Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
This article introduces you to the basics of vectorizing images using Aspose.SVG Python library. The article walks through several Python examples demonstrating the functionality of ImageVectorization and the impact of configuration properties on the result of vectorization.
There are two main types of images: vector and raster. The choice between them depends on the specific use case. A bitmap, also known as a raster image, is a two-dimensional array that maps colors to individual pixels. Raster images are typically much larger file sizes than vector images and work well for photographs or images with color gradients. However, a significant disadvantage of raster images is the loss of quality when scaled, leading to pixelation and blurriness.
Vector graphics, on the other hand, consist of geometric shapes such as Bezier curves, splines, and lines. These shapes are determined by mathematical equations, allowing vector images to be infinitely scaled without losing quality. This makes vector graphics ideal for logos, icons, page layouts, maps, graphs, line art, and illustrations. They often result in smaller file sizes than raster images, especially for simpler projects.
Image vectorization is the process of converting a raster image into vector graphics. This involves converting the pixel information of a raster image into a series of mathematical curves and shapes. The benefits of vector images include their scalability and typically smaller file sizes for certain types of images. However, vector images may be less effective for highly detailed images or photographs that require complex color variations and gradients.
Aspose.SVG for Python via .NET provides a robust solution for vectorizing images through the
ImageVectorization namespace. This allows users to convert various raster image formats such as JPG, PNG, BMP, TIFF, and GIF to the vector SVG file format. The vectorization process can be fine-tuned using configuration properties such as path_builder, colors_limit, error_threshold, trace_smoother, max_iterations, stencil, etc. which affect the quality and detail of the resulting vector graphics. This technology allows precise control of the vectorization process, ensuring high quality and scalability of vector images.
To vectorize an image with Aspose.SVG Python library, you should follow a few steps:
trace_smoother, error_threshold, and max_iterations.path_builder configuration (defined earlier) to the vectorizer object. This means the vectorizer will use the settings specified in the path_builder for path creation and optimization.colors_limit and line_width properties of the of the
ImageVectorizerConfiguration class.SVGDocument class. 1import os
2from aspose.svg.imagevectorization import ImageVectorizer, ImageTraceSmoother, BezierPathBuilder
3
4# Setup directories
5input_folder = "data/"
6output_folder = "output/"
7src_file = "fish.png"
8output_file = "fish-vectorized.svg"
9if not os.path.exists(output_folder):
10 os.makedirs(output_folder)
11
12# Configuration for vectorization
13path_builder = BezierPathBuilder()
14path_builder.trace_smoother = ImageTraceSmoother(3)
15path_builder.error_threshold = 10.0
16path_builder.max_iterations = 20
17
18vectorizer = ImageVectorizer()
19vectorizer.configuration.path_builder = path_builder
20vectorizer.configuration.colors_limit = 3
21vectorizer.configuration.line_width = 1.5
22
23# Vectorize an image
24with vectorizer.vectorize(os.path.join(input_folder, src_file)) as document:
25 output_file = os.path.join(output_folder, output_file)
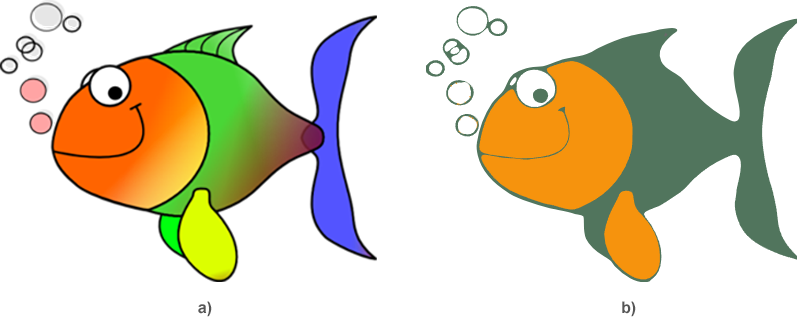
26 document.save(output_file)This code example allows you to vectorize a color raster image into a vector one. The vectorization options are selected in such a way as to achieve the desired result shown in figure (b). We wanted a simplified three-color image of the original. The following figure demonstrates the source image (a) and the vectorized image using the above Python code snippet (b).
