Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
Aspose.Words Document Object Model (DOM) は、Word ドキュメントのメモリ内表現です。 Aspose.Words DOM を使用すると、Word ドキュメントのコンテンツと書式設定をプログラムで読み取り、操作、変更できます。
このセクションでは、Aspose.Words DOM の主要なクラスとそれらの関係について説明します。 Aspose.Words DOM クラスを使用すると、ドキュメント要素と書式設定にプログラムからアクセスできます。
Document オブジェクト ツリー {#create-a-document-objects-tree} の作成ドキュメントが Aspose.Words DOM に読み込まれると、オブジェクト ツリーが構築され、ソース ドキュメントのさまざまなタイプの要素が、さまざまなプロパティを持つ独自の DOM ツリー オブジェクトを持ちます。
Aspose.Words が Word 文書をメモリに読み取ると、さまざまな文書要素を表すさまざまなタイプのオブジェクトが作成されます。テキスト、段落、表、セクションのすべてがノードであり、文書自体もノードです。 Aspose.Words は、ドキュメント ノード タイプごとにクラスを定義します。
Aspose.Words のドキュメント ツリーは、複合デザイン パターンに従います。
以下の図は、Aspose.Words Document Object Model (DOM) のノード クラス間の継承を示しています。抽象クラスの名前は斜体で表示されます。
