Create PowerPoint Presentation Charts in Python
Create Chart
Charts help people to quickly visualize data and gain insights, which may not be immediately obvious from a table or spreadsheet.
Why Create Charts?
Using charts, you get to
- aggregate, condense, or summarize large amounts of data on a single slide in a presentation
- expose patterns and trends in data
- deduce the direction and momentum of data over time or with respect to a specific unit of measurement
- spots outliers, aberrations, deviations, errors, nonsensical data, etc.
- communicate or present complex data
In PowerPoint, you can create charts through the insert function, which provides templates used to design many types of charts. Using Aspose.Slides, you can create regular charts (based on popular chart types) and custom charts.
Creating Normal Charts
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add a chart with some data and specify your preferred chart type.
- Add a title for the chart.
- Access the chart data worksheet.
- Clear all the default series and categories.
- Add new series and categories.
- Add some new chart data for the chart series.
- Add a fill color for chart series.
- Add labels for the chart series.
- Write the modified presentation as a PPTX file.
This Python code shows you how to create a normal chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
# Instantiate Presentation class that represents PPTX file
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
# Access first slide
sld = pres.slides[0]
# Add chart with default data
chart = sld.shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.CLUSTERED_COLUMN, 0, 0, 500, 500)
# Setting chart Title
chart.chart_title.add_text_frame_for_overriding("Sample Title")
chart.chart_title.text_frame_for_overriding.text_frame_format.center_text = 1
chart.chart_title.height = 20
chart.has_title = True
# Set first series to Show Values
chart.chart_data.series[0].labels.default_data_label_format.show_value = True
# Setting the index of chart data sheet
defaultWorksheetIndex = 0
# Getting the chart data worksheet
fact = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
# Delete default generated series and categories
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
s = len(chart.chart_data.series)
s = len(chart.chart_data.categories)
# Adding new series
chart.chart_data.series.add(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 0, 1, "Series 1"), chart.type)
chart.chart_data.series.add(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 0, 2, "Series 2"), chart.type)
# Adding new categories
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 1, 0, "Caetegoty 1"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 0, "Caetegoty 2"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 3, 0, "Caetegoty 3"))
# Take first chart series
series = chart.chart_data.series[0]
# Now populating series data
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 1, 1, 20))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 1, 50))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 3, 1, 30))
# Setting fill color for series
series.format.fill.fill_type = slides.FillType.SOLID
series.format.fill.solid_fill_color.color = draw.Color.red
# Take second chart series
series = chart.chart_data.series[1]
# Now populating series data
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 1, 2, 30))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 2, 10))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 3, 2, 60))
# Setting fill color for series
series.format.fill.fill_type = slides.FillType.SOLID
series.format.fill.solid_fill_color.color = draw.Color.green
# First label will be show Category name
lbl = series.data_points[0].label
lbl.data_label_format.show_category_name = True
lbl = series.data_points[1].label
lbl.data_label_format.show_series_name = True
# Show value for third label
lbl = series.data_points[2].label
lbl.data_label_format.show_value = True
lbl.data_label_format.show_series_name = True
lbl.data_label_format.separator = "/"
# Save presentation with chart
pres.save("AsposeChart_out-1.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Scattered Charts
Scattered charts (also known as scattered plots or x-y graphs) are often used to check for patterns or demonstrate correlations between two variables.
You may want to use a scattered chart when
- you have paired numerical data
- you have 2 variables that pair well together
- you want to determine whether 2 variables are related
- you have an independent variable that has multiple values for a dependent variable
This Python code shows you how to create a scattered charts with a different series of markers:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
slide = pres.slides[0]
# Creating the default chart
chart = slide.shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.SCATTER_WITH_SMOOTH_LINES, 0, 0, 400, 400)
# Getting the default chart data worksheet index
defaultWorksheetIndex = 0
# Getting the chart data worksheet
fact = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
# Delete demo series
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
# Add new series
chart.chart_data.series.add(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 1, 1, "Series 1"), chart.type)
chart.chart_data.series.add(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 1, 3, "Series 2"), chart.type)
# Take first chart series
series = chart.chart_data.series[0]
