Sending and Forwarding Messages - Send Outlook Email Messages using Java Program
The SmtpClient class allows applications to send email using the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
- The SmtpClient class is the only major entry developers use to send mail messages.
- The SmtpClient class also provides other common email delivery methods, including writing email messages to the file system, message queue etc.
- The SmtpClient class fully supports these two programming models:
- The SmtpClient class also supports sending messages as TNEF
To send the email message and block while waiting for the email to be transmitted to the SMTP server, use one of the synchronous Send methods. To allow your program main thread to continue executing while the email is transmitted, use the beginSend method.
Sending Emails Synchronously
An email message can be sent synchronously using the SmtpClient class send method. It sends the specified email message through an SMTP server for delivery. The message sender, recipients, subject, and message body are specified using String objects. To send an email message synchronously, follow the steps given below:
- Create an instance of MailMessage class and set its properties.
- Create an instance of SmtpClient class and specify the Host, port, username & Password.
- Send the Message using the SmtpClient class send method and pass the MailMessage instance.
The following Java code snippet shows you how to send outlook emails synchronously.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
// Declare msg as MailMessage instance
MailMessage msg = new MailMessage();
// Create an instance of SmtpClient class
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient();
// Specify your mailing host server, Username, Password, Port # and Security option
client.setHost("mail.server.com");
client.setUsername("username");
client.setPassword("password");
client.setPort(587);
client.setSecurityOptions(SecurityOptions.SSLExplicit);
try {
// Client.Send will send this message
client.send(msg);
System.out.println("Message sent");
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
Sending Emails Asynchronously
Sometimes, you may want to send mail asynchronously. For example, if you are sending a lot of mail through your application, the synchronous approach might not work. In such a scenario, you can use beginSend. The beginSend method of the SmtpClient class sends an email message to an SMTP server for delivery. This method does not block the calling thread and allows the caller to pass an object to the method that is invoked when the operation completes. To send an outlook email message asynchronously in Java, follow these steps:
- Create an instance of MailMessage class and use its different properties.
- Create an instance of SmtpClient class and specify the host, port, username, and password.
- Create a user-defined instance that will be passed to the method and invoked when the asynchronous operation completes.
- Send the message using beginSend method of SmtpClient class and pass the MailMessage instance and user-defined instance in it along with a callback function to be called when the operation is completed.
To receive a notification when the email has been sent or the operation has been canceled, the callback function passed to the beginSend method is called. After calling the SmtpClient class beginSend method it is not necessary to wait for an email message to be sent completely. We can call another method beginSend at the same time. When an email has been sent using the beginSend method, the code snippet prints a message (“Message Sent”). The following Java program or code snippet shows you how to send emails asynchronously.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
public static void run() {
sendMail();
}
static SmtpClient getSmtpClient() {
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient();
client.setHost("mail.server.com");
// Specify your mail Username, Password, Port # and security option
client.setUsername("username");
client.setPassword("password");
client.setPort(587);
client.setSecurityOptions(SecurityOptions.SSLExplicit);
return client;
}
static void sendMail() {
try {
// Declare msg as MailMessage instance
MailMessage msg = new MailMessage("sender@gmail.com", "receiver@gmail.com", "Test subject", "Test body");
SmtpClient client = getSmtpClient();
Object state = new Object();
IAsyncResult ar = client.beginSend(msg, callback, state);
// If the user canceled the send, and mail hasn't been sent yet,
client.cancelAsyncOperation(ar);
msg.dispose();
System.out.println("Goodbye.");
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
}
static AsyncCallback callback = new AsyncCallback() {
public void invoke(IAsyncResult ar) {
IAsyncResultExt task = null;
if (ar instanceof IAsyncResult)
task = (IAsyncResultExt) ar;
if (task != null && task.isCanceled()) {
System.out.println("Send canceled.");
}
if (task != null && task.getErrorInfo() != null) {
System.out.println(task.getErrorInfo());
} else {
System.out.println("Message Sent.");
}
}
};
Sending Stored Messages from Disc
EML files, (Outlook Express Electronic Mail files) contains an email header, message body, and any attachments. Aspose.Email lets developers work with EML files in different ways. This article shows how to load EML files from disk and send them as emails with SMTP. You can load .eml files from disk or stream into the MailMessage class and send the email message using the SmtpClient class. The MailMessage class is the main class for creating new email messages, loading email message files from disk or stream and saving the messages. The following Java code snippet shows how to send stored messages from the disc.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
// Load an EML file in MailMessage class
MailMessage message = MailMessage.load(dataDir + "test.eml");
// Send this message using SmtpClient
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient("host", "username", "password");
try {
client.send(message);
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
Sending Plain Text Email
The programming samples below show how to send a plain text email message. The Body property, a property of the MailMessage class, is used to specify the plain text content of the message body. To send a plain text email message, follow these steps:
- Create an instance of the MailMessage class.
