Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
SVG allows making for three types of graphic objects: vector graphic shapes, images and text. In the same way, as for the shapes, the SVG text elements can be applied coordinate system transformations, clipping and styling. In this article, we consider how to bring text into an SVG image.
This article introduces the SVG text elements such as <text>, <tspan>, and <textPath> and reviews some common attributes that help display, format, and style text into an SVG image. You learn how to manipulate text placement, orientation, and appearance through detailed examples and explanations. The article also provides basic information about glyphs, characters, and fonts.
Glyph – the visual representation of a character inside a font. A glyph is defined by one or more shapes (paths) and optional rendering hints.
“A glyph represents a unit of rendered content within a font.” – W3C SVG Specification
Font – a collection of glyphs that share a common design. Vector fonts store each glyph as Bézier curves, allowing unlimited scaling without loss of quality.
Character – the abstract code point (e.g., Unicode) that a program maps to a glyph in a font. Characters are arranged along an imaginary baseline, which can be horizontal or vertical depending on the script.
Understanding the relationship between characters, glyphs, and fonts is essential when you need precise control over SVG text rendering.
SVG defines three content elements that generate visible text:
| Element | Purpose |
|---|---|
<text> | Defines a block of text. |
<tspan> | Provides fine‑grained positioning and styling inside <text>. |
<textPath> | Aligns text along a <path> curve. |
<text> elementThe <text> element is used to define a text. x and y are the main attributes responsible for the text position. The baseline for the text begins from the bottom-left corner of the first text symbol. It is essential to set y value larger than the font size. Otherwise, the text does not get into the viewport.
The following example illustrates how to specify a start of baseline correctly. The x and y set the coordinates of the baseline beginning ( svg-text-position.svg).
1<svg height="100" width="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <text x="10" y="6" fill="red">The text is not fully visible </text>
3 <text x="10" y="30" fill="green">The text is fully visible </text>
4</svg>
The attributes of the <text> and <tspan> elements indicate writing direction, alignment, font, and other specifying properties and features that precisely describe how to render characters. The main attributes are:
textLength (spacing, spacingAndGlyphs).start, middle, end).lr, rl, tb, bt).These attributes can be combined to create complex layouts, such as stretched text, right‑to‑left scripts, or vertical writing.
1<svg height="300" width="400" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <text x="180" y="30" fill="red">Aspose.SVG</text>
3 <text x="180" y="60" fill="blue" textLength="140">Aspose.SVG</text>
4 <text x="180" y="90" fill="grey" textLength="160" lengthAdjust="spacingAndGlyphs"
5 style="direction: rtl; unicode-bidi: bidi-override">Aspose.SVG</text>
6 <text x="180" y="120" fill="green" style="text-anchor: middle">Aspose.SVG</text>
7 <text x="260" y="90" style="writing-mode: tb">Aspose.SVG</text>
8</svg>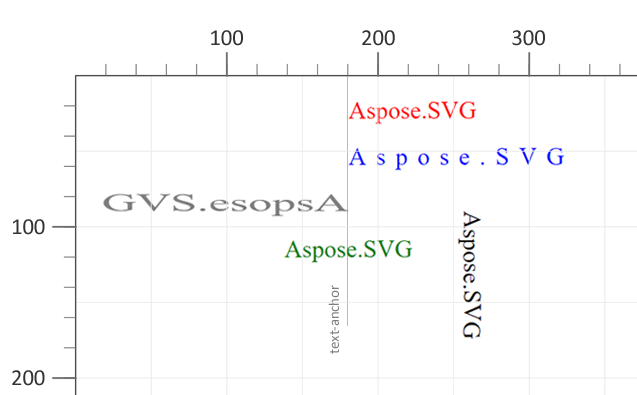