# Add new point (1:3) there.
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 1, 1), fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 2, 3))
# Add new point (2:10)
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 3, 1, 2), fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 3, 2, 10))
# Edit the type of series
series.type = charts.ChartType.SCATTER_WITH_STRAIGHT_LINES_AND_MARKERS
# Changing the chart series marker
series.marker.size = 10
series.marker.symbol = charts.MarkerStyleType.STAR
# Take second chart series
series = chart.chart_data.series[1]
# Add new point (5:2) there.
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 3, 5), fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 4, 2))
# Add new point (3:1)
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 3, 3, 3), fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 3, 4, 1))
# Add new point (2:2)
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 4, 3, 2), fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 4, 4, 2))
# Add new point (5:1)
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 5, 3, 5), fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 5, 4, 1))
# Changing the chart series marker
series.marker.size = 10
series.marker.symbol = charts.MarkerStyleType.CIRCLE
pres.save("AsposeChart_out-2.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Pie Charts
Pie charts are best used to show the part-to-whole relationship in data, especially when the data contains categorical labels with numeric values. However, if your data contains many parts or labels, you may want to consider using a bar chart instead.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add a chart with default data along with the desired type (in this case,
ChartType.PIE). - Access the chart data IChartDataWorkbook.
- Clear the default series and categories.
- Add new series and categories.
- Add new chart data for the chart series.
- Add new points for charts and add custom colors for the pie chart’s sectors.
- Set labels for series.
- Set leader lines for series labels.
- Set the rotation angle for pie chart slides.
- Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file
This Python code shows you how to create a pie chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
# Instantiate Presentation class that represents PPTX file
with slides.Presentation() as presentation:
# Access first slide
slide = presentation.slides[0]
# Add chart with default data
chart = slide.shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.PIE, 100, 100, 400, 400)
# Setting chart Title
chart.chart_title.add_text_frame_for_overriding("Sample Title")
chart.chart_title.text_frame_for_overriding.text_frame_format.center_text = 1
chart.chart_title.height = 20
chart.has_title = True
# Set first series to Show Values
chart.chart_data.series[0].labels.default_data_label_format.show_value = True
# Setting the index of chart data sheet
defaultWorksheetIndex = 0
# Getting the chart data worksheet
fact = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
# Delete default generated series and categories
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
# Adding new categories
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, 1, 0, "First Qtr"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, 2, 0, "2nd Qtr"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, 3, 0, "3rd Qtr"))
# Adding new series
series = chart.chart_data.series.add(fact.get_cell(0, 0, 1, "Series 1"), chart.type)
# Now populating series data
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_pie_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 1, 1, 20))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_pie_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 1, 50))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_pie_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 3, 1, 30))
# Not working in new version
# Adding new points and setting sector color
# series.IsColorVaried = True
chart.chart_data.series_groups[0].is_color_varied = True
point = series.data_points[0]
point.format.fill.fill_type = slides.FillType.SOLID
point.format.fill.solid_fill_color.color = draw.Color.cyan
# Setting Sector border
point.format.line.fill_format.fill_type = slides.FillType.SOLID
point.format.line.fill_format.solid_fill_color.color = draw.Color.gray
point.format.line.width = 3.0
point.format.line.style = slides.LineStyle.THIN_THICK
point.format.line.dash_style = slides.LineDashStyle.DASH_DOT
point1 = series.data_points[1]
point1.format.fill.fill_type = slides.FillType.SOLID
point1.format.fill.solid_fill_color.color = draw.Color.brown
# Setting Sector border
point1.format.line.fill_format.fill_type = slides.FillType.SOLID
point1.format.line.fill_format.solid_fill_color.color = draw.Color.blue
point1.format.line.width = 3.0
point1.format.line.style = slides.LineStyle.SINGLE
point1.format.line.dash_style = slides.LineDashStyle.LARGE_DASH_DOT
point2 = series.data_points[2]
point2.format.fill.fill_type = slides.FillType.SOLID
point2.format.fill.solid_fill_color.color = draw.Color.coral
# Setting Sector border
point2.format.line.fill_format.fill_type = slides.FillType.SOLID
point2.format.line.fill_format.solid_fill_color.color = draw.Color.red
point2.format.line.width = 2.0
point2.format.line.style = slides.LineStyle.THIN_THIN
point2.format.line.dash_style = slides.LineDashStyle.LARGE_DASH_DOT_DOT
# Create custom labels for each of categories for new series
lbl1 = series.data_points[0].label
