Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
Styl tabeli definiuje zestaw formatowania, który można łatwo zastosować do tabeli. Formatowanie takie jak granice, cieniowanie, wyrównanie i czcionka mogą być ustawione w stylu tabeli i stosowane do wielu tabel dla spójnego wyglądu.
Aspose.Words obsługuje stosowanie stylu tabeli do tabeli, a także właściwości czytania każdego stylu tabeli. Style tabeli są zachowywane podczas załadunku i oszczędzania w następujący sposób:
Użytkownik może stworzyć nowy styl i dodać go do kolekcji stylu. W Add metoda jest używana do tworzenia nowego stylu tabeli.
Poniższy przykład kodu pokazuje jak stworzyć nowy styl tabeli zdefiniowany przez użytkownika:
W razie potrzeby można skopiować styl tabeli, który już istnieje w określonym dokumencie do kolekcji stylu za pomocą AddCopy Metoda.
Ważne jest, aby wiedzieć, że z tego kopiowania, powiązane style są również kopiowane.
Poniższy przykład kodu pokazuje jak zaimportować styl z jednego dokumentu do innego dokumentu:
Aspose.Words zapewnia TableStyle po Style Klasa. TableStyle ułatwia użytkownikowi stosowanie różnych opcji stylu, takich jak cieniowanie, ścieranie, wgłębienie, CellSpacing oraz Font, itd.
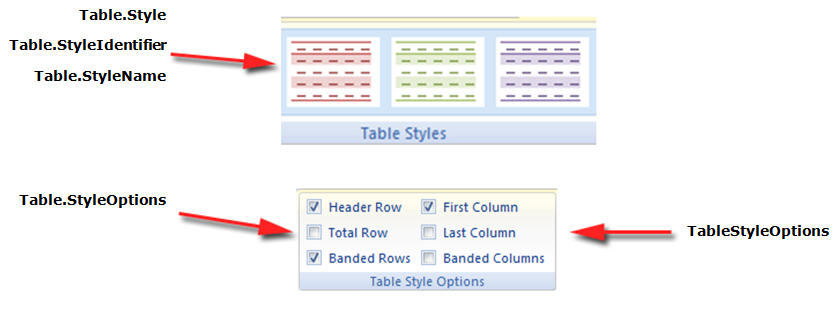
Ponadto, Aspose.Words zapewnia StyleCollection klasy i kilka właściwości Table klasa w celu określenia stylu tabeli będziemy pracować z: Style, StyleIdentifier, StyleName, oraz StyleOptions.
Aspose.Words również zapewnia ConditionalStyle klasy, która reprezentuje specjalne formatowanie stosowane na niektórych obszarach tabeli z przypisanym stylu tabeli, i ConditionalStyleCollection który reprezentuje kolekcję ConditionalStyle obiektów. Ta kolekcja zawiera stały zestaw elementów reprezentujących jedną pozycję dla każdej wartości ConditionalStyleType rodzaj wyliczenia. W ConditionalStyleType wyliczenie określa wszystkie możliwe obszary tabeli, do których można zdefiniować formatowanie warunkowe w stylu tabeli.
W takim przypadku można określić formatowanie warunkowe dla wszystkich możliwych powierzchni tabeli zdefiniowanych w ramach rodzaju wyliczenia ConditionalStyleType.
Poniższy przykład kodu pokazuje jak zdefiniować warunkowe formatowanie dla nagłówka tabeli:
Można również wybrać, które części tabeli do zastosowania stylów, takich jak pierwsza kolumna, ostatnia kolumna, rząd banded. Są one wymienione w TableStyleOptions wyliczenie i są stosowane przez StyleOptions nieruchomości. W TableStyleOptions wyliczenie pozwala na kombinację tych funkcji.
Poniższy przykład kodu pokazuje, jak stworzyć nową tabelę z zastosowaniem stylu tabeli:
Poniższe zdjęcia przedstawiają reprezentację Table Styles w Microsoft Word i ich właściwości w Aspose.Words.
Aspose.Words zapewnia również ExpandTableStylesToDirectFormatting metoda podejmowania formatowania znalezionego na stole stylu i rozszerza go na wiersze i komórki tabeli jako bezpośrednie formatowanie. Spróbuj połączyć formatowanie z stylu tabeli i stylu komórki.
Poniższy przykład kodu pokazuje jak rozszerzyć formatowanie ze stylów na wiersze i komórki tabeli jako bezpośrednie formatowanie:
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.