Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
Il nuovo metodo insertChart è stato aggiunto alla classe DocumentBuilder. Quindi, vediamo come inserire un semplice istogramma nel documento usando il metodo insertChart.
In questa sezione impareremo come inserire un grafico in un documento.
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come inserire istogramma:
Il codice produce il seguente risultato:
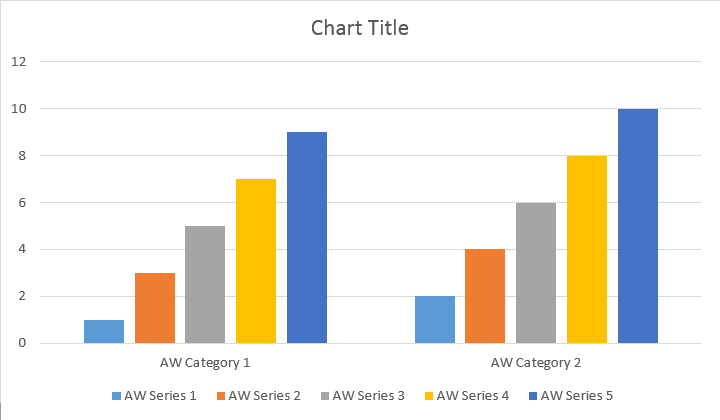
Esistono quattro diversi sovraccarichi per il metodo Add series, che sono stati esposti per coprire tutte le possibili varianti di origini dati per tutti i tipi di grafico:
Il codice produce il seguente risultato:
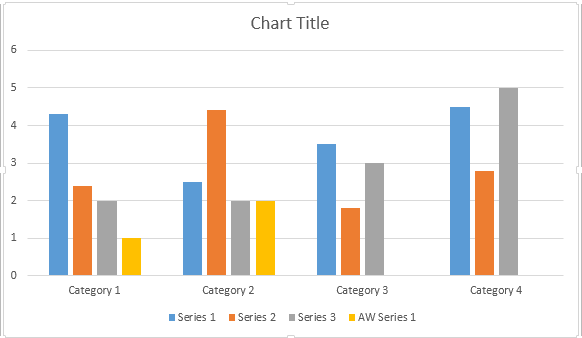
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come inserire un grafico a dispersione:
Il codice produce il seguente risultato:
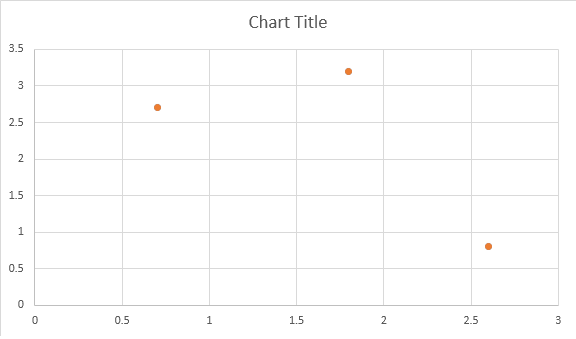
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come inserire un grafico ad area:
Il codice produce il seguente risultato:
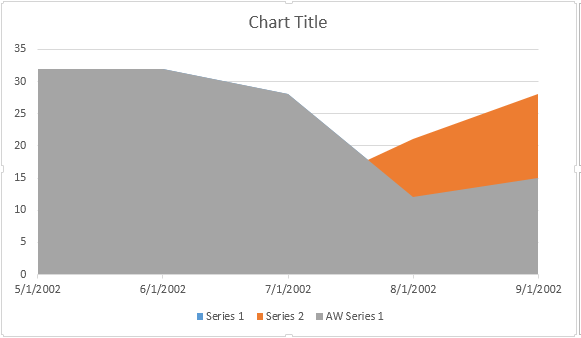
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come inserire un grafico a bolle:
Il codice produce il seguente risultato:
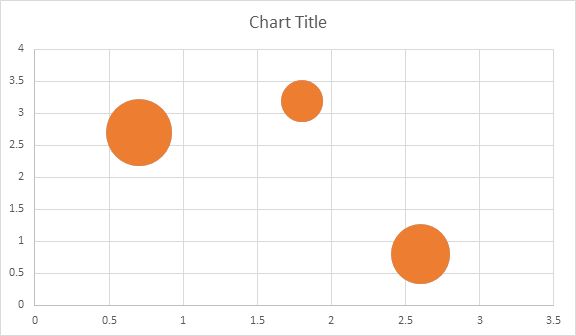
Shape.ChartUna volta che il grafico è stato inserito e riempito con i dati, è possibile modificarne l’aspetto. La proprietà Shape.Chart contiene tutte le opzioni relative al grafico disponibili tramite public API.
