How to use Aspose.CAD in Angular
Contents
[
Hide
]
Prerequisites
- Angular CLI
- Visual Code
- Node.js
Convert dgn image to png and display in browser
In this example, you create a simple conversion program that converts a drawing and saves it as an image.
Creating the Angular Project
- Ensure that you aren’t already in an Angular workspace directory.
- Start a new one and then the name of the program or use other programs to create a project such as Visual Code or WebStorm:
ng new angular-example - Install Aspose.CAD from npm package
npm install aspose-cad - Open the angular.json file and add an entry in the script field, this script starts loading with the project, it is required to start processing the files
"scripts": [ "node_modules/aspose-cad/dotnet.js" ] - In app.component.html, create an input type file and img tags to load and display the drawing
<span style="background-color: red"> <input type="file" class="file-upload" (change)="onFileSelected($event)" /> <img alt="" id="image" [src]="imageUrl" /> </span> - In app.component.ts, we describe the process of starting the helper processes, processing and saving the image
import {Component} from '@angular/core'; import {DomSanitizer} from '@angular/platform-browser'; import {Image} from "aspose-cad/commonjs/Core/Image"; import {PngOptions} from "aspose-cad/commonjs/Options/PngOptions"; //need to boot dotnet process declare let dotnet: any; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'] }) export class AppComponent { title = 'angular-example'; imageUrl: any; imgFile: Uint8Array | null | undefined; constructor(private sanitizer: DomSanitizer) { } // @ts-ignore async ngOnInit() { console.log("aspose-cad WASM loading..."); await dotnet.boot().then((ex: any) => { console.log("aspose-cad WASM has been loaded"); }); } // @ts-ignore async onFileSelected(event) { const file: File = event.target.files[0]; file.arrayBuffer().then(async buff => { let x = new Uint8Array(buff); this.imgFile = await Image.Load(x); //Load image console.log(this.imgFile); var exportedFile = await Image.Save(this.imgFile, new PngOptions()); //save image to png var urlCreator = window.URL || window.webkitURL; var blob = new Blob([exportedFile], { type: 'application/octet-stream' }); //create src for converted image this.imageUrl = this.sanitizer.bypassSecurityTrustUrl(urlCreator.createObjectURL(blob)); //download png image let url = window.URL.createObjectURL(blob); let a = document.createElement('a'); document.body.appendChild(a); a.setAttribute('style', 'display: none'); a.href = url; a.download = "file.png"; a.click(); window.URL.revokeObjectURL(url); a.remove(); }); } } - Start application
npm start //or ng serveThe ng serve command:
- Builds the application
- Starts the development server
- Watches the source files
- Rebuilds the application as you make changes
The –open flag opens a browser to http://localhost:4200.
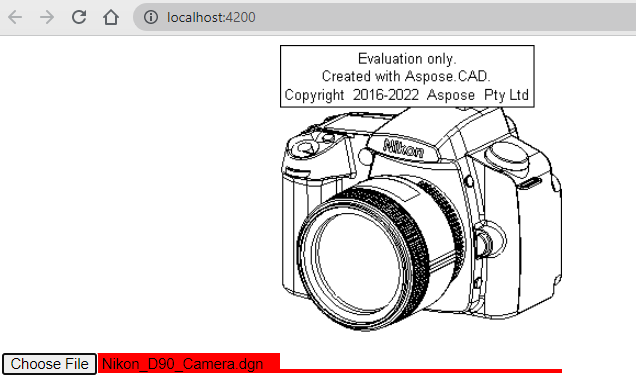
Execution example
- Choose file.
- Select any DXF, DWG, DGN, DWF, DWFX, IFC, STL, DWT, IGES, PLT, CF2, OBJ, HPGL, IGS, PCL, FBX, PDF, SVG file.
- If the answer is successful, the file will be displayed on the screen and will offer to download it.