Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
Simple vector shapes are the building blocks of logos, diagrams, and many other graphics. In an SVG file each shape is represented by an element whose attributes define its position, size, and visual style. You can customize fill color, opacity, corner rounding, stroke width, and more. Learn how to insert and edit these elements with the Aspose.SVG API in the Edit SVG File guide.
<rect> – Rectangle ElementThe <rect> element creates rectangles and rounded‑corner rectangles.
| Attribute | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| x | X‑coordinate of the top‑left corner | 0 |
| y | Y‑coordinate of the top‑left corner | 0 |
| width | Rectangle width | — |
| height | Rectangle height | — |
| rx | Horizontal radius for rounded corners | 0 |
| ry | Vertical radius for rounded corners | 0 |
You can style the rectangle with the style attribute (see Fills and Strokes in SVG).
1<svg width="500" height="550" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <rect x="60" y="100" width="70" height="40" rx="10" ry="10" style="fill:#778899; stroke:#FF4500; stroke-width:5; fill-opacity:0.7; stroke-opacity:0.6" />
3</svg>The example creates a rectangle whose top‑left corner is at (60, 100), with a width of 70 px, height of 40 px, rounded corners (10 px radius) and a 5 px orange stroke. Below is a rectangle without rounded corners.
1<svg width="500" height="550" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <rect x="120" y="140" width="90" height="90" style="fill:grey; stroke-width:3; stroke:rgb(0,0,0)" />
3</svg>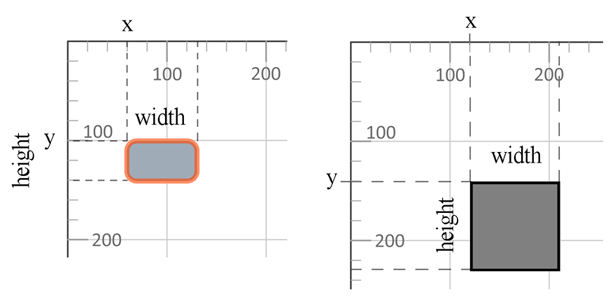
Colors can be specified as:
fill:blue (140+ CSS color names).fill:rgb(0,0,255).fill:#0000ff.<circle> – Circle ElementThe <circle> element draws a perfect circle.
| Attribute | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| cx | X‑coordinate of the circle center | 0 |
| cy | Y‑coordinate of the circle center | 0 |
| r | Radius of the circle | — |
1<svg width="300" height="550" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <circle cx="250" cy="100" r="60" style="fill:red; stroke-width:3; stroke:rgb(0,0,0); fill-opacity:0.7" />
3</svg>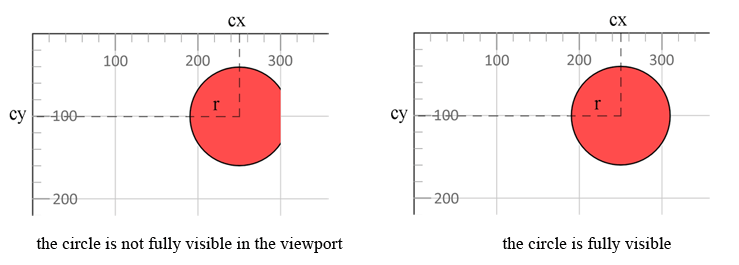
The circle extends beyond the 300 px viewport width; a width of at least 310 px (cx + r) is required for full visibility.
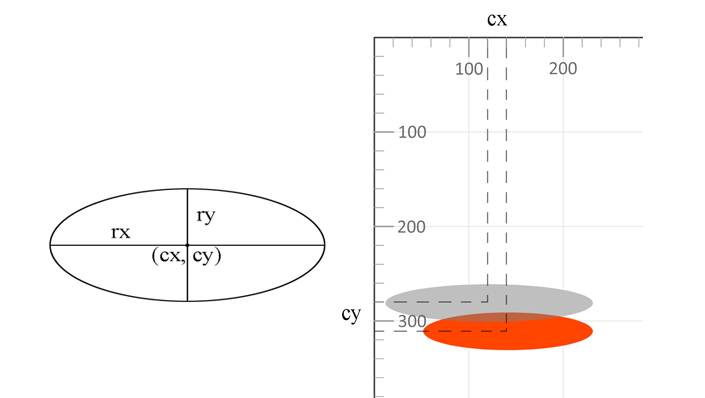
<ellipse> – Ellipse ElementThe <ellipse> element creates an oval shape.