Ad esempio, cambiamo il titolo del grafico o il comportamento della legenda:
Il codice genera i seguenti risultati:
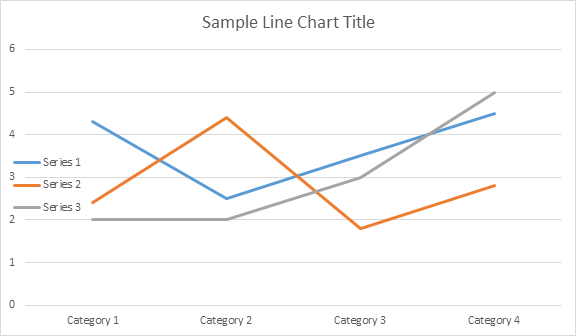
Diamo un’occhiata alla collezione ChartSeries. Tutte le serie di grafici sono disponibili attraverso la raccolta chart.getSeries(), che è Iterable:
È possibile rimuovere le serie una per una o cancellarle tutte e aggiungerne una nuova, se necessario. Il grafico appena inserito ha alcune serie predefinite aggiunte a questa raccolta. Per rimuoverli è necessario chiamare il metodo chart.getSeries().clear().
Ecco come lavorare con una serie particolare.
Si prega di vedere il risultato qui sotto:
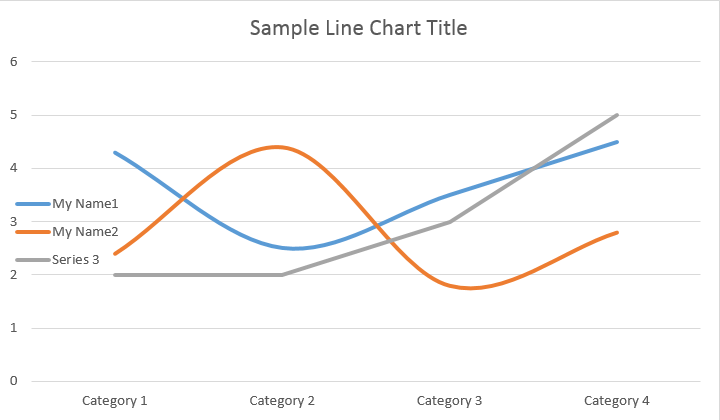
Tutti i singoli ChartSeries hanno opzioni predefinite ChartDataPoint, prova a utilizzare il seguente codice per modificarli:
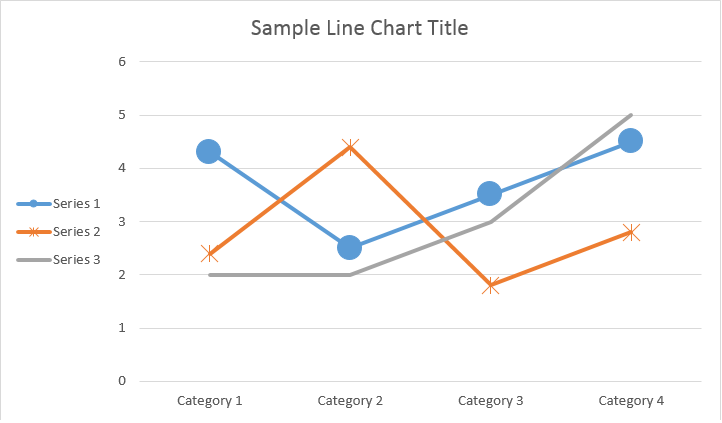
ChartSeriesUtilizzando ChartDataPoint è possibile personalizzare la formattazione di un singolo punto dati della serie di grafici:
Si prega di vedere il risultato qui sotto:
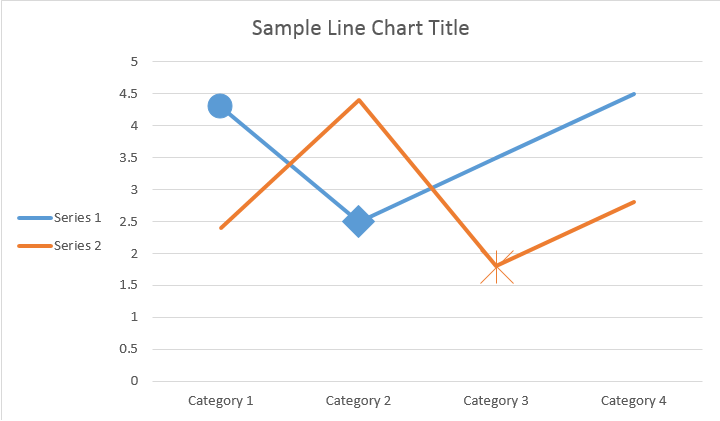
Utilizzando ChartDataLabel è possibile specificare la formattazione di una singola etichetta di dati della serie di grafici, ad esempio mostra / nascondi LegendKey, CategoryName, SeriesName, Valore ecc:
Si prega di vedere il risultato qui sotto:
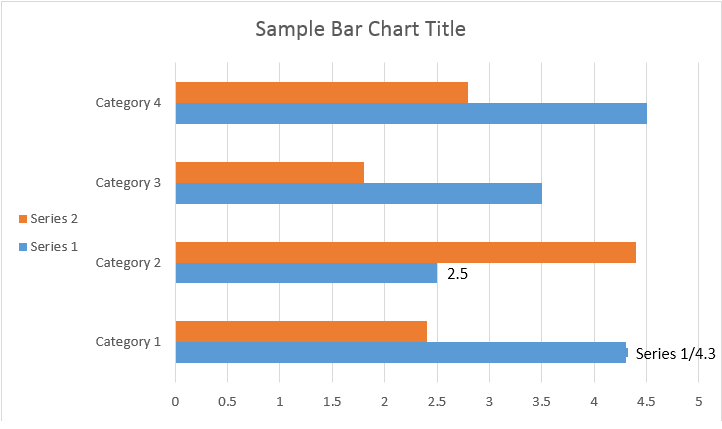
La classe ChartDataLabelCollection definisce le proprietà che possono essere utilizzate per impostare le opzioni predefinite per ChartDataLabels per il grafico Series. Queste proprietà includono setShowCategoryName, setShowBubbleSize, setShowPercentage, setShowSeriesName, setShowValue ecc:
Si prega di vedere il risultato qui sotto:
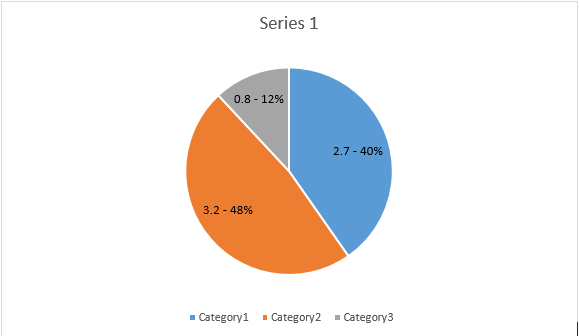
Utilizzando la proprietà NumberFormat, è possibile specificare la formattazione numerica di una singola etichetta dati del grafico.