- Specify the sender and receiver email addresses in the MailMessage instance.
- Specify the Body content, used for the plain text message.
- Create an instance of the SmtpClient class and send the email.
The following code snippet shows you how to send a plain text email.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
// Create an instance of the MailMessage class
MailMessage message = new MailMessage();
// Set From field, To field and Plain text body
message.setFrom(MailAddress.to_MailAddress("sender@sender.com"));
message.getTo().add("receiver@receiver.com");
message.setBody("This is Plain Text Body");
// Create an instance of the SmtpClient class
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient();
// And Specify your mailing host server, Username, Password and Port
client.setHost("smtp.server.com");
client.setUsername("Username");
client.setPassword("Password");
client.setPort(25);
try {
// Client.Send will send this message
client.send(message);
System.out.println("Message sent");
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
Sending Email with HTML body
The programming samples below show how you can send a simple HTML email message. The HtmlBody, a property of the MailMessage class, is used to specify the HTML content of the message body. To send a simple HTML email, follow these steps:
- Create an instance of the MailMessage class.
- Specify sender and receiver email address in the MailMessage instance.
- Specify the HtmlBody content.
- Create an instance of the SmtpClient class and send the email using the send method.
For the purposes of this article, the HTML content of the email is rudimentary:
This is the HTML body Most HTML emails will be more complex. The following Java program snippet shows you how to send an email with HTML body.public static void run() {
// Declare msg as MailMessage instance
MailMessage msg = new MailMessage();
// Use MailMessage properties like specify sender, recipient, message and HtmlBody
msg.setFrom(MailAddress.to_MailAddress("newcustomeronnet@gmail.com"));
msg.setTo(MailAddressCollection.to_MailAddressCollection("asposetest123@gmail.com"));
msg.setSubject("Test subject");
msg.setHtmlBody("<html><body>This is the HTML body</body></html>");
SmtpClient client = getSmtpClient();
try {
// Client will send this message
client.send(msg);
System.out.println("Message sent");
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
System.out.println("Email sent with HTML body.");
}
private static SmtpClient getSmtpClient() {
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient("smtp.gmail.com", 587, "your.email@gmail.com", "your.password");
client.setSecurityOptions(SecurityOptions.Auto);
return client;
}
Sending Email with Alternate Message Text
The programming samples below show how to send a simple HTML email message with alternative content. Use the AlternateView class to specify copies of an email message in different formats. For example, if you send a message in HTML, you might also want to provide a plain text version for recipients who use email readers that cannot display HTML content. Or, if you are sending a newsletter, you might want to provide a plain text copy of the text for those recipients who have chosen to receive a plain text version. To send an email with alternate text, follow these steps:
- Create an instance of the MailMessage class.
- Specify sender and receiver email addresses in the MailMessage instance.
- Create an instance of the AlternateView class.
This creates an alternate view to an email message using the content specified in the string.
- Add the instance of the AlternateView class to the MailMessage object.
- Create an instance of the SmtpClient class and send the email using the send method.
The following code snippet shows you how to send an email with alternate text.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
// Declare message as MailMessage instance
MailMessage message = new MailMessage();
// Creates AlternateView to view an email message using the content specified in the //String
AlternateView alternate = AlternateView.createAlternateViewFromString("Alternate Text");
// Adding alternate text
message.getAlternateViews().addItem(alternate);
Sending Bulk Emails
Sending emails in bulk means sending a batch of emails in one message. We can send a batch of email using the of SmtpClient class send method overload that accepts a MailMessageCollection class:
- Create an instance of SmtpClient class.
- Specify the SmtpClient class properties.
- Create an instance of the MailMessage class.
- Specify sender, receiver, mail subject and message in the instance of the MailMessage class.
