Create or Add Table In PDF using Python
Creating Table using Python
Tables are important when working with PDF documents. They provide great features for displaying information in a systematic manner. The Aspose.PDF namespace contains classes named Table, Cell, and Row which provides functionality for creating tables when generating PDF documents from scratch.
Table can be created by creating object of Table Class.
table = ap.Table()
Adding Table in Existing PDF Document
To add a table to an existing PDF file with Aspose.PDF for Python via .NET, take the following steps:
- Load the source file.
- Initialize a table and set its columns and rows.
- Set table setting (we’ve set the borders).
- Populate table.
- Add the table to a page.
- Save the file.
The following code snippets show how to add text in an existing PDF file.
import aspose.pdf as ap
# Load source PDF document
doc = ap.Document(input_file)
# Initializes a new instance of the Table
table = ap.Table()
# Set the table border color as LightGray
table.border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, 5, ap.Color.from_rgb(apd.Color.light_gray))
# Set the border for table cells
table.default_cell_border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, 5, ap.Color.from_rgb(apd.Color.light_gray))
# Create a loop to add 10 rows
for row_count in range(0, 10):
# Add row to table
row = table.rows.add()
# Add table cells
row.cells.add("Column (" + str(row_count) + ", 1)")
row.cells.add("Column (" + str(row_count) + ", 2)")
row.cells.add("Column (" + str(row_count) + ", 3)")
# Add table object to first page of input document
doc.pages[1].paragraphs.add(table)
# Save updated document containing table object
doc.save(output_file)
ColSpan and RowSpan in Tables
Aspose.PDF for Python via .NET provides col_span property to merge the columns in a table and row_span property to merge the rows.
We use col_span or row_span property on the Cell object which creates the table cell. After applying the required properties the created cell can be added to the table.
import aspose.pdf as ap
# Initialize the Document object by calling its empty constructor
pdf_document = ap.Document()
pdf_document.pages.add()
# Initializes a new instance of the Table
table = ap.Table()
# Set the table border color as LightGray
table.border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, 0.5, ap.Color.black)
# Set the border for table cells
table.default_cell_border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, 0.5, ap.Color.black)
# Add 1st row to table
row1 = table.rows.add()
for cellCount in range(1, 5):
# Add table cells
row1.cells.add("Test 1" + str(cellCount))
# Add 2nd row to table
row2 = table.rows.add()
row2.cells.add("Test 2 1")
cell = row2.cells.add("Test 2 2")
cell.col_span = 2
row2.cells.add("Test 2 4")
# Add 3rd row to table
row3 = table.rows.add()
row3.cells.add("Test 3 1")
row3.cells.add("Test 3 2")
row3.cells.add("Test 3 3")
row3.cells.add("Test 3 4")
# Add 4th row to table
row4 = table.rows.add()
row4.cells.add("Test 4 1")
cell = row4.cells.add("Test 4 2")
cell.row_span = 2
row4.cells.add("Test 4 3")
row4.cells.add("Test 4 4")
# Add 5th row to table
row5 = table.rows.add()
row5.cells.add("Test 5 1")
row5.cells.add("Test 5 3")
row5.cells.add("Test 5 4")
# Add table object to first page of input document
pdf_document.pages[1].paragraphs.add(table)
# Save updated document containing table object
pdf_document.save(output_file)
The result of the execution code below is the table depicted on the following image:
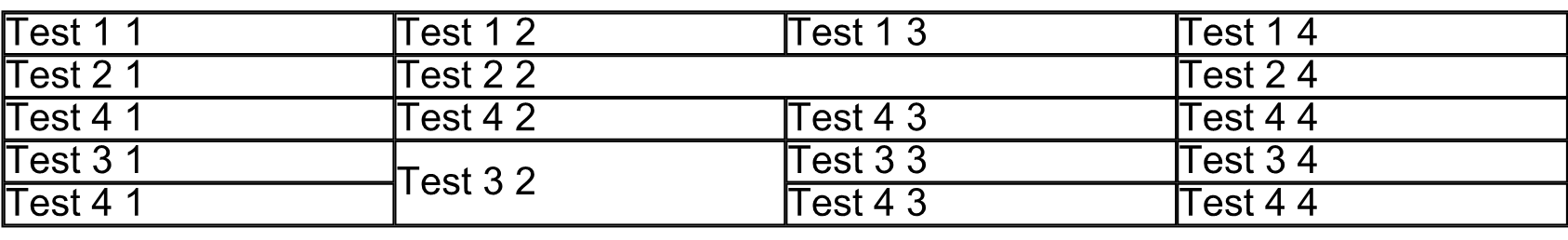
Working with Borders, Margins and Padding
Please note that it also supports the feature to set border style, margins and cell padding for tables. Before going into more technical details, it’s important to understand the concepts of border, margins and padding which are presented below in a diagram:
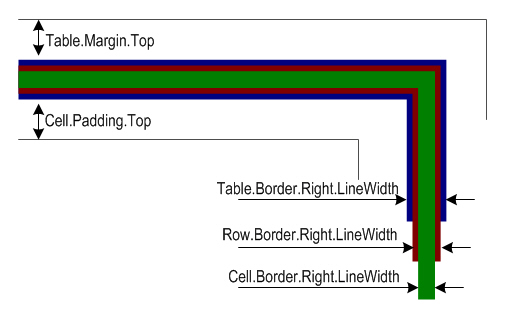
In the above figure, you can see that the borders of table, row and cell overlap. Using Aspose.PDF, a table can have margins and cells can have paddings. To set cell margins, we have to set cell padding.