# lbl.show_category_name = True
lbl1.data_label_format.show_value = True
lbl2 = series.data_points[1].label
lbl2.data_label_format.show_value = True
lbl2.data_label_format.show_legend_key = True
lbl2.data_label_format.show_percentage = True
lbl3 = series.data_points[2].label
lbl3.data_label_format.show_series_name = True
lbl3.data_label_format.show_percentage = True
# Showing Leader Lines for Chart
series.labels.default_data_label_format.show_leader_lines = True
# Setting Rotation Angle for Pie Chart Sectors
chart.chart_data.series_groups[0].first_slice_angle = 180
# Save presentation with chart
presentation.save("PieChart_out-3.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Line Charts
Line charts (also known as a line graphs) are best used in situations where you want demonstrate changes in value over time. Using a line chart, you can compare lots of data at once, track changes and trends over time, highlight anomalies in data series, etc.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add a chart with default data along with the desired type (in this case,
ChartType.Line). - Access the chart data IChartDataWorkbook.
- Clear the default series and categories.
- Add new series and categories.
- Add new chart data for the chart series.
- Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file
This Python code shows you how to create a line chart:
import aspose.slides as slides
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
lineChart = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(slides.charts.ChartType.LINE, 10, 50, 600, 350)
pres.save("lineChart.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
By default, points on a line chart are joined by straight continuous lines. If you want to the points to be joined by dashes instead, you can specify your preferred dash type this way:
lineChart = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(slides.charts.ChartType.LINE, 10, 50, 600, 350)
for series in lineChart.chart_data.series:
series.format.line.dash_style = slides.charts.LineDashStyle.DASH
Creating Tree Map Charts
Tree map charts are best used for sales data when you want to show the relative size of data categories and (at the same time) quickly draw attention to items that are large contributors to each category.
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add a chart with default data along with the desired type (in this case,
ChartType.TREEMAP). - Access the chart data IChartDataWorkbook.
- Clear the default series and categories.
- Add new series and categories.
- Add new chart data for the chart series.
- Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file
This Python code shows you how to create a tree map chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
chart = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.TREEMAP, 50, 50, 500, 400)
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
wb = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
wb.clear(0)
#branch 1
leaf = chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C1", "Leaf1"))
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Stem1")
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(2, "Branch1")
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C2", "Leaf2"))
leaf = chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C3", "Leaf3"))
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Stem2")
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C4", "Leaf4"))
#branch 2
leaf = chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C5", "Leaf5"))
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Stem3")
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(2, "Branch2")
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C6", "Leaf6"))
leaf = chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C7", "Leaf7"))
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Stem4")
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C8", "Leaf8"))
series = chart.chart_data.series.add(charts.ChartType.TREEMAP)
series.labels.default_data_label_format.show_category_name = True
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_treemap_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D1", 4))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_treemap_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D2", 5))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_treemap_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D3", 3))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_treemap_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D4", 6))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_treemap_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D5", 9))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_treemap_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D6", 9))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_treemap_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D7", 4))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_treemap_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D8", 3))
series.parent_label_layout = charts.ParentLabelLayoutType.OVERLAPPING
pres.save("Treemap-4.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Stock Charts
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add a chart with default data along with the desired type (ChartType.OPEN_HIGH_LOW_CLOSE).
- Access the chart data IChartDataWorkbook.
- Clear the default series and categories.
- Add new series and categories.