- Repeat the above two steps again, if you want to send email to a different person.
- Create an instance of MailMessageCollection class.
- Add an instance of MailMessage class in the object of the MailMessageCollection class.
- Now send your email using the SmtpClient class send method by passing the instance of MailMessageCollection class in it.
The following code snippet shows you how to send bulk emails.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
// Create SmtpClient as client and specify server, port, user name and password
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient("mail.server.com", 25, "Username", "Password");
// Create instances of MailMessage class and Specify To, From, Subject and Message
MailMessage message1 = new MailMessage("msg1@from.com", "msg1@to.com", "Subject1", "message1, how are you?");
MailMessage message2 = new MailMessage("msg1@from.com", "msg2@to.com", "Subject2", "message2, how are you?");
MailMessage message3 = new MailMessage("msg1@from.com", "msg3@to.com", "Subject3", "message3, how are you?");
// Create an instance of MailMessageCollection class
MailMessageCollection manyMsg = new MailMessageCollection();
manyMsg.addItem(message1);
manyMsg.addItem(message2);
manyMsg.addItem(message3);
// Use client.BulkSend function to complete the bulk send task
try {
// Send Message using BulkSend method
client.send(manyMsg);
System.out.println("Message sent");
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
Get Information about Bulk Messages Sent
When you send messages in bulk, you can get information about the number of successfully sent messages and the list of these messages. The SucceededSending event is used for this purpose.
The code sample below shows how to get information about the number of successfully sent messages:
try (SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient(host, SecurityOptions.Auto)) {
final AtomicInteger messageCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
client.setSucceededSending(new EventHandler<MailMessageEventArgs>() {
public void invoke(Object sender, MailMessageEventArgs eventArgs) {
System.out.println("The message " + eventArgs.getMessage().getSubject() + " was successfully sent.");
messageCount.incrementAndGet();
}
});
client.send(messages);
System.out.println(messageCount + " messages were successfully sent.");
}
Sending Emails with MultiConnection
SmtpClient provides a UseMultiConnection property which can be used to create multiple connections for heavy operations. You may also set the number of connections to be used during multiconnection mode by using SmtpClient.ConnectionsQuantity. The following code snippet demonstrates the use of the multiconnection mode for sending multiple messages.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
SmtpClient smtpClient = new SmtpClient();
smtpClient.setHost("<HOST>");
smtpClient.setUsername("<USERNAME>");
smtpClient.setPassword("<PASSWORD>");
smtpClient.setPort(587);
smtpClient.setSupportedEncryption(EncryptionProtocols.Tls);
smtpClient.setSecurityOptions(SecurityOptions.SSLExplicit);
List<MailMessage> messages = new ArrayList<MailMessage>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
MailMessage message = new MailMessage("<EMAIL ADDRESS>", "<EMAIL ADDRESS>", "Test Message - " + UUID.randomUUID().toString(),
"SMTP Send Messages with MultiConnection");
messages.add(message);
}
smtpClient.setConnectionsQuantity(5);
smtpClient.setUseMultiConnection(MultiConnectionMode.Enable);
smtpClient.send(messages);
Sending a Message as TNEF
TNEF emails have special formatting which may be lost if sent using the standard API. Aspose.Email provides the capability to send emails as TNEF, thus preserving the format. The SmtpClient class UseTnef property can be set to send the email as TNEF. The following code snippet shows you how to send a message as TNEF.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
String emlFileName = dataDir + "Message.eml"; // A TNEF Email
// Load from eml
MailMessage eml1 = MailMessage.load(emlFileName, new EmlLoadOptions());
eml1.setFrom(MailAddress.to_MailAddress("somename@gmail.com"));
eml1.getTo().clear();
eml1.getTo().addItem(new MailAddress("first.last@test.com"));
eml1.setSubject("With PreserveTnef flag during loading");
eml1.setDate(new Date());
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient("smtp.gmail.com", 587, "somename", "password");
client.setSecurityOptions(SecurityOptions.Auto);
client.setUseTnef(true); // Use this flag to send as TNEF
client.send(eml1);
Sending Meeting Requests
Microsoft Outlook offers calendar functions as well as email management. When a user opens an email with an invitation to an event, Outlook prompts them to accept or reject the invitation. Aspose.Email lets developers add calendar functions to your emails.
