Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML‑based language for creating 2D vector and mixed vector‑raster graphics. SVG is resolution‑independent, edit‑friendly, and ideal for logos, icons, simple graphics, and animations. Setting a background color improves visual clarity, maintains design consistency across patterned pages, and enhances accessibility when SVGs appear over varying webpage backgrounds. For more information about SVG Standard, please see the W3C page.
In this article, we will discuss what background is in SVG. You will also find SVG code examples and a comprehensive guide on how to set or change a background color.
SVG can be styled like HTML. However, SVG does not have a native background-color property like HTML elements. To simulate a background color, you can use an element that covers the entire canvas (such as a <rect>) and apply the color to it using CSS or JavaScript, typically using the style or fill attributes.
This guide shows the only cross-browser reliable way to add a background to SVG, explains why background-color does not work as expected, and provides copy-paste examples.
An SVG background is a visual layer that appears behind all other elements in an SVG image. Unlike HTML elements, SVGs do not have their native background property, so a common approach to creating a background is to add a rectangle element (<rect>) that spans the entire SVG canvas. This <rect> acts as a background, covering the entire SVG area, and is typically positioned as the first child element in the SVG to ensure that it appears behind all other graphic elements.
The background SVG element may not necessarily be a rectangle; it can be a circle, a polygon, etc., at your discretion. Choosing a rectangle as a background is the most common and convenient case. To create a colored background, you must define the fill color of the chosen SVG element. SVG supports two equivalent mechanisms for doing this:
| Method | Description | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
style="fill:…" | Applies fill via an inline CSS style | When styles are already managed via CSS |
fill="…" | Uses the SVG presentation attribute | Preferred for clarity and simplicity |
Building on the concept explained above, the most reliable way to add an SVG background is to insert a <rect> element that covers the entire canvas.
<rect> ElementRecommended approach: This method is fully SVG-standard compliant and works consistently across all browsers and rendering engines.
Place the <rect> as the first child so it sits behind all other graphics. To make the background cover the entire SVG canvas, we specify the width="100%" height="100%" of the rectangle. To set the background color, we use the fill attribute and set the color value to “aliceblue”:
1<svg width="200" height="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <!-- Background rectangle -->
3 <rect width="100%" height="100%" fill="aliceblue" />
4 <!-- Other SVG content -->
5 <circle cx="100" cy="100" r="70" fill="teal" stroke="salmon" stroke-width="10" />
6</svg>The figure illustrates the code snippet above:
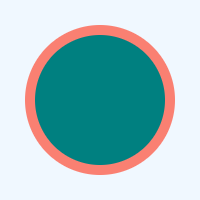
How to work with SVG color using the Aspose.SVG library for .NET and how to change the background color in SVG files, we covered in detail with C# examples in the article Change SVG Background Color – C# Examples.
background-color Does Not Work for SVG ContentThe
SVG specification does not support background-color as a valid property for the <svg> element itself. When you use the background-color property in the style attribute of an <svg> element, it does not actually set a background of the SVG content. Instead, it can set the background color of the space that the SVG occupies in a browser. This can give the impression that the SVG itself has a background color, but it is actually the background of the surrounding container – the area around or behind the SVG content.
In the following SVG code, we show how this property “works”. In the figure that illustrates the code, you will see that the actual background for the SVG image is the rectangle that covers the entire SVG canvas (200x200 px). Also, you will see the effect of the style="background-color: lightsteelblue" property applying – the background of the surrounding container is filled by lightsteelblue color.
1<svg width="200" height="200" style="background-color: lightsteelblue" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <!-- Background rectangle -->
3 <rect width="100%" height="100%" fill="aliceblue" />
4 <!-- Other SVG content -->
5 <circle cx="100" cy="100" r="70" fill="teal" stroke="salmon" stroke-width="10" />
6</svg>The figure illustrates the code snippet above:

Since this behavior is not standard, it might not work consistently across different browsers or platforms. What works in one browser might not work in another, leading to potential issues with design consistency and rendering.
Recommendation: To ensure that your SVG has a consistent and reliable background, you should use a method that is supported across all browsers and platforms, such as adding a <rect> element inside the SVG to serve as the background.
Inline CSS involves directly embedding CSS styles into individual SVG elements using the style attribute. This method allows you to apply specific styles to elements on a case-by-case basis without the need for external or internal style sheets.