L’esempio di codice seguente mostra come formattare un numero di etichetta dati:
Se si desidera lavorare con l’asse grafico, il ridimensionamento e le unità di visualizzazione per l’asse dei valori, utilizzare le classi ChartAxis, AxisDisplayUnit e AxisScaling.
L’esempio di codice seguente mostra come definire le proprietà degli assi X e Y:
L’esempio di codice seguente mostra come impostare i valori di data/ora sulle proprietà dell’asse:
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come modificare il formato dei numeri sull’asse dei valori:
La classe AxisBound rappresenta un limite minimo o massimo dei valori degli assi. Bound può essere specificato come un valore numerico, data-ora o uno speciale valore “auto”.
L’esempio di codice seguente mostra come impostare i limiti di un asse:
L’esempio di codice seguente mostra come impostare l’unità di intervallo tra le etichette su un asse:
Se si desidera mostrare o nascondere l’asse del grafico, è possibile ottenere questo semplicemente impostando il valore della proprietà ChartAxis.Hidden.
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come nascondere l’asse Y del grafico:
Se si desidera impostare un allineamento del testo per le etichette a più righe, è sufficiente impostare il valore della proprietà setTickLabelAlignment().
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come spuntare l’allineamento delle etichette:
La formattazione del riempimento e del tratto può essere impostata per serie di grafici, punti dati e marcatori. Per fare ciò, è necessario utilizzare le proprietà del tipo ChartFormat nelle classi ChartSeries, ChartDataPoint e ChartMarker, nonché gli alias per alcune proprietà, ad esempio ForeColor, BackColor, Visible e Transparency nella classe Stroke.
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come impostare il colore della serie:
Document doc = new Document();
DocumentBuilder builder = new DocumentBuilder(doc);
Shape shape = builder.InsertChart(ChartType.Column, 432, 252);
Chart chart = shape.Chart;
ChartSeriesCollection seriesColl = chart.Series;
// Delete default generated series.
seriesColl.Clear();
// Create category names array.
string[] categories = new string[] { "AW Category 1", "AW Category 2" };
// Adding new series. Value and category arrays must be the same size.
ChartSeries series1 = seriesColl.Add("AW Series 1", categories, new double[] { 1, 2 });
ChartSeries series2 = seriesColl.Add("AW Series 2", categories, new double[] { 3, 4 });
ChartSeries series3 = seriesColl.Add("AW Series 3", categories, new double[] { 5, 6 });
// Set series color.
series1.Format.Fill.ForeColor = Color.Red;
series2.Format.Fill.ForeColor = Color.Yellow;
series3.Format.Fill.ForeColor = Color.Blue;
doc.Save("ColumnColor.docx");
Il seguente esempio di codice mostra come impostare il colore e il peso della linea:
Document doc = new Document();
DocumentBuilder builder = new DocumentBuilder(doc);
Shape shape = builder.InsertChart(ChartType.Line, 432, 252);
Chart chart = shape.Chart;
ChartSeriesCollection seriesColl = chart.Series;
// Delete default generated series.
seriesColl.Clear();
// Adding new series.
ChartSeries series1 = seriesColl.Add("AW Series 1", new double[] { 0.7, 1.8, 2.6 }, new double[] { 2.7, 3.2, 0.8 });
ChartSeries series2 = seriesColl.Add("AW Series 2", new double[] { 0.5, 1.5, 2.5 }, new double[] { 3, 1, 2 });
// Set series color.
series1.Format.Stroke.ForeColor = Color.Red;
series1.Format.Stroke.Weight = 5;
series2.Format.Stroke.ForeColor = Color.LightGreen;
series2.Format.Stroke.Weight = 5;
doc.Save("LineColorAndWeight.docx");
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.