Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
Někdy některé řádky v tabulce vyžadují nadpis nebo velké bloky textu, které zabírají celou šířku tabulky. Pro správný návrh tabulky může uživatel sloučit několik buněk tabulky do jedné. Aspose.Words podporuje sloučené buňky při práci se všemi vstupními formáty, včetně importu HTML obsahu.
In Aspose.Words, Sloučené buňky jsou zastoupeny následujícími vlastnostmi: CellFormat třída:
Hodnoty těchto vlastností určují slučovací chování buněk:
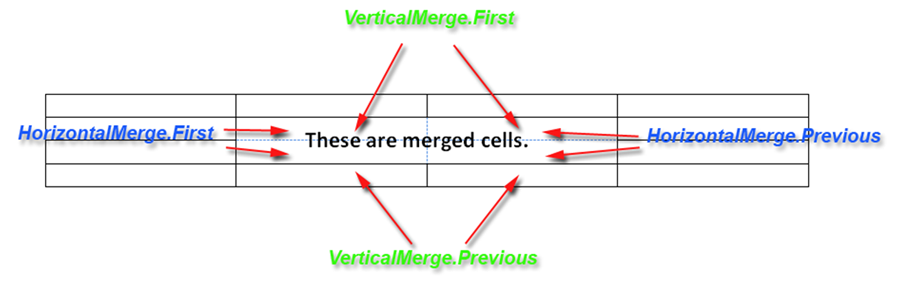
Chcete-li zjistit, zda je buňka součástí sekvence sloučených buněk, stačí zkontrolovat HorizontalMerge a VerticalMerge vlastnosti.
Následující příklad kódu ukazuje, jak tisknout horizontální a vertikální typ sloučení buňky:
Sloučit buňky v tabulce vytvořené s DocumentBuilder, Musíte nastavit vhodný typ sloučení pro každou buňku, kde se předpokládá sloučení nejdříve? CellMerge.First a pak CellMerge.Previous.
Musíte také pamatovat na to, abyste vyčistili nastavení sloučení pro ty buňky, kde není nutné sloučit. CellMerge.None. Pokud tomu tak není, všechny buňky v tabulce budou sloučeny.
Následující příklad kódu ukazuje, jak vytvořit tabulku se dvěma řádky, kde jsou buňky v prvním řádku sloučeny vodorovně:
Následující příklad kódu ukazuje, jak vytvořit tabulku dvou sloupců, kde jsou buňky v prvním sloupci vertikálně sloučeny:
V jiných situacích, kdy DocumentBuilder není používán, jako například ve stávající tabulce, slučovací buňky předchozí cestou nemusí být tak snadné. Místo toho můžeme zabalit základní operace, které se podílejí na aplikaci vlastností sloučení na buňky metodou, která tento úkol mnohem usnadňuje. Tato metoda je podobná metodě automatizace sloučení, která se volá ke sloučení řady buněk v tabulce.
Níže uvedený kód sloučí buňky tabulky ve stanoveném rozsahu, počínaje danou buňkou a končí na konci buňky. V tomto případě může rozsah rozdělit více řádků nebo sloupců:
Následující příklad kódu ukazuje, jak sloučit rozsah buněk mezi dvěma specifikovanými buňkami:
Jak jsme řekli v předchozích článcích, tabulka v Microsoft Word je soubor nezávislých řádků. Každá řada má sadu buněk, které jsou nezávislé na buňkách jiných řádků. Proto v Microsoft Word Tabulka neexistuje takovýto předmět, jako je sloupec To umožňuje uživatelům mít tabulku, v níž například 1. řádek se skládá ze dvou buněk 2cm a 1cm, a 2. řádek se skládá ze dvou různých buněk 1cm a 2cm široké. A Aspose.Words podporuje tento koncept tabulek.
Tabulka v HTML má v podstatě jinou strukturu: každý řádek má stejný počet buněk a (je to důležité pro úkol) každá buňka má šířku odpovídajícího sloupce, stejný pro všechny buňky v jednom sloupci. Takže pokud HorizontalMerge a VerticalMerge vrátit nesprávnou hodnotu, použijte následující příklad kódu:
Někdy není možné zjistit, které buňky jsou sloučeny, protože některé novější verze Microsoft Word Pokud jsou buňky sloučeny vodorovně, nesmí již používat vlajky sloučení. Ale pro situace, kdy jsou buňky sloučeny do buňky horizontálně podle jejich šířky pomocí slučovacích vlajek, Aspose.Words poskytuje ConvertToHorizontallyMergedCells způsob přeměny buněk. Tato metoda jednoduše přeměňuje tabulku a přidává nové buňky podle potřeby.
Následující příklad kódu ukazuje výše uvedenou metodu v provozu:
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.