- Add new chart data for the chart series.
- Specify HiLowLines format.
- Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file
Sample Python code used to create a stock chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
chart = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.OPEN_HIGH_LOW_CLOSE, 50, 50, 600, 400, False)
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
wb = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, 1, 0, "A"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, 2, 0, "B"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, 3, 0, "C"))
chart.chart_data.series.add(wb.get_cell(0, 0, 1, "Open"), chart.type)
chart.chart_data.series.add(wb.get_cell(0, 0, 2, "High"), chart.type)
chart.chart_data.series.add(wb.get_cell(0, 0, 3, "Low"), chart.type)
chart.chart_data.series.add(wb.get_cell(0, 0, 4, "Close"), chart.type)
series = chart.chart_data.series[0]
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 1, 1, 72))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 2, 1, 25))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 3, 1, 38))
series = chart.chart_data.series[1]
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 1, 2, 172))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 2, 2, 57))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 3, 2, 57))
series = chart.chart_data.series[2]
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 1, 3, 12))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 2, 3, 12))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 3, 3, 13))
series = chart.chart_data.series[3]
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 1, 4, 25))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 2, 4, 38))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_stock_series(wb.get_cell(0, 3, 4, 50))
chart.chart_data.series_groups[0].up_down_bars.has_up_down_bars = True
chart.chart_data.series_groups[0].hi_low_lines_format.line.fill_format.fill_type = slides.FillType.SOLID
for ser in chart.chart_data.series:
ser.format.line.fill_format.fill_type = slides.FillType.NO_FILL
pres.save("output-5.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Box and Whisker Charts
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add a chart with default data along with the desired type (ChartType.BOX_AND_WHISKER).
- Access the chart data IChartDataWorkbook.
- Clear the default series and categories.
- Add new series and categories.
- Add new chart data for the chart series.
- Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file
This Python code shows you how to create a box and whisker chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
chart = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.BOX_AND_WHISKER, 50, 50, 500, 400)
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
wb = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
wb.clear(0)
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A1", "Category 1"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A2", "Category 1"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A3", "Category 1"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A4", "Category 1"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A5", "Category 1"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A6", "Category 1"))
series = chart.chart_data.series.add(charts.ChartType.BOX_AND_WHISKER)
series.quartile_method = charts.QuartileMethodType.EXCLUSIVE
series.show_mean_line = True
series.show_mean_markers = True
series.show_inner_points = True
series.show_outlier_points = True
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_box_and_whisker_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B1", 15))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_box_and_whisker_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B2", 41))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_box_and_whisker_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B3", 16))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_box_and_whisker_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B4", 10))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_box_and_whisker_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B5", 23))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_box_and_whisker_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B6", 16))
pres.save("BoxAndWhisker-6.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Funnel Charts
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Obtain a slide’s reference by its index.
- Add a chart with default data along with the desired type (ChartType.Funnel).
- Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file
This Python code shows you how to create a funnel chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
chart = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.FUNNEL, 50, 50, 500, 400)
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
wb = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
wb.clear(0)
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A1", "Category 1"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A2", "Category 2"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A3", "Category 3"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A4", "Category 4"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A5", "Category 5"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "A6", "Category 6"))
series = chart.chart_data.series.add(charts.ChartType.FUNNEL)
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_funnel_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B1", 50))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_funnel_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B2", 100))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_funnel_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B3", 200))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_funnel_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B4", 300))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_funnel_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B5", 400))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_funnel_series(wb.get_cell(0, "B6", 500))
pres.save("Funnel-7.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Sunburst Charts
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add a chart with default data along with the desired type (in this case,
ChartType.SUNBURST). - Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file
This Python code shows you how to create a sunburst chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
chart = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.SUNBURST, 50, 50, 500, 400)
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
wb = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
wb.clear(0)
#branch 1
leaf = chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C1", "Leaf1"))
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Stem1")
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(2, "Branch1")
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C2", "Leaf2"))
leaf = chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C3", "Leaf3"))
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Stem2")
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C4", "Leaf4"))
#branch 2
leaf = chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C5", "Leaf5"))
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Stem3")
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(2, "Branch2")
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C6", "Leaf6"))
leaf = chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C7", "Leaf7"))
leaf.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Stem4")
chart.chart_data.categories.add(wb.get_cell(0, "C8", "Leaf8"))
series = chart.chart_data.series.add(charts.ChartType.SUNBURST)
series.labels.default_data_label_format.show_category_name = True
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_sunburst_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D1", 4))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_sunburst_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D2", 5))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_sunburst_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D3", 3))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_sunburst_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D4", 6))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_sunburst_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D5", 9))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_sunburst_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D6", 9))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_sunburst_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D7", 4))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_sunburst_series(wb.get_cell(0, "D8", 3))
pres.save("Sunburst-8.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Histogram Charts
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add some chart with some data and specify your preferred chart type (
ChartType.HISTOGRAMin this case). - Access the chart data
IChartDataWorkbook. - Clear the default series and categories.