| Attribute | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| cx | X‑coordinate of the ellipse center | 0 |
| cy | Y‑coordinate of the ellipse center | 0 |
| rx | Horizontal radius (half the width) | — |
| ry | Vertical radius (half the height) | — |
1<svg width="500" height="550" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <ellipse cx="140" cy="310" rx="90" ry="20" style="fill:OrangeRed" />
3 <ellipse cx="120" cy="280" rx="110" ry="20" style="fill:grey; fill-opacity:0.5" />
4</svg>The second ellipse (grey, 50 % opacity) is rendered on top of the first. In SVG, later elements overlay earlier ones.
<line> – Line ElementThe <line> element draws a straight line between two points.
| Attribute | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| x1 | X‑coordinate of the start point | — |
| y1 | Y‑coordinate of the start point | — |
| x2 | X‑coordinate of the end point | — |
| y2 | Y‑coordinate of the end point | — |
| style (stroke, stroke-width) | Visual styling of the line | — |
1<svg width="500" height="550" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <line x1="30" y1="30" x2="350" y2="290" style="stroke:rgb(255,0,0); stroke-width:3" />
3 <line x1="30" y1="50" x2="300" y2="350" style="stroke:grey; stroke-width:5" />
4 <line x1="20" y1="80" x2="100" y2="200" style="stroke:orangered; stroke-width:8" />
5</svg>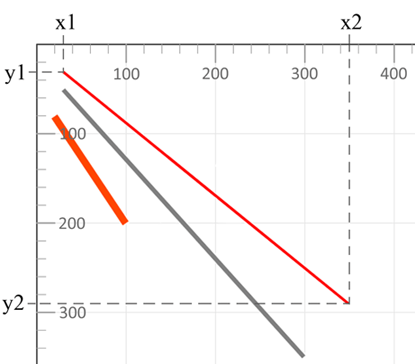
The stroke property defines line color, while stroke-width sets its thickness.
<polyline> – Polyline ElementThe <polyline> element draws a series of connected straight segments (open shape).
| Attribute | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| points | List of x,y coordinate pairs defining the polyline vertices | — |
| style (fill, stroke, stroke-width) | Visual styling of the shape | — |
1<svg width="500" height="550" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <polyline points="280,290 300,220 320,290" style="fill:grey; stroke:grey; stroke-width:2; fill-opacity:0.5" />
3 <polyline points="220,200 240,180 260,200 280,180 300,200 320,180 340,200" style="fill:none; stroke:red; stroke-width:6" />
4</svg>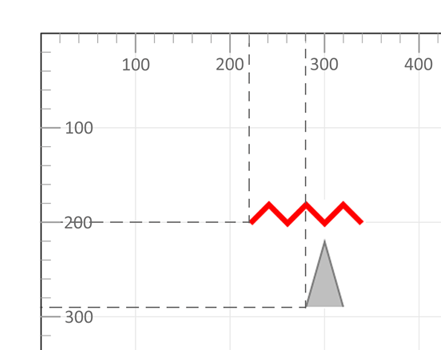
The first polyline creates a closed triangle that is partially filled with grey (default fill is black). The second polyline is an open red line with no fill.
For more details on SVG styling, see Fills and Strokes in SVG and the official W3C painting specification.
<polygon> – Polygon ElementThe <polygon> element defines a closed shape formed by a series of connected points.
| Attribute | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| points | List of x,y coordinate pairs for each vertex (must contain at least three points) | — |
| style (fill, stroke, stroke-width) | Visual styling of the polygon | — |
1<svg width="500" height="550" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <polygon points="160,10 350,140 210,350 50,199" style="fill:orange;stroke:purple;stroke-width:1" />
3</svg>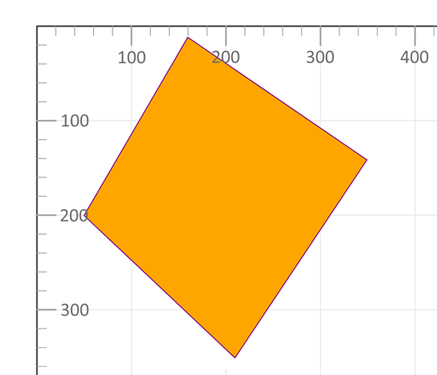
A minimal SVG document can combine all basic shapes into a single illustration.
