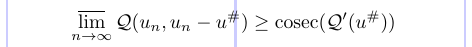6. 数学公式中的文本
6.1. \text 命令
要在数学公式中放入普通文本,最好使用 \text 命令,而不是像 \mathrm 这样的命令。\text 命令确保文本使用正确的字号。该字体将是当前数学材料之外使用的正文字体。
1\usepackage{amsmath}
2% -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3\begin{gather}
4\text{Also, if } \Delta_{\text{max up}} = \Delta_{\text{min down}} \notag \\
5\text{(for all ups and downs) then} \notag \\
6\Delta_{\text{sum of ups}} = \Delta_{\text{sum of downs}}
7\end{gather}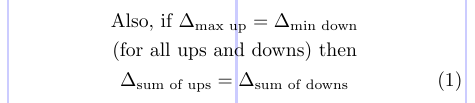
6.2. 运算符名称
常用数学函数(例如 sin 和 log)和运算符(例如 min 和 sup)的名称通常需要与斜体变量名区分开来。因此,它们传统上以罗马体文本形式设置。标准 LaTeX 为最常用的函数和运算符提供了预定义的命令。amsmath 宏包大幅扩展了这些命令的集合。下表列出了“标准”命令以及 amsmath 提供的命令。后者用粗体标出。斜体形式的命令在显示公式中使用时,其下标/上标可以位于极限位置。
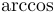 | \arccos | 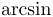 | \arcsin | 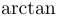 | \arctan |
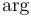 | \arg | 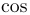 | \cos | 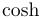 | \cosh |
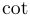 | \cot | 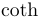 | \coth | 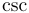 | \csc |
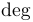 | \deg | 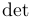 | \det | 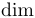 | \dim |
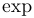 | \exp | 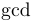 | \gcd | 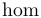 | \hom |
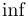 | \inf | 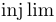 | \injlim | 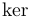 | \ker |
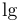 | \lg | 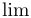 | \lim | 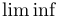 | \liminf |
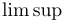 | \limsup | 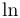 | \ln | 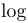 | \log |
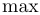 | \max | 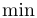 | \min |  | \Pr |
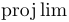 | \projlim | 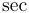 | \sec | 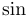 | \sin |
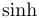 | \sinh | 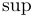 | \sup | 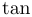 | \tan |
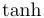 | \tanh | 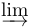 | \varinjlim | 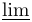 | \varliminf |
 | \varlimsup | 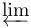 | \varprojlim |
1\usepackage[fleqn]{amsmath}
2\newcommand\abs[1]{\lvert#1\rvert}
3\setlength\mathindent{0pt}
4% -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5\begin{gather*}
6\lim_{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{ \sin^2(x) }{ x^2 } = 1 \\
7\varliminf_{n \rightarrow \infty}
8\abs{a_{n+1}} / \abs{a_n} = 0 \\
9\varinjlim (m_i^\lambda \cdot M)^* \le
10\varprojlim_{A/p \rightarrow \lambda(A)}A_p \le 0
11\end{gather*}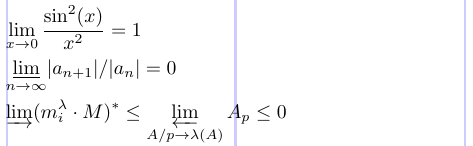
通常会发现此列表并不足够。amsmath 宏包定义了一种通用方法来定义新的“运算符名称”。
1\DeclareMathOperator*{cmd}{text}\DeclareMathOperator 命令定义 cmd 以在适当的“文本运算符”字体中生成 text。如果新运算符在显示公式中需要在极限位置拥有下标/上标,则应使用带星号的形式 \DeclareMathOperator*。除了使用正确的字体外,\DeclareMathOperator 还会在运算符名称两侧设置良好的间距。其文本参数采用一种“伪文本模式”进行处理,其中:
- 连字符会作为普通文本连字符打印(而不是减号),(参见下一个示例中的
\supminus)。 - 星号字符
*会作为上标的文本星号打印(而不是居中)。 - 否则,文本在数学模式下处理,空格会被忽略,并且可以使用下标、上标以及其他元素。
下面的示例展示了如何为新函数名 “meas”(measure)提供命令 \meas,以及运算符函数 \esssup 和 \supminus(它们都可以在极限位置拥有下标/上标)。
1\usepackage[fleqn]{amsmath}
2\DeclareMathOperator \meas {meas}
3\DeclareMathOperator*\esssup {ess \, sup}
4\DeclareMathOperator*\supminus{sup - minus*}
5\newcommand\abs [1]{\lvert#1\rvert}
6\newcommand\norm[1]{\lVert#1\rVert}
7% -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8\begin{gather*}
9 \norm{f}_\infty = \esssup_{x \in R^n} \abs{f(x)} \\
10 \meas_1 \{ u \in R_+^1 \colon f^*(u)>\alpha \} \\
11 \quad \esssup_{x \in R^i} \; \meas_i
12 \{ u \in R^n \colon \abs{f(u)} \geq \alpha \} \\
13 \quad (\forall \alpha \in \supminus_{f^*} R_{*+})
14\end{gather*}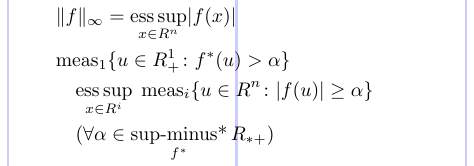
此类声明必须写在导言区,且无法临时更改。严格来说,\DeclareMathOperator 只能用于尚未使用过的命令名。若要替换已有命令,必须先取消先前的定义,然后再重新声明。
1\usepackage{amsmath}
2%% Low-level TeX needed here to cancel the old the definition of \csc:
3\let \csc \relax
4\DeclareMathOperator\csc{cosec}
5\newcommand\calQ{\mathcal{Q}}
6% -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7\[
8\varlimsup_{n\to\infty} \calQ (u_n, u_n - u^{\#})
9 \ge \csc (\calQ' (u^{\#}))
10\]