Sending Requests via Email
To send meeting requests via email, follow these steps:
- Create an instance of the MailMessage class.
- Specify sender and recipient addresses using an instance of the MailMessage class.
- Initialize an instance of the Appointment class and pass its values.
- Specify summary and description in the Calendar instance.
- Add the Calendar) to the MailMessage instance and pass it the Appointment instance.
| iCalendar meeting request sent by email |
|---|
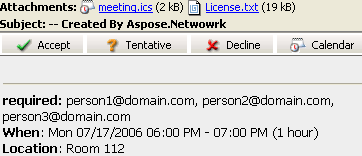 |
| The following code snippet shows you how to send requests via Email. |
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
// Create an instance of the MailMessage class
MailMessage msg = new MailMessage();
// Set the sender, recipient, who will receive the meeting request. Basically, the recipient is the same as the meeting attendees
msg.setFrom(MailAddress.to_MailAddress("newcustomeronnet@gmail.com"));
msg.setTo(MailAddressCollection.to_MailAddressCollection("person1@domain.com, person2@domain.com, person3@domain.com, asposetest123@gmail.com"));
// Create Appointment instance
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.set(2015, Calendar.JULY, 17, 13, 0, 0);
Date startDate = cal.getTime();
cal.set(2015, Calendar.JULY, 17, 14, 0, 0);
Date endDate = cal.getTime();
Appointment app = new Appointment("Room 112", startDate, endDate, msg.getFrom(), msg.getTo());
app.setSummary("Release Meetting");
app.setDescription("Discuss for the next release");
// Add appointment to the message and Create an instance of SmtpClient class
msg.addAlternateView(app.requestApointment());
SmtpClient client = getSmtpClient();
try {
// Client.Send will send this message
client.send(msg);
System.out.println("Message sent");
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
iCalendar supports for IBM Lotus Notes
Aspose.Email calendar feature is based on the iCalendar standard, a standard for calendar data exchange (RFC 2445 or RFC2445 Syntax Reference). Therefore, it supports not only Microsoft Outlook but also IBM Lotus Notes. To send a meeting request in Lotus Notes, follow the same steps as mentioned above.
Forward an Email using SMTP Client
Forwarding Email with SMTP client
Forwarding an email is a common practice in daily life digital communication. An email received can be forwarded to specific recipients without sharing with the original senders. Aspose.Email API SmtpClient provides the capability to forward an email to specific recipients. Its Forward method can be used to forward a received or saved email to desired recipients as shown in this article. The following code snippet shows you how to forward an email using SMTP Client.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
// Create an instance of SmtpClient class
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient();
// Specify your mailing host server, Username, Password, Port and SecurityOptions
client.setHost("mail.server.com");
client.setUsername("username");
client.setPassword("password");
client.setPort(587);
client.setSecurityOptions(SecurityOptions.SSLExplicit);
MailMessage message = MailMessage.load(dataDir + "Message.eml");
client.forward("Recipient1@domain.com", "Recipient2@domain.com", message);
Forwarding Email without using MailMessage
The API also supports forwarding EML messages without first loading into MailMessage. This is useful in cases where there are limited resources in terms of system memory.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
String host = "mail.server.com";
String username = "username";
String password = "password";
int smtpPort = 587;
String sender = "Sender@domain.com";
MailAddressCollection recipients = new MailAddressCollection();
recipients.add("recepient1@domain.com, recepient2@domain.com");
try (SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient(host, smtpPort, username, password, SecurityOptions.Auto)) {
String fileName = "test.eml";
try (FileInputStream fs = new FileInputStream(new File(dataDir + fileName))) {
client.forward(sender, recipients, fs);
}
}
Performing Mail Merge
Mail merges help you create and send a batch of similar email messages. The core of the emails are the same, but the content can be personalized. Typically, a recipient’s contact details (first name, second name, company and so on) are used to personalize the email.
| Illustration of how a mail merge works: |
|---|
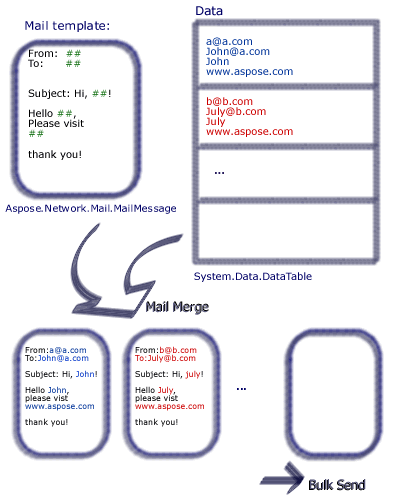 |
| Aspose.Email lets developers set up mail merges that include data from a variety of data sources. |
To perform a mail merge with Aspose.Email, take the following steps:
- Create a function with the name signature
- Create an instance of the MailMessage class.