Borders
To set the borders of Table, Row and Cell objects, use the Table.border, Row.border and Cell.border properties. Cell borders can also be set using the Table or Row class default_cell_border property. All border related properties discussed above are assigned an instance of the Row class, which is created by calling its constructor. The Row class has many overloads that take almost all the parameters required to customize the border.
Margins or Padding
Cell padding can be managed using the Table class’ default_cell_padding property. All padding related properties are assigned an instance of the MarginInfo class that takes information about the left, right, top and bottom parameters to create custom margins.
In the following example, the width of the cell border is set to 0.1 point, the width of the table border is set to 1 point and cell padding is set to 5 points.
import aspose.pdf as ap
# Instantiate the Document object by calling its empty constructor
doc = ap.Document()
page = doc.pages.add()
# Instantiate a table object
tab1 = ap.Table()
# Add the table in paragraphs collection of the desired section
page.paragraphs.add(tab1)
# Set with column widths of the table
tab1.column_widths = "50 50 50"
# Set default cell border using BorderInfo object
tab1.default_cell_border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, 0.1)
# Set table border using another customized BorderInfo object
tab1.border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, 1)
# Create MarginInfo object and set its left, bottom, right and top margins
margin = ap.MarginInfo()
margin.top = 5
margin.left = 5
margin.right = 5
margin.bottom = 5
# Set the default cell padding to the MarginInfo object
tab1.default_cell_padding = margin
# Create rows in the table and then cells in the rows
row1 = tab1.rows.add()
row1.cells.add("col1")
row1.cells.add("col2")
row1.cells.add()
my_text = ap.text.TextFragment("col3 with large text string")
# Row1.Cells.Add("col3 with large text string to be placed inside cell")
row1.cells[2].paragraphs.add(my_text)
row1.cells[2].is_word_wrapped = False
row2 = tab1.rows.add()
row2.cells.add("item1")
row2.cells.add("item2")
row2.cells.add("item3")
# Save the Pdf
doc.save(output_file)
To create table with rounded corner, use the BorderInfo class rounded_border_radius value and set the table corner style to round.
import aspose.pdf as ap
tab1 = ap.Table()
graph = ap.GraphInfo()
graph.color = ap.Color.red
# Create a blank BorderInfo object
b_info = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, graph)
# Set the border a rounder border where radius of round is 15
b_info.rounded_border_radius = 15
# Set the table Corner style as Round
tab1.corner_style = ap.BorderCornerStyle.ROUND
# Set the table border information
tab1.border = b_info
Appling Different AutoFit Settings to a Table
When designing a table using a visual tool like Microsoft Word, you’ll frequently utilize one of the AutoFit features to conveniently adjust the table’s size to the desired width. For example, you can employ the “AUTO_FIT_TO_WINDOW” option to match the table’s width to the page or AUTO_FIT_TO_CONTENT. By default, when using Aspose.Pdf to create a new table, it employs the column_adjustment with a “Customized” value. In the following code snippet, we set the object parameters MarginInfo and BorderInfo objects in the table. Test the example and evaluate the result.
import aspose.pdf as ap
# Instantiate the Pdf object by calling its empty constructor
doc = ap.Document()
# Create the section in the Pdf object
sec1 = doc.pages.add()
# Instantiate a table object
tab1 = ap.Table()
# Add the table in paragraphs collection of the desired section
sec1.paragraphs.add(tab1)
# Set with column widths of the table
tab1.column_widths = "50 50 50"
tab1.column_adjustment = ap.ColumnAdjustment.AUTO_FIT_TO_WINDOW
# Set default cell border using BorderInfo object
tab1.default_cell_border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, 0.1)
# Set table border using another customized BorderInfo object
tab1.border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, 1)
# Create MarginInfo object and set its left, bottom, right and top margins
margin = ap.MarginInfo()
margin.top = 5
margin.left = 5
margin.right = 5
margin.bottom = 5
# Set the default cell padding to the MarginInfo object
tab1.default_cell_padding = margin
# Create rows in the table and then cells in the rows
row1 = tab1.rows.add()
row1.cells.add("col1")
row1.cells.add("col2")
row1.cells.add("col3")
row2 = tab1.rows.add()
row2.cells.add("item1")
row2.cells.add("item2")
row2.cells.add("item3")
# Save updated document containing table object
doc.save(output_file)
Get Table Width
Sometimes, it is required to get table width dynamically. Aspose.PDF.Table class has a method get_width() for the purpose. For example, you have not set table columns width explicitly and set column_adjustment to ‘AUTO_FIT_TO_CONTENT’. In this case you can get table width as following.
