Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
Untuk kontrol lebih besar atas cara kerja tabel, pelajari cara memanipulasi kolom dan baris.
Kolom, baris, dan sel dikelola dengan mengakses simpul dokumen yang dipilih berdasarkan indeksnya. Menemukan indeks dari setiap node melibatkan pengumpulan semua node turunan dari tipe elemen dari node induk, dan kemudian menggunakan metode IndexOf untuk menemukan indeks dari node yang diinginkan dalam koleksi.
Terkadang Anda mungkin perlu membuat perubahan pada tabel tertentu dalam dokumen. Untuk melakukan ini, Anda dapat merujuk ke tabel berdasarkan indeksnya.
Contoh kode berikut menunjukkan cara mengambil indeks tabel dalam dokumen:
Demikian pula, Anda mungkin perlu membuat perubahan pada baris tertentu dalam tabel yang dipilih. Untuk melakukan ini, Anda juga dapat merujuk ke baris berdasarkan indeksnya.
Contoh kode berikut menunjukkan cara mengambil indeks baris dalam tabel:
Terakhir, Anda mungkin perlu membuat perubahan pada sel tertentu, dan Anda juga dapat melakukannya dengan indeks sel.
Contoh kode berikut menunjukkan cara mengambil indeks sel dalam satu baris:
Dalam Model Objek Dokumen Aspose.Words (DOM), simpul Table terdiri dari Row simpul dan kemudian Cell simpul. Jadi, dalam Model Objek Document dari Aspose.Words, seperti pada dokumen Word, tidak ada konsep kolom.
Secara desain, baris tabel di Microsoft Word dan Aspose.Words sepenuhnya independen, dan properti serta operasi dasar hanya terdapat di baris dan sel tabel. Ini memberi tabel kemampuan untuk memiliki beberapa atribut yang menarik:
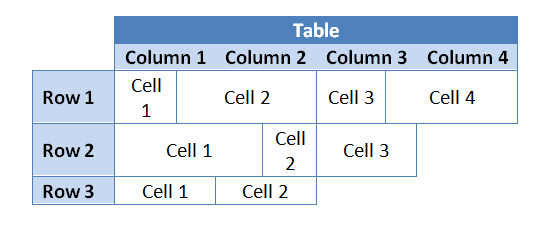
Setiap operasi yang dilakukan pada kolom sebenarnya adalah “pintasan” yang melakukan operasi dengan mengubah sel baris secara kolektif sedemikian rupa sehingga terlihat seperti diterapkan ke kolom. Artinya, Anda dapat melakukan operasi pada kolom hanya dengan mengulangi indeks sel baris tabel yang sama.
Contoh kode berikut menyederhanakan operasi tersebut dengan membuktikan kelas facade yang mengumpulkan sel-sel yang membentuk “kolom” dari sebuah tabel:
Contoh kode berikut menunjukkan cara menyisipkan kolom kosong ke dalam tabel:
Contoh kode berikut menunjukkan cara menghapus kolom dari tabel dalam dokumen:
Anda dapat memilih untuk mengulang baris pertama dalam tabel sebagai Baris Header hanya di halaman pertama atau di setiap halaman jika tabel dibagi menjadi beberapa. Di Aspose.Words, Anda dapat mengulang Baris Header di setiap halaman menggunakan properti HeadingFormat.
Anda juga dapat menandai beberapa baris header jika baris tersebut ditempatkan satu demi satu di awal tabel. Untuk melakukan ini, Anda perlu menerapkan properti HeadingFormat ke baris ini.
Contoh kode berikut menunjukkan cara membuat tabel yang menyertakan Baris Header yang berulang di halaman berikutnya:
Ada kalanya konten tabel tidak boleh dibagi menjadi beberapa halaman. Misalnya, jika judul berada di atas tabel, judul dan tabel harus selalu disatukan pada halaman yang sama untuk mempertahankan tampilan yang tepat.
Ada dua teknik terpisah yang berguna untuk mencapai fungsionalitas ini:
Allow row break across pages, yang diterapkan ke baris tabelKeep with next, yang diterapkan pada paragraf dalam sel tabelSecara default, properti di atas dinonaktifkan.
Ini melibatkan pembatasan konten di dalam sel baris agar tidak dipisah di seluruh halaman. Di Microsoft Word, ini dapat ditemukan di bawah Properti Tabel sebagai opsi “Izinkan baris untuk melintasi halaman”. Dalam Aspose.Words ini ditemukan di bawah objek RowFormat dari Row sebagai properti RowFormat.AllowBreakAcrossPages.
Contoh kode berikut menunjukkan cara menonaktifkan pemutusan baris di seluruh halaman untuk setiap baris dalam tabel:
Untuk menghentikan tabel agar tidak terbelah di seluruh halaman, kita perlu menentukan bahwa kita ingin konten yang terkandung di dalam tabel tetap bersama.
Untuk melakukannya, Aspose.Words menggunakan metode, yang memungkinkan pengguna memilih tabel dan mengaktifkan parameter KeepWithNext menjadi true untuk setiap paragraf di dalam sel tabel. Pengecualian adalah paragraf terakhir dalam tabel, yang harus disetel ke false.
Contoh kode berikut menunjukkan cara mengatur tabel agar tetap bersama di halaman yang sama:
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.