Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
SVG allows modifying graphic elements using translation, rotation, scaling, and skewing. All these SVG transformations refer to the geometric kind. SVG objects can be altering using the transform attribute’s properties: translate, scale, rotate, skewX, skewY, and matrix.
The translation moves all the object points at the same distance along parallel lines. This can be interpreted as shifting the origin of the element’s system of coordinates. There are three transform functions: translateX (tx), translateY (ty) and translate (tx, ty). The translate (tx, ty) function moves an element by a tx value along the x-axis and by ty along the y-axis. If one of the values is not specified, it defaults to zero.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
tx | Horizontal offset (positive → right, negative → left) |
ty | Vertical offset (positive → down, negative → up) |
The action of attribute transform="translate(tx, ty)" means the changing of object coordinates according to the formula:
x(new) = x(old) + tx
y(new) = y(old) + ty
Here is a simple example:
1<svg viewBox="0 0 100 100" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <g fill="none">
3 <!-- no translation -->
4 <circle cx="15" cy="15" r="10" stroke="blue" />
5 <!-- horizontal translation -->
6 <circle cx="15" cy="15" r="10" stroke="black" transform="translate(22)" />
7 <circle cx="15" cy="15" r="10" stroke="red" transform="translate(44)" />
8 <!-- both horizontal and vertical translation -->
9 <circle cx="15" cy="15" r="10" stroke="green" transform="translate(33,13)" />
10 <circle cx="15" cy="15" r="10" stroke="yellow" transform="translate(11,13)" />
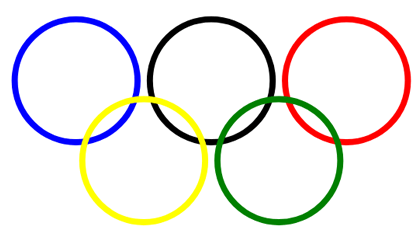
11 </g>
12</svg>In the code example, the <g> element is used to group circles together. The fill attribute applies inside <g> to all shapes once. Here is the resulting image (
translation.svg):
Scaling is an SVG transformation that enlarges or reduces an object using a scaling factor. You have to distinguish the uniform and directional scaling. The scale(sx, sy) function multiplies the element’s width by sx and height by sy. If sy is omitted, it defaults to sx (uniform scaling).
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
sx | Horizontal scaling factor |
sy | Vertical scaling factor (optional) |
1<svg viewBox="-50 -50 200 200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <!-- uniform scale -->
3 <circle cx="0" cy="0" r="10" fill="#B0C4DE" transform="scale(4)" />
4 <circle cx="0" cy="0" r="10" fill="#DDA0DD" transform="scale(3)" />
5 <circle cx="0" cy="0" r="10" fill="#FFB6C1" transform="scale(2)" />
6 <!-- no scale -->
7 <circle cx="0" cy="0" r="10" fill="#5F9EA0" />
8 <g transform="translate(100)">
9 <!-- uniform scale -->
10 <circle cx="0" cy="0" r="10" fill="#B0C4DE" transform="scale(4)" />
11 <!-- vertical scale -->
12 <circle cx="0" cy="0" r="10" fill="#DDA0DD" transform="scale(1,4)" />
13 <!-- horizontal scale -->
14 <circle cx="0" cy="0" r="10" fill="#FFB6C1" transform="scale(4,1)" />
15 <!-- no scale -->
16 <circle cx="0" cy="0" r="10" fill="#5F9EA0" />
17 </g>
18</svg>Here is the resulting image ( scaling.svg):
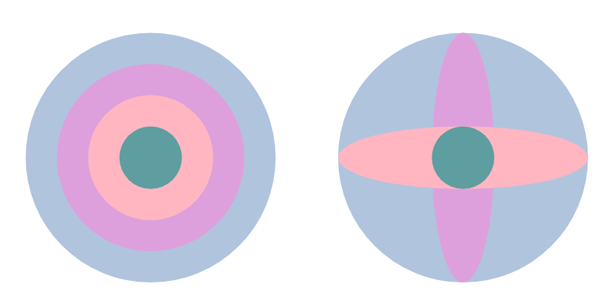
The code above uses the scale and translate functions. The first group of circles on the figure displays an example of uniform scaling, and the second group illustrates the circle scaling along the y-axis (line 12) and the x-axis (line 14). A scale value of “4” renders a graphic at four times its original size, while a value of “4,1” increases four times its source width, and saves its height.