import aspose.pdf as ap
# Create a new document
doc = ap.Document()
# Add page in document
page = doc.pages.add()
# Initialize new table
table = ap.Table()
table.column_adjustment = ap.ColumnAdjustment.AUTO_FIT_TO_CONTENT
# Add row in table
row = table.rows.add()
# Add cell in table
cell = row.cells.add("Cell 1 text")
cell = row.cells.add("Cell 2 text")
# Get table width
print(table.get_width())
Add SVG Image to Table Cell
Aspose.PDF for Python via .NET provides the capability to insert table cells into a PDF file. When constructing a table, you can include both text and images within these cells. Additionally, the API offers the functionality to transform SVG files into PDF format. By leveraging these functionalities together, you can load an SVG image and place it within a table cell.
The following code excerpt demonstrates the process of creating a table object and embedding an SVG image inside one of its cells.
import aspose.pdf as ap
# Instantiate Document object
doc = ap.Document()
# Create an image instance
img = ap.Image()
# Set image type as SVG
img.file_type = ap.ImageFileType.SVG
# Path for source file
img.file = DIR_INPUT_TABLE + "SVGToPDF.svg"
# Set width for image instance
img.fix_width = 50
# Set height for image instance
img.fix_height = 50
# Create table instance
table = ap.Table()
# Set width for table cells
table.column_widths = "100 100"
# Create row object and add it to table instance
row = table.rows.add()
# Create cell object and add it to row instance
cell = row.cells.add()
# Add textfragment to paragraphs collection of cell object
cell.paragraphs.add(ap.text.TextFragment("First cell"))
# Add another cell to row object
cell = row.cells.add()
# Add SVG image to paragraphs collection of recently added cell instance
cell.paragraphs.add(img)
# Create page object and add it to pages collection of document instance
page = doc.pages.add()
# Add table to paragraphs collection of page object
page.paragraphs.add(table)
# Save PDF file
doc.save(output_file)
Insert a Page Break between rows of table
By default, when you create a table within a PDF file, the table will span across multiple pages if it extends beyond the table’s bottom margin. However, there are situations where we need to enforce page breaks after a specific number of rows have been added to the table. The following code excerpt outlines the process of inserting a page break when 10 rows have been included in the table.
import aspose.pdf as ap
# Instantiate Document instance
doc = ap.Document()
# Add page to pages collection of PDF file
doc.pages.add()
# Create table instance
tab = ap.Table()
# Set border style for table
tab.border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, ap.Color.red)
# Set default border style for table with border color as Red
tab.default_cell_border = ap.BorderInfo(ap.BorderSide.ALL, ap.Color.red)
# Specify table columns width
tab.column_widths = "100 100"
# Create a loop to add 200 rows for table
for counter in range(0, 201):
row = ap.Row()
tab.rows.add(row)
cell1 = ap.Cell()
cell1.paragraphs.add(ap.text.TextFragment("Cell " + str(counter) + ", 0"))
row.cells.add(cell1)
cell2 = ap.Cell()
cell2.paragraphs.add(ap.text.TextFragment("Cell " + str(counter) + ", 1"))
row.cells.add(cell2)
# When 10 rows are added, render new row in new page
if counter % 10 == 0 and counter != 0:
row.is_in_new_page = True
# Add table to paragraphs collection of PDF file
doc.pages[1].paragraphs.add(tab)
# Save the PDF document
doc.save(output_file)
Render a Table on a New Page
By default, paragraphs are added to a Page object’s Paragraphs collection. However, it is possible to render a table on a new page instead of directly after the previously added paragraph-level object on the page.
Sample: How to Render a Table on a New Page using Python
To render a table on a new page, use the is_in_new_page property in the BaseParagraph class. The following code snippet shows how.
import aspose.pdf as ap
doc = ap.Document()
page_info = doc.page_info
margin_info = page_info.margin
margin_info.left = 37
margin_info.right = 37
margin_info.top = 37
margin_info.bottom = 37
page_info.is_landscape = True
table = ap.Table()
table.column_widths = "50 100"
# Added page.
cur_page = doc.pages.add()
for i in range(1, 121):
row = table.rows.add()
row.fixed_row_height = 15
cell1 = row.cells.add()
cell1.paragraphs.add(ap.text.TextFragment("Content 1"))
cell2 = row.cells.add()
cell2.paragraphs.add(ap.text.TextFragment("HHHHH"))
paragraphs = cur_page.paragraphs
paragraphs.add(table)
table1 = ap.Table()
table1.column_widths = "100 100"
for i in range(1, 11):
row = table1.rows.add()
cell1 = row.cells.add()
cell1.paragraphs.add(ap.text.TextFragment("LAAAAAAA"))
cell2 = row.cells.add()
cell2.paragraphs.add(ap.text.TextFragment("LAAGGGGGG"))
table1.is_in_new_page = True
# I want to keep table 1 to next page please...
paragraphs.add(table1)
doc.save(output_file)