Работа с преобразованиями в PS-файле | Python
Преобразование содержимого в PS Document
В этой статье рассказывается, как применять различные преобразования — перемещение, масштабирование, вращение и сдвиг — к прямоугольному контуру, добавленному в PsDocument.
Мы разбили один фрагмент кода на несколько разделов: начало, конец и каждое преобразование в отдельности. В PostScript преобразования всегда выполняются в графическом состоянии, ограниченном операторами “gsave” и “grestore”. Поэтому наш PsDocument включает такие методы, как “write_graphics_save()” и “write_graphics_restore()” для установки и сброса этих графических состояний. Между этими методами можно добавлять любой контент, включая вложенные графические состояния, что позволяет выполнять преобразования или обрезку. Эти преобразования влияют только на вложенные графические состояния и не влияют на внешние. Однако если преобразование выполняется без использования методов “write_graphics_save()” и “write_graphics_restore()”, это влияет на состояние графики верхнего уровня, и этому подвергается все содержимое внутри PsDocument. трансформация.
Алгоритм применения любого преобразования к содержимому документа с нуля включает следующие шаги:
- Создайте выходной поток для полученного PS-файла.
- Создайте PsSaveOptions.
- Создайте PsDocument с уже созданным выходным потоком и сохраните параметры.
- Сохраните состояние графики. Когда мы создавали новое графическое состояние, предыдущее графическое состояние помещалось в стек графических состояний.
- Примените необходимые преобразования: перемещение, масштабирование, вращение, сдвиг или любую их комбинацию. В нашем коде мы показываем влияние каждого компонента трансформации отдельно и в итоге по 3 одновременно.
- Добавьте необходимый контент, который требуется трансформировать. В нашем случае мы создали реактивный угол aspose.pydrawing.GraphicsPath и затем залили его. Мы создали один прямоугольник перед любыми преобразованиями и просто заполняли его после каждого преобразования в текущем графическом состоянии.
- Восстановите состояние графики, чтобы вернуться к предыдущему состоянию, на которое не влияют примененные преобразования. В нашем случае это состояние графики верхнего уровня.
В этом фрагменте кода мы инициируем создание PsDocument, используя выходной поток и PsSaveOptions. Затем мы выполняем перевод состояния графики верхнего уровня в координаты (100, 100), чтобы сместить первый прямоугольник. Наконец, мы генерируем первый прямоугольник.
1data_dir = Util.get_data_dir_working_with_canvas()
2
3# Create an output stream for the PostScript document
4with open(data_dir + "Transformations_outPS.ps", "wb") as out_ps_stream:
5 # Create save options with default values
6 options = PsSaveOptions()
7
8 # Create a new 1-paged PS Document
9 document = PsDocument(out_ps_stream, options, False)
10
11 document.translate(100, 100)
12
13 # Create a graphics path from the rectangle
14 path = aspose.pydrawing.drawing2d.GraphicsPath()
15 path.add_rectangle(aspose.pydrawing.RectangleF(0, 0, 150, 100))
16
17 ##################################### No transformations ###############################################################
18 # Set the paint in the graphics state on upper level
19 document.set_paint(aspose.pydrawing.SolidBrush(aspose.pydrawing.Color.orange))
20
21 # Fill the first rectangle that is on the upper level graphics state and is without any transformations.
22 document.fill(path)
23 ########################################################################################################################
24
25
26 ##################################### Translation ######################################################################
27
28 # Save the graphics state in order to return back to this state after the transformation
29 document.write_graphics_save()
30
31 # Displace the current graphics state on 250 to the right. So we add a translation component to the current transformation.
32 document.translate(250., 0.)
33
34 # Set the paint in the current graphics state
35 document.set_paint(aspose.pydrawing.SolidBrush(aspose.pydrawing.Color.blue))
36
37 # Fill the second rectangle in the current graphics state (has translation transformation)
38 document.fill(path)
39
40 # Restore the graphics state to the previus (upper) level
41 document.write_graphics_restore()
42 ########################################################################################################################
43
44
45 # Displace on 200 to the bottom.
46 document.translate(0., 200.)
47
48 ##################################### Scaling ##########################################################################
49 # Save graphics state in order to return back to this state after transformation
50 document.write_graphics_save()
51
52 # Scale the current graphics state on 0.5 in X axis and on 0.75f in Y axis. So we add a scale component to the current transformation.
53 document.scale(0.5, 0.75)
54
55 # Set the paint in the current graphics state
56 document.set_paint(aspose.pydrawing.SolidBrush(aspose.pydrawing.Color.red))
57
58 # Fill the third rectangle in the current graphics state (has scale transformation)
59 document.fill(path)
60
61 # Restore the graphics state to the previus (upper) level
62 document.write_graphics_restore()
63 #####################################################################################################################
64
65
66 # Displace the upper level graphics state on 250 to the right.
