Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
有时,表中的某些行需要标题或占用表全宽的大文本块。 为了正确设计表格,用户可以将几个表格单元格合并为一个。 Aspose.Words在处理所有输入格式(包括导入HTML内容)时支持合并单元格。
在Aspose.Words中,合并的单元格由CellFormat类的以下属性表示:
这些属性的值确定单元格的合并行为:
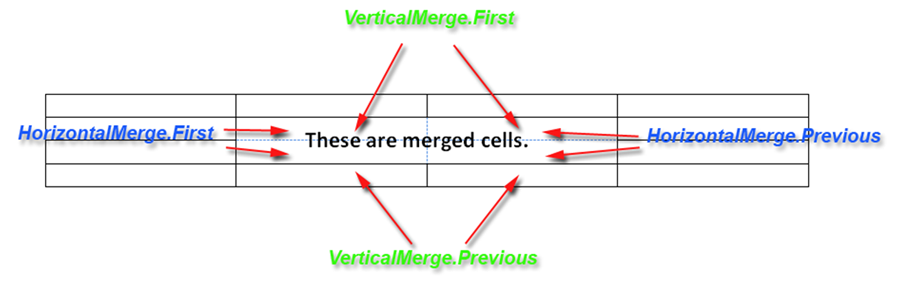
要检查单元格是否是合并单元格序列的一部分,我们只需检查HorizontalMerge和VerticalMerge属性。
下面的代码示例演示如何打印水平和垂直单元格合并类型:
要合并使用DocumentBuilder创建的表中的单元格,您需要为预期合并的每个单元格设置适当的合并类型–首先是CellMerge.First,然后是CellMerge.Previous。
此外,您必须记住清除那些不需要合并的单元格的合并设置–这可以通过将第一个非合并单元格设置为CellMerge.None来完成。 如果不这样做,表中的所有单元格都将被合并。
下面的代码示例演示如何创建具有两行的表,其中第一行中的单元格水平合并:
下面的代码示例演示如何创建一个两列表,其中第一列中的单元格垂直合并:
在不使用DocumentBuilder的其他情况下,例如在现有表中,以前面的方式合并单元格可能不那么容易。 相反,我们可以将合并属性应用于单元格的基本操作包装在一个使任务更容易的方法中。 此方法类似于合并自动化方法,它被称为合并表中的单元格范围。
下面的代码将合并指定范围内的表格单元格,从给定单元格开始,到结束单元格结束。 在这种情况下,范围可以跨越多行或多列:
下面的代码示例演示如何在两个指定单元格之间合并单元格范围:
正如我们在前面的文章中所说,Microsoft Word中的表是一组独立的行。 每行都有一组独立于其他行的单元格的单元格。 因此,在Microsoft Word表中没有"列"这样的对象,“第一列"类似于"表中每行的第一个单元格的集合”。 这允许用户有一个表,其中,例如,第1行由两个单元格–2cm和1cm组成,而第2行由两个不同的单元格–1cm和2cm宽组成。 Aspose.Words支持这种表的概念。
HTML中的表具有本质上不同的结构:每行具有相同数量的单元格,并且(对于任务很重要)每个单元格具有相应列的宽度,对于一列中的所有单元格都相同。 因此,如果HorizontalMerge和VerticalMerge返回不正确的值,请使用以下代码示例:
有时无法检测哪些单元格被合并,因为某些较新版本的Microsoft Word在单元格水平合并时不再使用合并标志。 但是对于使用合并标志按单元格宽度水平合并到单元格的情况,Aspose.Words提供了ConvertToHorizontallyMergedCells方法来转换单元格。 此方法只需转换表格并根据需要添加新单元格。
下面的代码示例在操作中显示了上述方法:
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.