Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
テーブルの動作をより詳細に制御するには、列と行を操作する方法を学習します。
列、行、およびセルは、選択したドキュメントノードにインデックスでアクセスすることによって管理されます。 ノードのインデックスを見つけるには、親ノードから要素タイプのすべての子ノードを収集し、IndexOfメソッドを使用してコレクション内の目的のノードのイン
場合によっては、ドキュメント内の特定のテーブルに変更を加える必要があることがあります。 これを行うには、そのインデックスでテーブルを参照できます。
次のコード例は、ドキュメント内のテーブルのインデックスを取得する方法を示しています:
同様に、選択したテーブルの特定の行に変更を加える必要がある場合があります。 これを行うには、そのインデックスで行を参照することもできます。
次のコード例は、テーブル内の行のインデックスを取得する方法を示しています:
最後に、特定のセルに変更を加える必要がある場合があり、セルインデックスでもこれを行うことができます。
次のコード例は、行のセルのインデックスを取得する方法を示しています:
Aspose.Wordsドキュメントオブジェクトモデル(DOM)では、TableノードはRowノードとCellノードで構成されます。 したがって、Aspose.WordsのDocumentオブジェクトモデルでは、Word文書のように、列の概念はありません。
設計上、Microsoft WordとAspose.Wordsのテーブル行は完全に独立しており、基本的なプロパティと操作はテーブルの行とセルにのみ含まれています。 これにより、テーブルにいくつかの興味深い属性を持たせることができます:
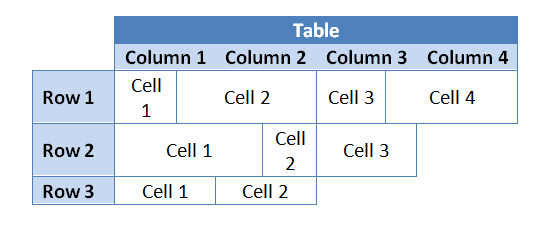
列に対して実行される操作は、実際には、列に適用されているように見えるように行セルをまとめて変更することによって操作を実行する「ショートカット」です。 つまり、同じテーブル行のセルインデックスを反復処理するだけで、列に対して操作を実行できます。
次のコード例では、テーブルの"列"を構成するセルを収集するファサードクラスを証明することにより、このような操作を簡素化します:
次のコード例は、テーブルに空白の列を挿入する方法を示しています:
次のコード例は、ドキュメント内のテーブルから列を削除する方法を示しています:
テーブルの最初の行をヘッダー行として最初のページでのみ繰り返すか、テーブルが複数に分割されている場合は各ページで繰り返すかを選択できます。 Aspose.Wordsでは、HeadingFormatプロパティを使用してすべてのページでヘッダー行を繰り返すことができます。
そのような行がテーブルの先頭に次々に配置されている場合は、複数のヘッダー行にマークを付けることもできます。 これを行うには、これらの行にHeadingFormatプロパティを適用する必要があります。
次のコード例は、後続のページで繰り返されるヘッダー行を含むテーブルを作成する方法を示しています:
テーブルの内容をページ間で分割してはならない場合があります。 たとえば、タイトルがテーブルの上にある場合、適切な外観を維持するために、タイトルとテーブルは常に同じページにまとめておく必要があります。
この機能を実現するのに便利な2つの別々の手法があります:
Allow row break across pagesは、テーブル行に適用されますKeep with nextは、表のセルの段落に適用されますデフォルトでは、上記のプロパティは無効になっています。
これには、行のセル内のコンテンツがページ間で分割されないように制限することが含まれます。 Microsoft Wordでは、これはテーブルのプロパティの下に"行をページ間で分割することを許可する"オプションとしてあります。 Aspose.Wordsでは、これはRowのRowFormatオブジェクトの下にプロパティRowFormat.AllowBreakAcrossPagesとしてあります。
次のコード例は、テーブル内の各行のページ間で行を分割することを無効にする方法を示しています:
テーブルがページ間で分割されないようにするには、テーブル内に含まれるコンテンツを一緒に保つように指定する必要があります。
これを行うために、Aspose.Wordsは、ユーザーがテーブルを選択し、テーブルセル内の各段落に対してKeepWithNextパラメータをtrueに有効にするメソッドを使用します。 例外は、テーブルの最後の段落であり、falseに設定する必要があります。
次のコード例は、同じページに一緒に滞在するようにテーブルを設定する方法を示しています:
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.