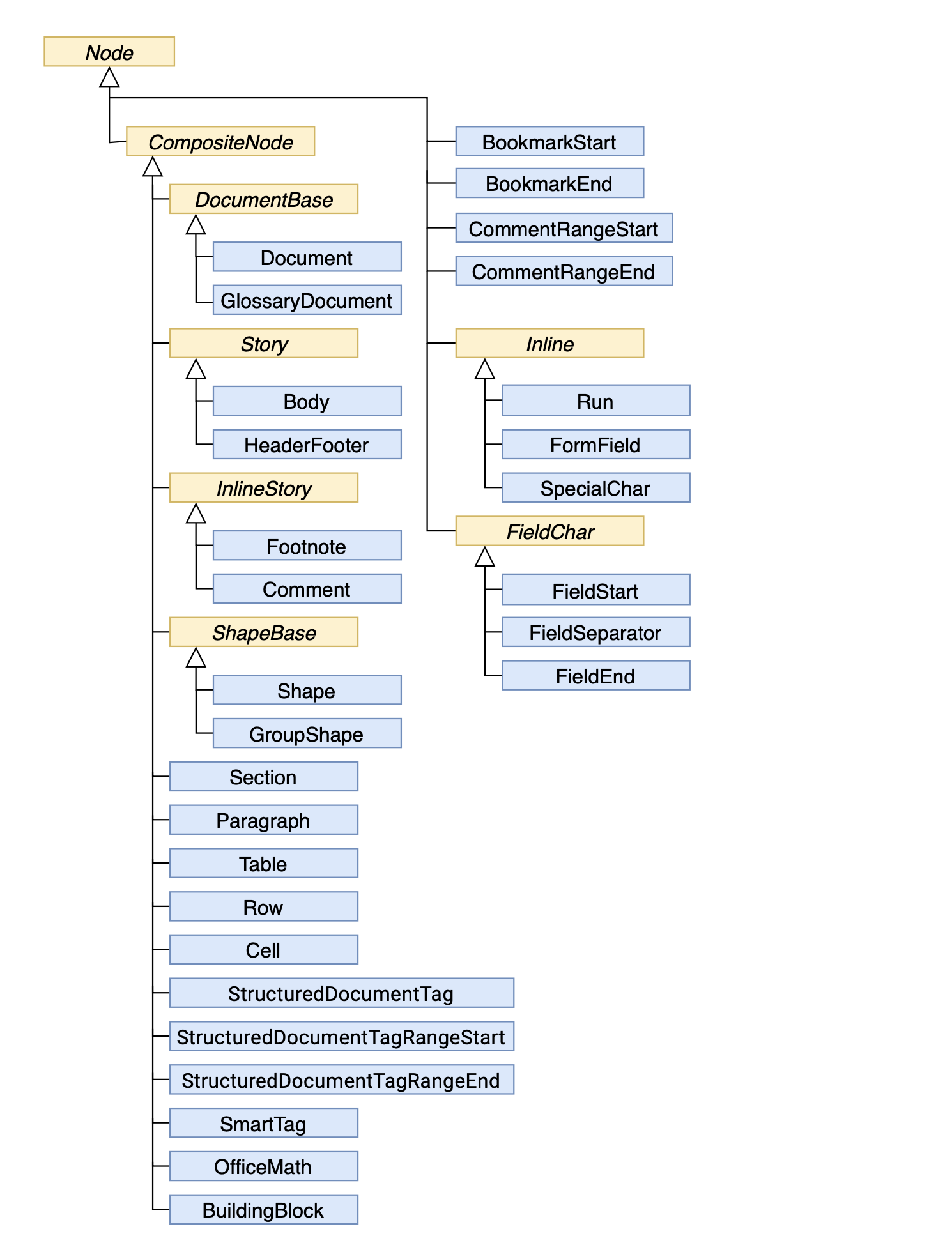
Node クラスから継承されていないため、この図には示されていません。
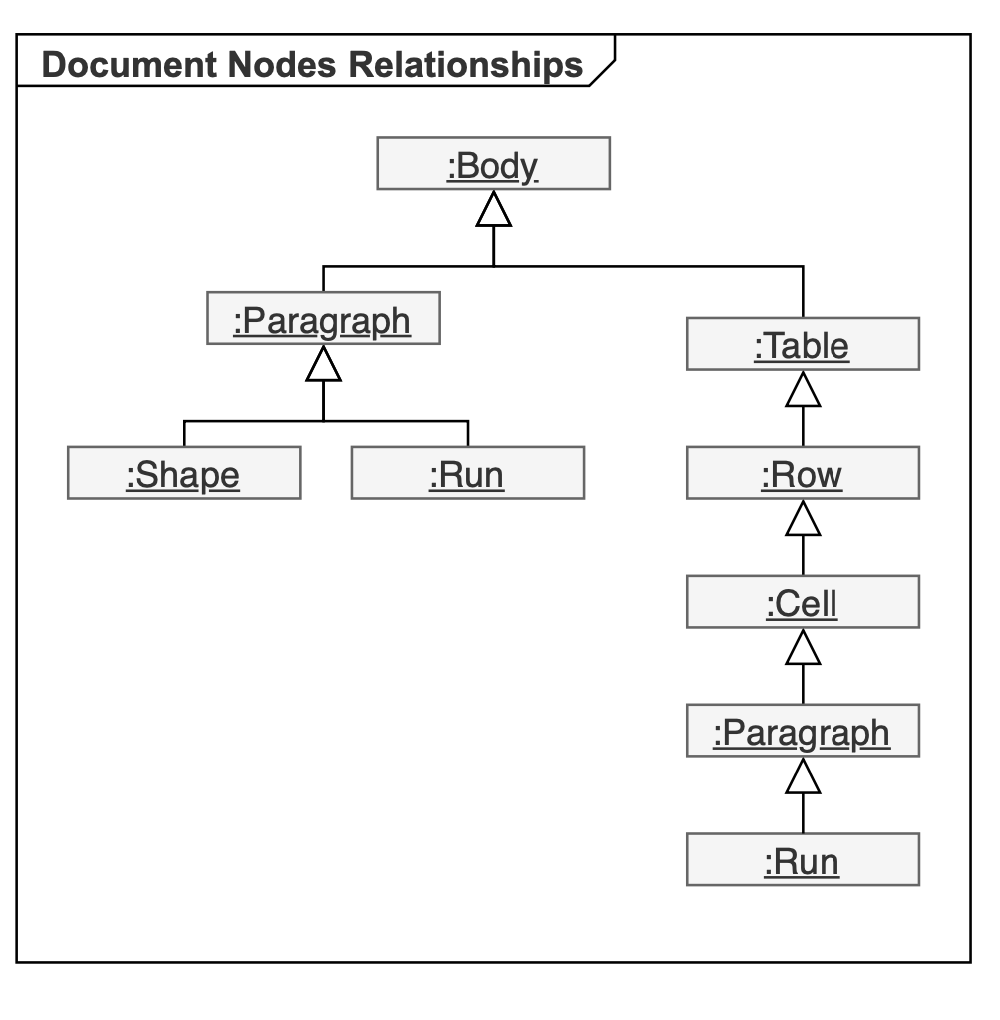
例を見てみましょう。次の図は、さまざまなタイプのコンテンツを含む Microsoft Word ドキュメントを示しています。
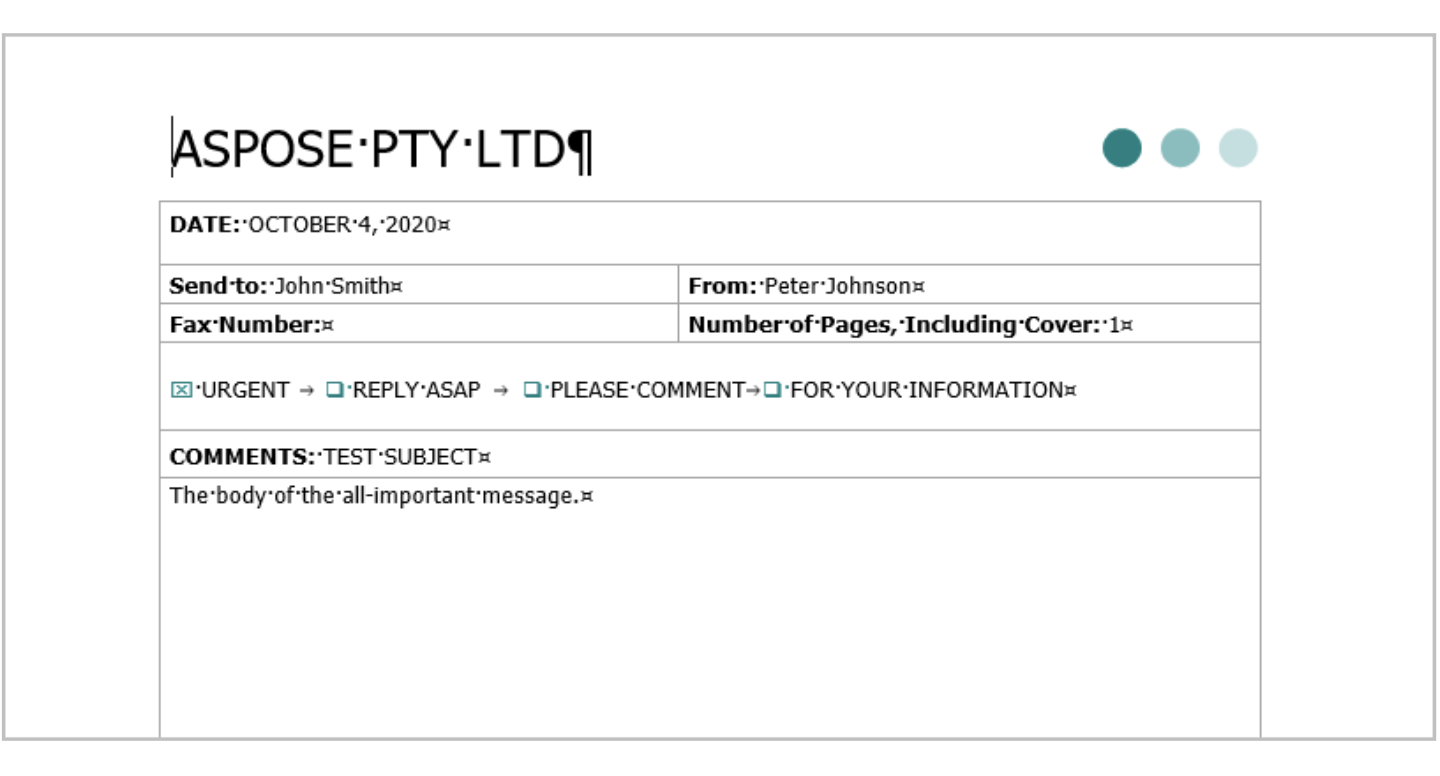
上記のドキュメントを Aspose.Words DOM に読み込むと、以下のスキーマに示すようにオブジェクトのツリーが作成されます。
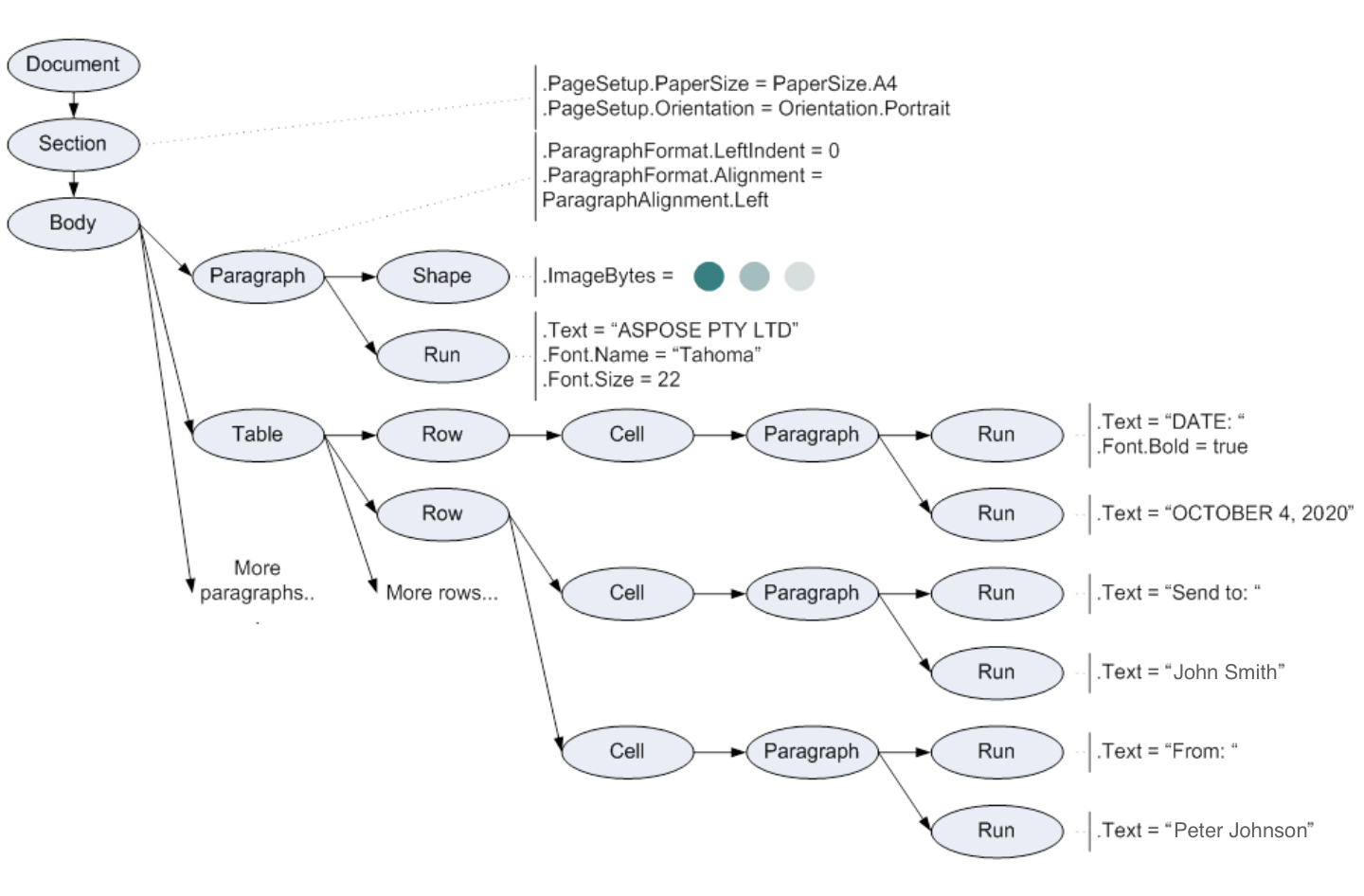
Document、Section、Paragraph、Table、Shape、Run、および図上のその他すべての省略記号は、Word 文書の要素を表す Aspose.Words オブジェクトです。
Node タイプ {#get-a-node-type} を取得するNode クラスは異なるノードを相互に区別するのに十分ですが、Aspose.Words は特定のタイプのノードの選択など、一部の API タスクを簡素化する NodeType 列挙を提供します。
各ノードのタイプは、NodeType プロパティを使用して取得できます。このプロパティは、NodeType 列挙値を返します。たとえば、Paragraph クラスで表される段落ノードは NodeType.Paragraph を返し、Table クラスで表される表ノードは NodeType.Table を返します。
次の例は、NodeType 列挙を使用してノード タイプを取得する方法を示しています。
