Zbuduj stół z DataTable
Często Twoja aplikacja będzie pobierać dane z bazy danych i przechowywać je w formie DataTable. Można łatwo umieścić te dane w dokumencie jako nową tabelę i szybko zastosować formatowanie do całej tabeli.
Należy zauważyć, że preferowany sposób wprowadzania danych z
DataTable do tabeli dokumentu jest za pomocą
Mail Merge z regionami. Technika przedstawiona w tym artykule jest sugerowana tylko wtedy, gdy nie jesteś w stanie utworzyć odpowiedniego szablonu wcześniej, aby połączyć dane z innymi słowy, jeśli wymagasz, aby wszystko działo się programowo.
Stosowanie Aspose.Words, można łatwo pobrać dane z bazy danych i przechowywać je jako tabelę:
- Utwórz nowy DocumentBuilder obiekt na Twoim Document.
- Uruchom nową tabelę używając DocumentBuilder.
- Jeśli chcemy dodać nazwy każdej kolumny z naszej DataTable jako wiersz nagłówka następnie iterate przez każdą kolumnę danych i zapisać nazwy kolumn do wiersza w tabeli.
- Iterate przez każdy DataRow w DataTable:
- Iterate przez każdy obiekt w DataRow.
- Wstaw obiekt do dokumentu używając DocumentBuilder. Zastosowana metoda zależy od typu wstawianego obiektu np. DocumentBuilder.writeln() dla tekstu oraz DocumentBuilder.insertImage() dla tablicy bajtów, która reprezentuje obraz.
- Na koniec przetwarzania wiersza danych kończy się również wiersz tworzony przez DocumentBuilder za pomocą DocumentBuilder.endRow().
- Raz wszystkie rzędy z DataTable zostały przetworzone zakończyć stół przez wywołanie DocumentBuilder.endTable().
- Wreszcie, możemy ustawić pożądany styl tabeli przy użyciu jednej z odpowiednich właściwości tabeli, takich jak Table.getStyleIdentifier() automatycznie stosować formatowanie do całej tabeli.
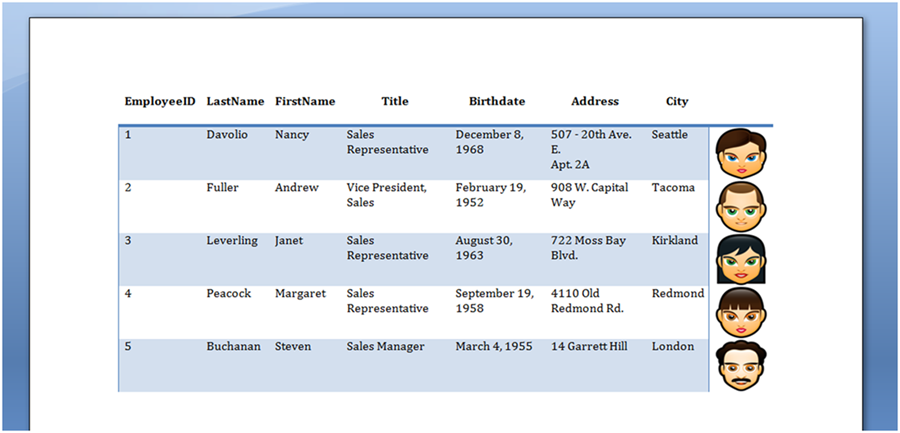
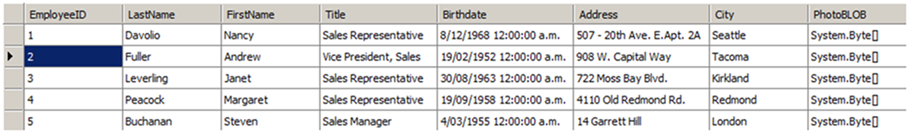
Poniższe dane w naszym DataTable jest stosowany w tym przykładzie:
Poniższy przykład kodu pokazuje jak wykonać powyższy algorytm w Aspose.Words:
Metoda ta może być łatwo wywołana za pomocą DocumentBuilder i dane.
Poniższy przykład kodu pokazuje, jak importować dane z DataTable i umieścić go w nowej tabeli w dokumencie:
Tabela pokazana na poniższym obrazku jest wytwarzana przez uruchomienie powyższego kodu.