Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
要更好地控制表的工作方式,请了解如何操作列和行。
列,行和单元格通过其索引访问所选文档节点来管理。 查找任何节点的索引涉及从父节点收集元素类型的所有子节点,然后使用IndexOf方法在集合中查找所需节点的索引。
有时您可能需要对文档中的特定表进行更改。 为此,您可以通过其索引引用表。
下面的代码示例演示如何检索文档中表的索引:
同样,您可能需要对选定表中的特定行进行更改。 为此,您还可以通过其索引引用行。
下面的代码示例演示如何检索表中的行的索引:
最后,您可能需要对特定单元格进行更改,您也可以通过单元格索引执行此操作。
下面的代码示例演示如何检索行中单元格的索引:
在Aspose.Words文档对象模型(DOM)中,Table节点由Row个节点和Cell个节点组成。 因此,在Aspose.Words的Document对象模型中,与Word文档中一样,没有列的概念。
根据设计,Microsoft Word和Aspose.Words中的表行是完全独立的,基本属性和操作仅包含在表的行和单元格中。 这使表具有一些有趣的属性的能力:
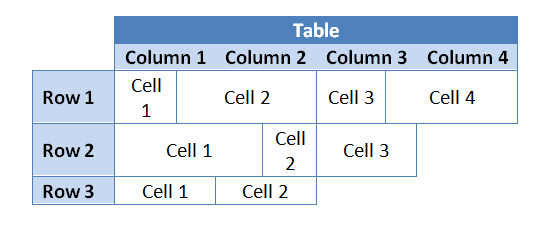
对列执行的任何操作实际上都是"快捷方式",通过集体更改行单元格来执行操作,使其看起来像是应用于列。 也就是说,您可以通过简单地迭代相同的表行单元格索引来对列执行操作。
下面的代码示例通过证明facade类来简化此类操作,该类收集构成表的"列"的单元格:
下面的代码示例演示如何将空白列插入到表中:
下面的代码示例演示如何从文档中的表中删除列:
您可以选择仅在第一页上或在每页上重复表中的第一行作为标题行(如果表被拆分为多个)。 在Aspose.Words中,您可以使用HeadingFormat属性在每个页面上重复标题行。
如果这些行一个接一个地位于表的开头,则还可以标记多个标题行。 为此,您需要将HeadingFormat属性应用于这些行。
下面的代码示例演示如何生成一个表,其中包括在后续页上重复的标题行:
有些时候,表的内容不应该跨页分割。 例如,如果标题位于表格上方,则标题和表格应始终保持在同一页面上,以保持正确的外观。
有两种不同的技术可用于实现此功能:
Allow row break across pages,应用于表行Keep with next,应用于表格单元格中的段落默认情况下,上述属性处于禁用状态。
这涉及到限制行单元格内的内容在页面上被分割。 在Microsoft Word中,这可以在表属性下找到,作为选项"允许行跨页中断"。 在Aspose.Words中,这是在Row的RowFormat对象下作为属性RowFormat.AllowBreakAcrossPages找到的。
下面的代码示例演示如何为表中的每行禁用跨页分隔行:
为了阻止表跨页面拆分,我们需要指定我们希望表中包含的内容保持在一起。
为此,Aspose.Words使用一种方法,该方法允许用户选择一个表,并为表单元格中的每个段落启用KeepWithNext参数为true。 例外情况是表中的最后一段,应将其设置为false。
下面的代码示例演示如何将表设置为在同一页上保持在一起:
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.