Aspose.Words はドキュメントをノード ツリーとして表現し、ノード間を移動できるようにします。このセクションでは、Aspose.Words でドキュメント ツリーを探索および移動する方法について説明します。
前に示したサンプル ドキュメントをドキュメント エクスプローラーで開くと、ノード ツリーが Aspose.Words で表現されているとおりに表示されます。
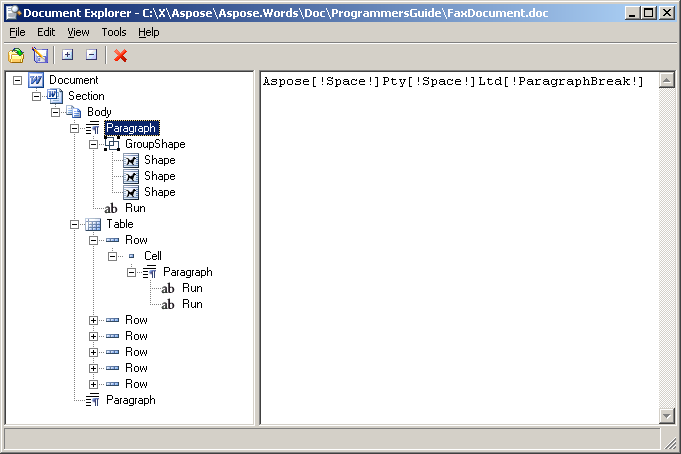
ツリー内のノード間には次のような関係があります。
他のノードを含むことができるノードは CompositeNode クラスから派生し、すべてのノードは最終的に Node クラスから派生します。これら 2 つの基本クラスは、ツリー構造のナビゲーションと変更のための共通のメソッドとプロパティを提供します。
次の UML オブジェクト図は、サンプル ドキュメントのいくつかのノードと、親、子、兄弟プロパティを介したそれらの相互関係を示しています。
スタイルやリストなどの重要なドキュメント全体の構造が Document ノードに格納されるため、ノードは常に特定のドキュメントに属します。これは、ノードが作成されたばかりか、ツリーから削除されたばかりであってもです。たとえば、各段落にはドキュメントに対してグローバルに定義されたスタイルが割り当てられているため、Document なしで Paragraph を作成することはできません。このルールは、新しいノードを作成するときに使用されます。新しい Paragraph を DOM に直接追加するには、ドキュメント オブジェクトをコンストラクターに渡す必要があります。
DocumentBuilder を使用して新しい段落を作成する場合、ビルダーには常に、DocumentBuilder.Document プロパティを通じてそれにリンクされた Document クラスがあります。