You can apply custom settings to get the best result from the image vectorization. Below are some of the main settings you can control, along with their default values:
severity) that defines the degree of smoothing applied.Is it possible to convert a photo in vector format to look identical to the photo?
SVG is not well suited for drawing photorealistic images. Vector pictures do not allow for natural color transitions yet. Vector graphics are the best for creating logos, illustrations, technical drawings. It is not the most suitable format for continuous-tone images with blends of color or to edit photographs. However, vectorizing photos can result in impressive artistic effects that can be interesting and useful.
In this section, we convert a photo to vector format and try to choose vectorization options so that the result looks identical to the photo:
1import os
2from aspose.svg.imagevectorization import ImageVectorizer, ImageTraceSmoother, BezierPathBuilder
3
4# Setup directories
5input_folder = "data/"
6output_folder = "output/"
7src_file = "lioness.jpg"
8output_file = "lioness.svg"
9if not os.path.exists(output_folder):
10 os.makedirs(output_folder)
11
12# Configuration for vectorization
13path_builder = BezierPathBuilder()
14path_builder.trace_smoother = ImageTraceSmoother(1)
15path_builder.error_threshold = 30.0
16path_builder.max_iterations = 30
17
18vectorizer = ImageVectorizer()
19vectorizer.configuration.path_builder = path_builder
20vectorizer.configuration.colors_limit = 25
21vectorizer.configuration.line_width = 1.5
22
23# Vectorize a photo
24with vectorizer.vectorize(os.path.join(input_folder, src_file)) as document:
25 output_file = os.path.join(output_folder, output_file)
26 document.save(output_file)The figure demonstrates the source photo (a), the vectorized image using the Python code snippet (b).
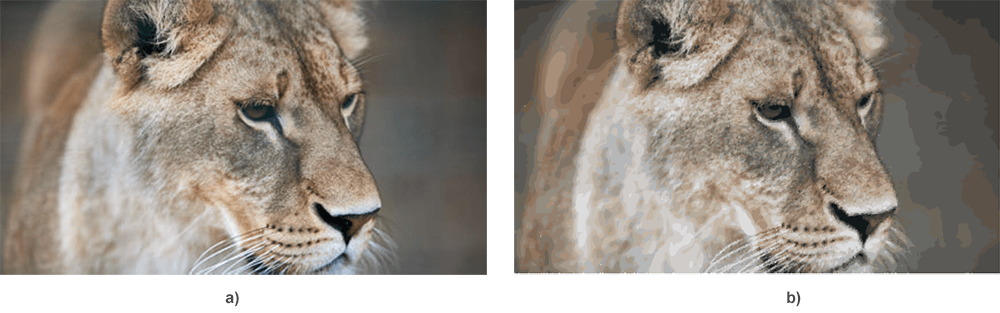
As mentioned above, SVG is not the most suitable format for continuous-tone images with blends of color, etc. The vectorization process uses color image quantization. All small same colored spots or pixels, we replace by geometric shapes or curves. The source photo (a) and resulting SVG file (b) you may find and view in details by following the links – lioness.jpg, lioness.svg.
A free evaluation version of Aspose.SVG for Python via .NET provides all the features for image vectorization except the following:
If you want to try Aspose.SVG for Python via .NET without evaluation limitations request a 30-day temporary license. For more information, please refer to How to get a Temporary License?
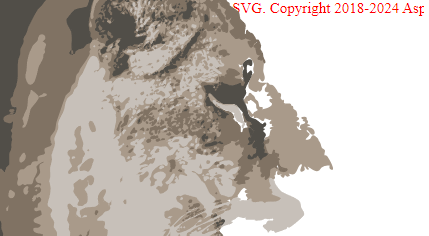
The figure shows the result of the photo to vector conversion without applying a license.
Aspose.SVG offers a Free Online Image Vectorizer that is designed to convert bitmap images such as JPG, PNG, BMP, TIFF, and GIF into vector graphics. After conversion, all vector graphic elements are saved as SVG files. Our free vectorizer works on any platform. With this app, you can apply various options to achieve the perfect result. Save time and experience the advantages of vector graphics with our free Image Vectorizer!
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.