67 document.translate(250., 0.)
68
69
70 ##################################### Rotation ######################################################################
71 #Save graphics state in order to return back to this state after transformation
72 document.write_graphics_save()
73
74 # Rotate the current graphics state on 45 degrees around the origin of the current graphics state (350, 300). So we add a rotation component to the current transformation.
75 document.rotate(float(45))
76
77 # Set the paint in the current graphics state
78 document.set_paint(aspose.pydrawing.SolidBrush(aspose.pydrawing.Color.green))
79
80 # Fill the fourth rectangle in the current graphics state (has rotation transformation)
81 document.fill(path)
82
83 # Restore the graphics state to the previus (upper) level
84 document.write_graphics_restore()
85 #####################################################################################################################
86
87
88 # Returns the upper level graphics state back to the left and displace on 200 to the bottom.
89 document.translate(-250., 200.)
90
91
92 ##################################### Shearing ######################################################################
93 # Save the graphics state in order to return back to this state after the transformation
94 document.write_graphics_save()
95
96 # Shear the current graphics state. So we add shear component to the current transformation.
97 document.shear(0.1, 0.2)
98
99 # Set the paint in the current graphics state
100 document.set_paint(aspose.pydrawing.SolidBrush(aspose.pydrawing.Color.pink))
101
102 # Fill the fifth rectangle in the current graphics state (has shear transformation)
103 document.fill(path)
104
105 # Restore the graphics state to the previus (upper) level
106 document.write_graphics_restore()
107 #####################################################################################################################
108
109
110 # Displace the upper level graphics state on 250 to the right.
111 document.translate(250., 0.)
112
113
114 ##################################### Complex transformation ########################################################
115 # Save the graphics state in order to return back to this state after the transformation
116 document.write_graphics_save()
117
118 # Transform the current graphics state with the complex transformation. So we add the translation, scale and rotation components to the current transformation.
119 document.transform(aspose.pydrawing.drawing2d.Matrix(1.2, -0.965925, 0.258819, 1.5, 0., 50.))
120
121 # Set the paint in the current graphics state
122 document.set_paint(aspose.pydrawing.SolidBrush(aspose.pydrawing.Color.aquamarine))
123
124 # Fill the sixth rectangle in the current graphics state (has complex transformation)
125 document.fill(path)
126
127 # Restore graphics state to the previus (upper) level
128 document.write_graphics_restore()
129 #####################################################################################################################
130
131
132 # Returns the upper level graphics state back to the left and displace on 200 to the bottom.
133 document.translate(-250., 200.)
134
135
136 ##################################### Again no transformation ########################################################
137 # Demonstrates that current graphics state's color is orange that was set up at the beginning of the code.
138 # Fill the seventh rectangle in the current graphics state (has no transformation)
139 document.fill(path)
140 #####################################################################################################################
141
142 # Close the current page
143 document.close_page()
144
145 # Save the document
146 document.save()Результат запуска этого кода:
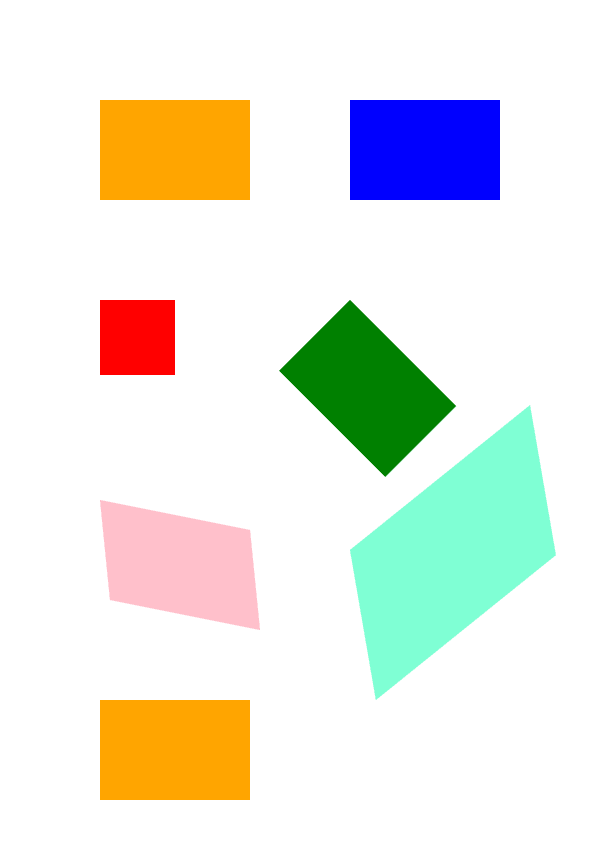
Вы можете загрузить примеры и файлы данных с сайта GitHub.