次のコード例は、ノードを作成するときに、そのノードを所有するドキュメントが常に定義されることを示しています。
各ノードには、ParentNode プロパティで指定された親があります。次の場合、ノードには親ノードがありません。つまり、ParentNode は null です。
Remove メソッドを呼び出すことで、親からノードを削除できます。次のコード例は、親ノードにアクセスする方法を示しています。
CompositeNode の子ノードにアクセスする最も効率的な方法は、最初と最後の子ノードをそれぞれ返す FirstChild プロパティと LastChild プロパティを使用することです。子ノードがない場合、これらのプロパティは null を返します。
CompositeNode は、子ノードへのインデックス付きまたは列挙型のアクセスを可能にする GetChildNodes メソッドも提供します。 ChildNodes プロパティはノードのライブ コレクションです。つまり、ノードの削除または追加など、ドキュメントが変更されるたびに、ChildNodes コレクションが自動的に更新されます。
ノードに子がない場合、ChildNodes プロパティは空のコレクションを返します。 HasChildNodes プロパティを使用して、CompositeNode に子ノードが含まれているかどうかを確認できます。
次のコード例は、ChildNodes コレクションによって提供される列挙子を使用して CompositeNode の直接の子ノードを列挙する方法を示しています。
次のコード例は、インデックス付きアクセスを使用して CompositeNode の直接の子ノードを列挙する方法を示しています。
PreviousSibling プロパティと NextSibling プロパティをそれぞれ使用して、特定のノードの直前または直後のノードを取得できます。ノードがその親の最後の子である場合、NextSibling プロパティは null です。逆に、ノードがその親の最初の子の場合、PreviousSibling プロパティは null になります。
次のコード例は、複合ノードのすべての直接および間接の子ノードに効率的にアクセスする方法を示しています。
これまで、基本タイプの 1 つである Node または CompositeNode を返すプロパティについて説明してきました。ただし、場合によっては、Run や Paragraph などの特定のノード クラスに値をキャストする必要がある場合があります。つまり、複合である Aspose.Words DOM を使用する場合、キャストから完全に逃れることはできません。
キャストの必要性を減らすために、ほとんどの Aspose.Words クラスは、厳密に型指定されたアクセスを提供するプロパティとコレクションを提供します。型付きアクセスには 3 つの基本パターンがあります。
型付きプロパティは単なる便利なショートカットであり、Node.ParentNode や CompositeNode.FirstChild から継承された汎用プロパティよりも簡単にアクセスできる場合があります。
次のコード例は、型付きプロパティを使用してドキュメント ツリーのノードにアクセスする方法を示しています。
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.