:Value xsi:type="xsd:integer">210000</psf:Value>
</psf:ScoredProperty>
<psf:ScoredProperty name="psk:MediaSizeHeight">
<psf:Value xsi:type="xsd:integer">297000</psf:Value>
</psf:ScoredProperty>
</psf:Option>
</psf:Feature>
<psf:Feature name="psk:JobInputBin">
<psf:Option name="psk:AutoSelect"/>
</psf:Feature>
<psf:Feature name="ns0000:JobInterleaving">
<psf:Option name="ns0000:OFF"/>
</psf:Feature>
<psf:Feature name="ns0000:JobImageType">
<psf:Option name="ns0000:JPEGMed"/>
</psf:Feature>
<psf:Feature name="psk:PageOrientation">
<psf:Option name="psk:Portrait"/>
</psf:Feature>
<psf:Feature name="psk:DocumentCollate">
<psf:Option name="psk:Uncollated"/>
</psf:Feature>
<psf:Feature name="psk:PageResolution">
<psf:Option name="ns0000:Option1">
<psf:ScoredProperty name="psk:ResolutionX">
<psf:Value xsi:type="xsd:integer">600</psf:Value>
</psf:ScoredProperty>
<psf:ScoredProperty name="psk:ResolutionY">
<psf:Value xsi:type="xsd:integer">600</psf:Value>
</psf:ScoredProperty>
</psf:Option>
</psf:Feature>
<psf:Feature name="psk:PageOutputColor">
<psf:Option name="psk:Color">
<psf:ScoredProperty name="psk:DeviceBitsPerPixel">
<psf:Value xsi:type="xsd:integer">24</psf:Value>
</psf:ScoredProperty>
<psf:ScoredProperty name="psk:DriverBitsPerPixel">
<psf:Value xsi:type="xsd:integer">24</psf:Value>
</psf:ScoredProperty>
</psf:Option>
</psf:Feature>
</psf:PrintTicket>
缩略图。
在“元数据”文件夹中,还存储了缩略图图像。
SignatureDefinitions。
“ SignaturoDefinitions”部分允许根据签署“ SignaturedEfinitions”部分定义的签署策略的签名,请求和验证任意XPS文档的零件。

支持XPS文档中字体,颜色和图像
Font formats - Compact Fonts (CFF)- TrueType | Color space types - sRGB- scRGB- CMYK- N-Channel- ICC version 2 | Image formats - JPEG- PNG- TIFF- Windows Media Photo Image (WDP) |
XPS仅支持Opentype字体格式,该格式通过Microsoft TrueType格式结合TrueType字体(TTF)和紧凑型字体(CFF)格式扩展。
如何打开XPS文件?
可以使用Microsoft的XPS Viewer打开XPS文件。它是以Windows Vista开头的标准Windows组件。另一种方法是使用 Aspose.Page xps查看器Web应用程序查看XPS文件。
我可以将XPS文件转换为PDF吗?
将XPS文件转换为PDF的最快方法是使用 Aspose.Page转换Web应用程序。 Aspose XPS Converter支持XPS到PDF,DOC,DOCX,HTML,TEX,SVG,PNG,JPG,JPG,TIFF,BMP转换。如果您是开发人员,并且想将我们的库进行此类转换,请学习 PDLS转换器文章,以查找使用代码片段的示例示例的示例。
我可以在Word中打开XPS文件吗?
这是不可能的,但是您可以通过 Aspose.Page转换Web应用程序将XPS文件转换为Word文档,然后打开IT Microsoft Word Text Editor。
XPS文件可以转换为Excel吗?
是的,您可以将XPS转换为 ASPOSE.PAGE转换Web应用程序中的XPS。 XPS文档将被识别为表。图片未传输到生成的XLSX文件中。
如何在Photoshop中打开XPS文件?
这不可能直接实现,但您可以在 Aspose.Page Conversion Web 应用程序中打开由 XPS 到图像(JPG、PNG、TIFF、BMP)转换生成的光栅图像文件,或者您可以直接使用 ZIP 实用程序打开 XPS 文件,如前所述,在“Resources”文件夹中的资源中找到必要的图像,将其提取到您的文件夹中,最后在 Adobe Photoshop 中打开它。
XPS比PDF好吗?
这取决于您的需求。请参阅文章 页面描述语言的比较。希望它可以帮助您做出正确的决定。
如何在手机上打开XPS文件?
您可以在任何浏览器中使用 Aspose.Page xps vieverWeb应用程序中的XPS文件。