text-anchor:start.text-anchor:middle.direction:rtl.textLength and lengthAdjust stretch the glyphs.writing-mode:tb (top‑to‑bottom).<tspan> – Inline Styling and Line Breaks<tspan> can be nested inside <text> or another <tspan>. Being a child element, <tspan> serves several important functions in text displaying and formatting:
<tspan> element. Each <tspan> element can contain different formatting and position.<tspan> element. It allows you to switch the style or position of the displayed text within the <tspan> element relative to the parent element.1<svg height="300" width="600" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <text x="20" y="60" style="font-family:arial">
3 <tspan style="font-weight:bold; font-size:55px">ASPOSE</tspan>
4 <tspan x="50" y="90" style="font-size:20px; fill:grey">Your File Format APIs </tspan>
5 </text>
6</svg>
<tspan> start a new line at the specified coordinates.font-weight, font-size, fill) affect only that <tspan>.<textPath> – Text Along a Curve<textPath> attaches text to a <path> element, allowing characters to follow any vector curve. The path can be referenced in two ways:
xlink:href) – points to a <path> by its id. 1<svg height="300" width="800" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <path id="my_path1" d="M 50 100 Q 25 10 180 100 T 350 100 T 520 100 T 690 100"
3 fill="transparent" />
4 <path id="my_path2" d="M 50 100 Q 25 10 180 100 T 350 100"
5 transform="translate(0,75)" fill="transparent" />
6 <text>
7 <textPath href="#my_path1">
8 Aspose.SVG for .NET is a flexible library for SVG file processing and is fully compatible with its specifications.
9 </textPath>
10 <textPath href="#my_path2">
11 Aspose.SVG for .NET is a flexible library for SVG file processing and is fully compatible with its specifications.
12 </textPath>
13 </text>
14</svg>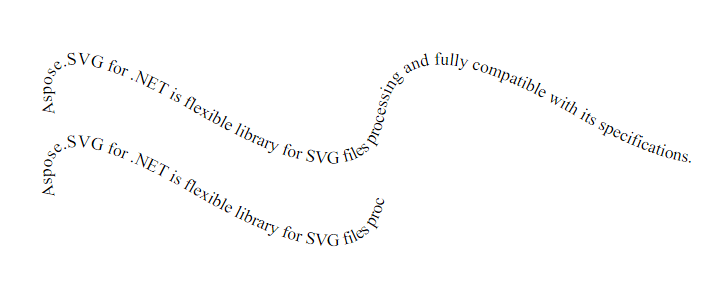
If the path is shorter than the text, the overflow is clipped at the path’s end. Styling works the same way as with regular text: CSS properties such as font-weight, font-style, text-decoration, and text-transform can be applied.
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Text is cut off at the top of the viewport | y value is smaller than the font size | Set y larger than the font size (e.g., y="30" for 24 px text) |
| Text does not follow the curve as expected | href points to a non‑existent <path> ID | Verify the <path> id and ensure the href value matches exactly |
| Glyphs appear distorted | lengthAdjust set to spacing while using textLength | Use lengthAdjust="spacingAndGlyphs" to scale both spacing and glyphs |
| Right‑to‑left text still displays left‑to‑right | Missing unicode-bidi:bidi-override | Add style="direction: rtl; unicode-bidi: bidi-override" to the <text> or <tspan> |
| Text does not wrap to a new line | Relying on automatic wrapping | Insert a new <tspan> with its own x/y coordinates for each line |
| Goal | SVG Snippet (copy‑paste) |
|---|---|
| Center text horizontally | <text x="50%" y="50%" text-anchor="middle" dominant-baseline="middle">Centered</text> |
| Vertical text (top‑to‑bottom) | <text x="20" y="20" writing-mode="tb">Vertical</text> |
| Stretch text to exact width | <text x="10" y="40" textLength="200" lengthAdjust="spacingAndGlyphs">Stretch me</text> |
| Place text on a curve | <path id="curve" d="M10,80 C40,10 65,10 95,80" fill="none"/> <text><textPath href="#curve">On a curve</textPath></text> |
| Apply underline and overline | <text x="10" y="40" style="text-decoration: underline overline;">Styled</text> |
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.