1<svg width="500" height="550" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <line x1="30" y1="30" x2="350" y2="290" style="stroke:rgb(255,0,0); stroke-width:3" />
3 <line x1="30" y1="50" x2="300" y2="350" style="stroke:grey; stroke-width:5" />
4 <rect x="60" y="100" width="70" height="40" rx="10" ry="10" style="fill:#778899; stroke:#FF4500; stroke-width:5; fill-opacity:0.7; stroke-opacity:0.6" />
5 <polygon points="160,10 350,140 210,350 50,199" style="fill:orange; stroke:purple; stroke-width:1; fill-opacity:1" />
6 <rect x="120" y="150" width="90" height="90" style="fill:grey; stroke-width:3; stroke:rgb(0,0,0)" />
7 <circle cx="250" cy="100" r="60" style="fill:red; stroke:black; stroke-width:3; fill-opacity:0.7" />
8 <ellipse cx="140" cy="310" rx="90" ry="20" style="fill:OrangeRed" />
9 <ellipse cx="120" cy="280" rx="110" ry="20" style="fill:grey; fill-opacity:0.5" />
10 <polyline points="220,200 240,180 260,200 280,180 300,200 320,180 340,200" style="fill:none; stroke:red; stroke-width:6" />
11 <line x1="20" y1="80" x2="100" y2="200" style="stroke:orangered; stroke-width:8" />
12 <polyline points="280,290 300,220 320,290" style="fill:grey; stroke:grey; stroke-width:2; fill-opacity:0.5" />
13</svg>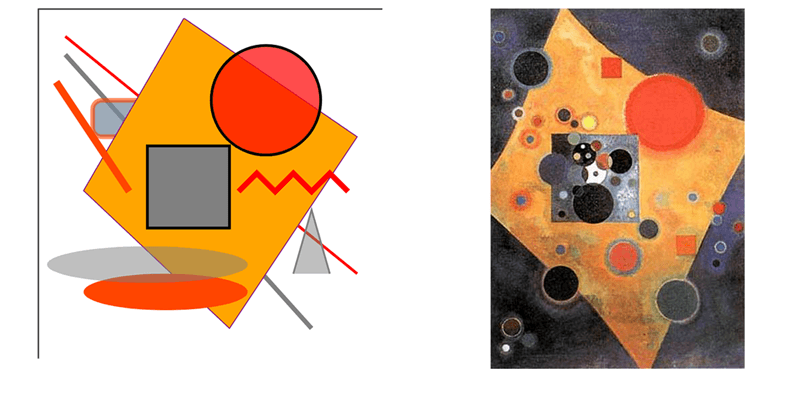
his simple picture “SVG Basic Shapes” contains all the figures described above. Nearby is the famous painting “Pink Accent” by Wassily Kandinsky. Understanding SVG markup lets you craft graphics directly in a text editor; for more complex scenes, consider using the Aspose.SVG Builder API.
| Problem | Likely Cause | How to Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Shape is not visible | SVG viewport is smaller than the shape | Increase width / height or adjust the viewBox |
| Shape is clipped | Coordinates exceed the viewport bounds | Recalculate coordinates or expand the SVG canvas |
| Fill color does not appear | fill="none" or fill-opacity="0" is set | Set a valid fill value and opacity |
| Stroke is invisible | stroke-width="0" or missing stroke | Define both stroke and a positive stroke-width |
| Rounded corners do not work | rx / ry values are missing or zero | Set non-zero rx and ry attributes |
| Elements overlap unexpectedly | SVG renders elements in source order | Reorder elements in the markup or use grouping |
| Task | Example |
|---|---|
| Solid fill color | fill="blue" |
| Semi-transparent fill | fill="red" fill-opacity="0.5" |
| Transparent fill with visible outline | fill="none" stroke="black" |
| Semi-transparent stroke | stroke="black" stroke-opacity="0.4" |
| Thick colored outline | stroke="orange" stroke-width="6" |
| Dashed outline | stroke-dasharray="5,3" |
For advanced SVG styling techniques, see Fills and Strokes in SVG.
Related Resources
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.