You can resize SVG in C# using Aspose.SVG for .NET API. The
SVG Scaling – C# Examples article covers C# examples for SVG scaling. You will find cases of using the scale() function in the transform attribute as well as a transformation matrix – matrix(a,b,c,d,e,f).
The rotate(angle, cx, cy) function rotates an element by angle around the point with coordinates (cx, cy). If coordinates are not specified, then the rotation will be performed around the point (0, 0) of the initial coordinate system.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
angle | Rotation angle in degrees (positive → clockwise) |
cx | X‑coordinate of rotation center (optional) |
cy | Y‑coordinate of rotation center (optional) |
All rotate or skew angle values should be specified in degrees, you cannot use the other units we have available in CSS. If we use a positive angle value, then the rotation will be clockwise, and conversely, a negative angle value gives us counterclockwise spin.
Note: Specifying just the angle and the cx parameter makes the value invalid, and no SVG rotation is applied.
Like translation, SVG rotation does not distort the element and saves parallelism, angles, and distances.
1<svg width="450" height="450" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <rect x="100" y="250" width="200" height="30" fill="CadetBlue" />
3 <rect x="100" y="250" width="200" height="30" fill="#DDA0DD" transform ="rotate(-45 200 265)" />
4 <rect x="100" y="250" width="200" height="30" fill="Pink" transform ="rotate(-90 200 265)" />
5 <rect x="100" y="250" width="200" height="30" fill="#B0C4DE" transform ="rotate(45 200 265)" />
6 <rect x="100" y="250" width="200" height="30" fill="CadetBlue" transform ="rotate(-35)" />
7</svg>The function transform="rotate(-90 200 265)" used in line 4 means that the pink rectangle should be rotated 90 degrees counterclockwise with the center of rotation at (200,265). For rectangle in line 6, coordinates (cx, cy) are not specified, and the rotation on -35 degrees is performed around the point (0, 0) of the initial coordinate system. The result of SVG rotation can be seen on the figure:
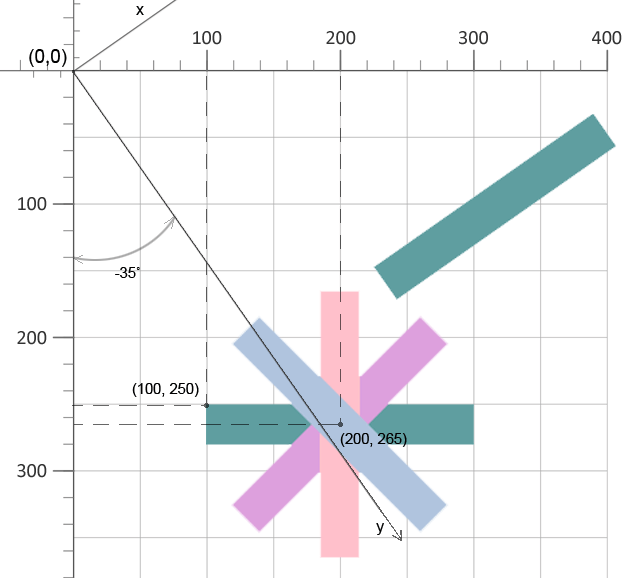
You can view and then save the file that illustrates SVG rotation by clicking on the link rotation.svg.
You can rotate SVG in C# using Aspose.SVG for .NET API. The
Rotate SVG – C# Examples article covers C# examples for SVG rotation. It considers cases of using the rotate() function in the transform attribute and the transformation matrix – matrix(a,b,c,d,e,f).