1<svg width="200" height="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <!-- Background rectangle -->
3 <rect style="width: 100%; height: 100%; fill: aliceblue;" />
4 <!-- Other SVG content -->
5 <circle cx="100" cy="100" r="70" fill="teal" stroke="salmon" stroke-width="10" />
6</svg>The advantages of inline CSS in SVG include precise control over individual elements and easy portability. However, if multiple elements share the same style, it can lead to repetitive code, which makes maintenance challenging, especially in large SVGs.
To set a background color for an SVG using internal CSS, you can use the <style> tag within the SVG itself, allowing you to create centralized style rules that can be applied to multiple elements. This method provides a cleaner and more manageable way to apply consistent styles across an SVG.
In this example, the <style> tag is used to define a CSS class .background. This class is then applied to the <rect> element via the class attribute. The .background class sets the fill property to aliceblue, coloring the <rect> and creating the color background.
1<svg width="200" height="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <style>
3 .background {
4 fill: aliceblue;
5 }
6 </style>
7 <!-- Background rectangle -->
8 <rect width="100%" height="100%" class="background" />
9 <!-- Other SVG content -->
10 <circle cx="100" cy="100" r="70" fill="teal" stroke="salmon" stroke-width="10" />
11</svg>Internal CSS is a little more complex than inline CSS. However, it allows you to reuse styles across multiple elements, reducing code redundancy and making it easier to update styles across elements they apply to.
JavaScript can be used within SVG to manipulate its elements, just like in HTML. JavaScript in SVG is particularly useful for creating interactive graphics, animations, and dynamic changes to SVG content.
In the following example, the SVG contains a rectangle <rect> that acts as the background, filling the entire SVG canvas. When the SVG is clicked, a JavaScript function toggles the background color between two colors aliceblue and mistyrose.
1<svg id="mySvg" width="200" height="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <!-- Background rectangle -->
3 <rect width="100%" height="100%" fill="aliceblue" />
4
5 <!-- Some content in the SVG -->
6 <circle cx="100" cy="100" r="50" fill="#f3622a" />
7
8 <script type="text/javascript">
9 document.getElementById("mySvg").addEventListener("click", function() {
10 var rect = document.querySelector("#mySvg rect");
11 rect.setAttribute("fill", rect.getAttribute("fill") === "aliceblue" ? "mistyrose" : "aliceblue");
12 });
13 </script>
14</svg>This SVG image illustrates the code snippet above. Click on SVG and change the background color!
Note: JavaScript should be used only for interactive or state-driven backgrounds. For static SVG files (icons, logos), prefer <rect> with fill to avoid unnecessary complexity.
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Background appears transparent | No <rect> element was added | Insert a <rect> covering 100 % width/height as the first child |
background-color seems to work in one browser only | Property is applied to the outer SVG container, not the canvas | Use a <rect> background for cross‑browser consistency |
| Inline styles conflict with external CSS | Duplicate fill definitions on the same element | Consolidate styles using internal CSS or class selectors |
| JavaScript does not change the color | Wrong selector or missing id on the <rect> | Ensure the rectangle has a unique selector (#mySvg rect) and the script runs after the SVG is parsed |
| SVG scales but background does not fill the viewBox | Rectangle uses fixed pixel dimensions | Use width="100%" height="100%" or match the SVG’s viewBox dimensions |
Add a solid background with a <rect>
1<svg width="300" height="150" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <rect width="100%" height="100%" fill="#f0f0f0"/>
3 <!-- your graphics -->
4</svg>Change background on hover using CSS
1<svg class="hover-bg" width="200" height="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <style>
3 .hover-bg:hover rect { fill: #ffebcd; }
4 </style>
5 <rect width="100%" height="100%" fill="aliceblue"/>
6 <circle cx="100" cy="100" r="70" fill="teal"/>
7</svg>Toggle background with JavaScript
1<svg id="toggleSvg" width="200" height="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <rect width="100%" height="100%" fill="aliceblue"/>
3 <script>
4 document.getElementById('toggleSvg').addEventListener('click', function(){
5 const r = this.querySelector('rect');
6 r.setAttribute('fill', r.getAttribute('fill') === 'aliceblue' ? 'mistyrose' : 'aliceblue');
7 });
8 </script>
9</svg>Reuse a background class with internal CSS
1<svg width="250" height="250" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <style>.bg{fill:#e6e6fa;}</style>
3 <rect class="bg" width="100%" height="100%"/>
4 <!-- other elements -->
5</svg>SVG does not provide a native background-color attribute, but you can reliably add a background using a <rect> element, inline or internal CSS, or JavaScript for dynamic effects. Choose the method that matches your project’s complexity and maintenance needs.
Key takeaway: If you need a consistent SVG background across browsers, always use a
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.