- Add new series and categories.
- Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file
This Python code shows you how to create an histogram chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
chart = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.HISTOGRAM, 50, 50, 500, 400)
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
wb = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
wb.clear(0)
series = chart.chart_data.series.add(charts.ChartType.HISTOGRAM)
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_histogram_series(wb.get_cell(0, "A1", 15))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_histogram_series(wb.get_cell(0, "A2", -41))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_histogram_series(wb.get_cell(0, "A3", 16))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_histogram_series(wb.get_cell(0, "A4", 10))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_histogram_series(wb.get_cell(0, "A5", -23))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_histogram_series(wb.get_cell(0, "A6", 16))
chart.axes.horizontal_axis.aggregation_type = charts.AxisAggregationType.AUTOMATIC
pres.save("Histogram-9.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Radar Charts
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add a chart with some data and specify your preferred chart type (
ChartType.RADARin this case). - Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file
This Python code shows you how to create a radar chart:
import aspose.slides as slides
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(slides.charts.ChartType.RADAR, 20, 20, 400, 300)
pres.save("Radar-chart.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Multi Category Charts
- Create an instance of the Presentation class.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Add a chart with default data along with the desired type (ChartType.ClusteredColumn).
- Access the chart data IChartDataWorkbook.
- Clear the default series and categories.
- Add new series and categories.
- Add new chart data for the chart series.
- Write the modified presentation to a PPTX file.
This Python code shows you how to create a multicategory chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
slide = pres.slides[0]
ch = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.CLUSTERED_COLUMN, 100, 100, 600, 450)
ch.chart_data.series.clear()
ch.chart_data.categories.clear()
fact = ch.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
fact.clear(0)
defaultWorksheetIndex = 0
category = ch.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, "c2", "A"))
category.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Group1")
category = ch.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, "c3", "B"))
category = ch.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, "c4", "C"))
category.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Group2")
category = ch.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, "c5", "D"))
category = ch.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, "c6", "E"))
category.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Group3")
category = ch.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, "c7", "F"))
category = ch.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, "c8", "G"))
category.grouping_levels.set_grouping_item(1, "Group4")
category = ch.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, "c9", "H"))
# Adding Series
series = ch.chart_data.series.add(fact.get_cell(0, "D1", "Series 1"), charts.ChartType.CLUSTERED_COLUMN)
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, "D2", 10))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, "D3", 20))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, "D4", 30))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, "D5", 40))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, "D6", 50))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, "D7", 60))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, "D8", 70))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, "D9", 80))
# Save presentation with chart
pres.save("AsposeChart_out-10.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Map Charts
A map chart is a visualization of an area containing data. Map charts are best used to compare data or values across geographical regions.
This Python code shows you how to create a map chart:
import aspose.slides as slides
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
chart = pres.slides[0].shapes.add_chart(slides.charts.ChartType.MAP, 50, 50, 500, 400, False)
pres.save("mapChart.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Creating Combination Charts
A combination chart (or combo chart) is a chart that combines two or more charts on a single graph. Such a chart allows you to highlight, compare, or review differences between two (or more) sets of data. This way, you see the relationship (if any) between the sets of data.