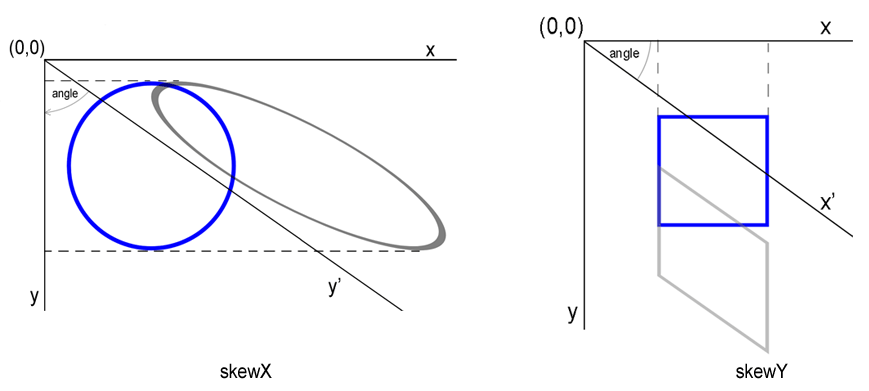
Skewing is a transformation that rotates one of the axes of the element’s coordinate system by a certain angle clockwise or counterclockwise. SVG elements can be skewed through the use of the skewX(angle) and skewY(angle) functions. The angle value included within these functions represents a skew SVG transformation in degrees along the appropriate axis. The using skewX(angle), only the x coordinate of the points of the shape changes, but the y coordinate remains unchanged. The skewX(angle) function makes the vertical lines look like they have been rotated by a given angle. The x coordinate of each point changes on a value proportional to the specified angle and distance to the origin.
Here is shown an example of the circle with skewX(55) value ( skew-x.svg):
1<svg viewBox="0 0 100 100" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <circle cx="20" cy="20" r="15" stroke="blue" fill="none" />
3 <circle cx="20" cy="20" r="15" stroke="grey" stroke-opacity="0.7" fill="none" transform="skewX(55)" />
4</svg>A simple example of the rectangle skewed by skewY(35) function ( skew-y.svg):
1<svg width="800" height="800" viewBox="0 0 200 200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <rect x="20" y="20" width="30" height="30" stroke="blue" stroke-opacity="1" fill="none" />
3 <rect x="20" y="20" width="30" height="30" stroke="grey" stroke-opacity="0.5" fill="none" transform="skewY(35)" />
4 </svg>The rendered examples look like:
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
Rectangle does not move after applying translate | transform attribute misspelled or missing quotes | Ensure transform="translate(150,50)" is set correctly on the element |
| Translation does not apply | transform attribute placed on a parent element instead of the target element | Set transform directly on the element you want to move (e.g., the <rect>). |
| Unexpected rotation direction | Angle sign interpreted opposite to expectation | Use positive values for clockwise rotation, negative for counter‑clockwise |
| Rotation occurs around the wrong point | cx/cy omitted or set to the element’s origin | Provide explicit rotation center coordinates or apply a pre‑translation to shift the pivot. |
| Skew appears too extreme | Angle supplied in radians instead of degrees | Provide angles in degrees (e.g., skewX(30)) |
| Element disappears after scaling | Scale factor set to 0 or negative unintentionally | Use positive non‑zero scale values; verify the order of transforms if combined. |
| Combined transforms produce wrong result | Order of functions is reversed | Remember that transforms are applied right‑to‑left; write translate(...) rotate(...) to rotate first then translate |
| Effect | Copy-Paste SVG Code |
|---|---|
| Move right 50px, down 30px | <rect x="10" y="10" width="40" height="20" transform="translate(50,30)" /> |
| Double size (uniform) | <circle cx="20" cy="20" r="10" transform="scale(2)" /> |
| Stretch horizontally 3× | <rect x="0" y="0" width="20" height="20" transform="scale(3,1)" /> |
| Rotate 45° around center (100,100) | <polygon points="90,90 110,90 100,110" transform="rotate(45 100 100)" /> |
| Rotate 90° clockwise around origin | <line x1="0" y1="0" x2="50" y2="0" stroke="black" transform="rotate(90)" /> |
| Skew X by 30° | <rect x="10" y="10" width="30" height="30" transform="skewX(30)" /> |
| Skew Y by -20° | <circle cx="25" cy="25" r="15" transform="skewY(-20)" /> |
| Chain: move then rotate | <g transform="translate(100,50) rotate(30)"><rect width="40" height="10" fill="red"/></g> |
Next Steps and Related Resources
Aspose.SVG offers SVG Free Web Applications for converting SVG or image files, merging SVG files, image vectorizing, SVG sprite generating, SVG to base64 data encoding, and text vectorizing. These online Apps work on any operating system with a web browser and don’t require additional software installation. It’s a fast and easy way to efficiently and effectively solve your SVG-related tasks!
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.