Costruire una tabella da un DataTable
Spesso l’applicazione estrae i dati da un database e li memorizza sotto forma di DataTable. È possibile inserire facilmente questi dati nel documento come nuova tabella e applicare rapidamente la formattazione all’intera tabella.
Si noti che il modo preferito di inserire i dati da un
DataTable in una tabella documento è utilizzando
Mail Merge con Regioni. La tecnica presentata in questo articolo è suggerita solo se non si è in grado di creare un modello adatto in anticipo per unire i dati, in altre parole, se si richiede che tutto avvenga a livello di programmazione.
Utilizzando Aspose.Words, è possibile recuperare facilmente i dati da un database e memorizzarli come tabella:
- Crea un nuovo oggetto DocumentBuilder sul tuo Document.
- Inizia una nuova tabella usando DocumentBuilder.
- Se vogliamo inserire i nomi di ciascuna delle colonne dal nostro DataTable come riga di intestazione, scorrere ciascuna colonna di dati e scrivere i nomi delle colonne in una riga nella tabella.
- Scorrere ogni DataRow nel DataTable:
- Scorrere ogni oggetto nel DataRow.
- Inserire l’oggetto nel documento usando DocumentBuilder. Il metodo utilizzato dipende dal tipo di oggetto inserito, ad esempio DocumentBuilder.writeln() per il testo e DocumentBuilder.insertImage() per un array di byte che rappresenta un’immagine.
- Al termine dell’elaborazione della riga di dati termina anche la riga creata da DocumentBuilder utilizzando DocumentBuilder.endRow().
- Una volta che tutte le righe di DataTable sono state elaborate, termina la tabella chiamando DocumentBuilder.endTable().
- Infine, possiamo impostare lo stile di tabella desiderato utilizzando una delle proprietà della tabella appropriate come Table.getStyleIdentifier() per applicare automaticamente la formattazione all’intera tabella.
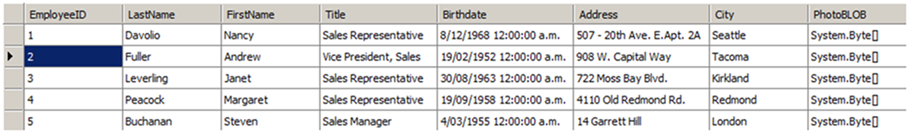
In questo esempio vengono utilizzati i seguenti dati nel nostro DataTable:
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come eseguire l’algoritmo di cui sopra in Aspose.Words:
Il metodo può quindi essere facilmente chiamato usando DocumentBuilder e data.
L’esempio di codice seguente mostra come importare i dati da un DataTable e inserirli in una nuova tabella nel documento:
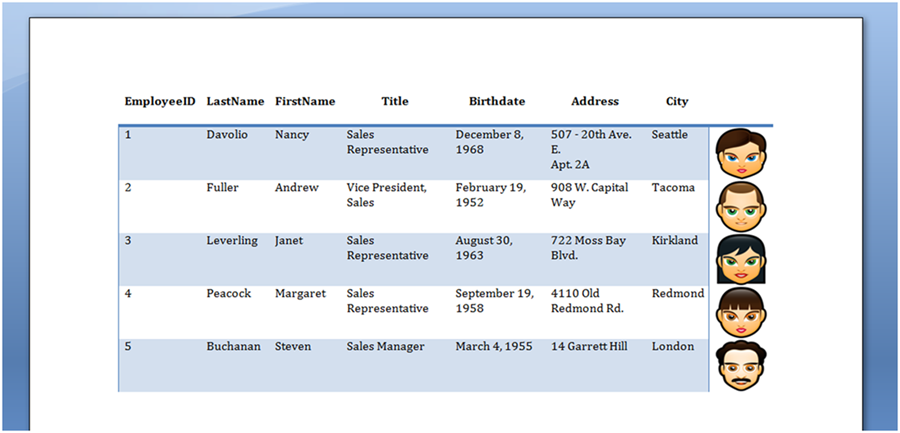
La tabella mostrata nell’immagine qui sotto è prodotta eseguendo il codice sopra.