- Specify the sender, receiver, subject, and body.
- Create a signature for the end of the email.
- Create an instance of the TemplateEngine class and pass it the MailMessage instance.
- Take signature in the TemplateEngine instance.
- Create an instance of the DataTable class.
- Add the columns Receipt, FirstName and LastName as data sources in the DataTable class.
- Create an instance of the DataRow class.
- Specify the receipt address, first and last names in the DataRow object.
- Create an instance of the MailMessageCollection class
- Specify the TemplateEngine and DataTable instances in the MailMessageCollection instance.
- Create an instance of the SmtpClient class and specify the server, port, username, and password.
- Send emails using the SmtpClient class send method.
In the sample below, #FirstName# indicates a DataTable column, whose value is set by the user. The following code snippet shows you how to perform Mail Merge.
// For complete examples and data files, please go to https://github.com/aspose-email/Aspose.Email-for-Java
public static void run() {
// The path to the File directory.
String dstEmail = dataDir + "EmbeddedImage.msg";
// Create a new MailMessage instance
MailMessage msg = new MailMessage();
// Add subject and from address
msg.setSubject("Hello, #FirstName#");
msg.setFrom(MailAddress.to_MailAddress("sender@sender.com"));
// Add email address to send email also Add mesage field to HTML body
msg.getTo().add("your.email@gmail.com");
String htmlBody = "Your message here/r/n" + "Thank you for your interest in <STRONG>Aspose.Email</STRONG>.";
// Use GetSignment as the template routine, which will provide the same signature
htmlBody += "<br><br>Have fun with it.<br><br>#GetSignature()#";
msg.setHtmlBody(htmlBody);
// Create a new TemplateEngine with the MSG message, Register GetSignature routine. It will be used in MSG.
TemplateEngine engine = new TemplateEngine(msg);
engine.registerRoutine("GetSignature", new TemplateRoutine() {
public Object invoke(Object[] args) {
return getSignature(args);
}
});
// Create an instance of DataTable and Fill a DataTable as data source
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
dt.getColumns().add("Receipt");
dt.getColumns().add("FirstName");
dt.getColumns().add("LastName");
DataRow dr;
dr = dt.newRow();
dr.set("Receipt", "Nancy<Nancy@somedomain.com>");
dr.set("FirstName", "Nancy");
dr.set("LastName", "Doe");
dt.getRows().add(dr);
dr = dt.newRow();
dr.set("Receipt", "Andrew<Andrew@somedomain.com>");
dr.set("FirstName", "Andrew");
dr.set("LastName", "Doe");
dt.getRows().add(dr);
dr = dt.newRow();
dr.set("Receipt", "Janet<Janet@somedomain.com>");
dr.set("FirstName", "Janet");
dr.set("LastName", "Doe");
dt.getRows().add(dr);
MailMessageCollection messages;
try {
// Create messages from the message and datasource.
messages = engine.instantiate(dt);
// Create an instance of SmtpClient and specify server, port, username and password
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient("smtp.gmail.com", 587, "your.email@gmail.com", "your.password");
client.setSecurityOptions(SecurityOptions.Auto);
// Send messages in bulk
client.send(messages);
} catch (MailException ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
catch (SmtpException ex) {
System.err.println(ex);
}
System.out.println("Message sent after performing mail merge.");
}
// Template routine to provide signature
static Object getSignature(Object[] args) {
return "Aspose.Email Team<br>Aspose Ltd.<br>" + new Date().toString();
}
Performing Row-Wise Mail Merge
User can merge individual data row as well to get a complete and prepared MailMessage object. The TemplateEngine.merge method can be used to perform a row-wise mail merge.
// Create message from the data in current row.
MailMessage message = engine.merge(currentRow);