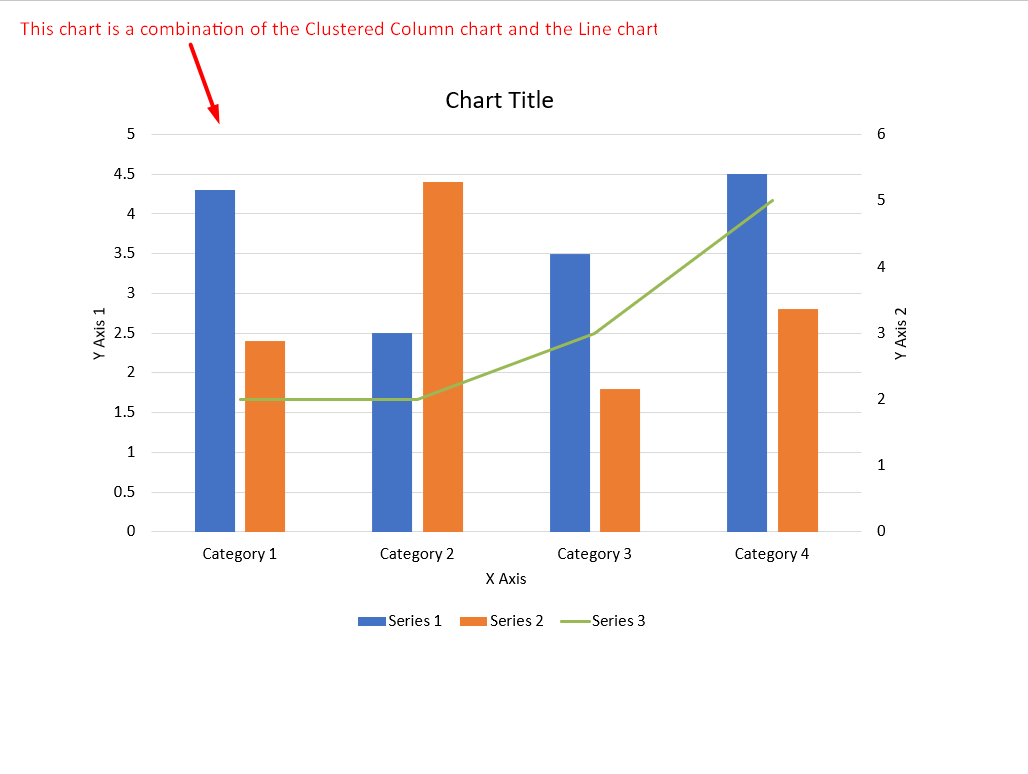
This Python code shows you how to create a combination chart in PowerPoint:
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
def create_combo_chart():
pres = slides.Presentation()
chart = create_chart(pres.slides[0])
add_first_series_to_chart(chart)
add_second_series_to_chart(chart)
pres.save("combo-chart.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
def create_chart(slide):
chart = slide.shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.CLUSTERED_COLUMN, 50, 50, 500, 400)
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
workbook = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
worksheet_index = 0
chart.chart_data.series.add(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 0, 1, "Series 1"), chart.type)
chart.chart_data.series.add(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 0, 2, "Series 2"), chart.type)
chart.chart_data.categories.add(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 1, 0, "Caetegoty 1"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 2, 0, "Caetegoty 2"))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 3, 0, "Caetegoty 3"))
series = chart.chart_data.series[0]
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 1, 1, 20))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 2, 1, 50))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 3, 1, 30))
series = chart.chart_data.series[1]
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 1, 2, 30))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 2, 2, 10))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 3, 2, 60))
return chart
def add_first_series_to_chart(chart):
workbook = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
worksheet_index = 0
series = chart.chart_data.series.add(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 0, 3, "Series 3"), charts.ChartType.SCATTER_WITH_SMOOTH_LINES)
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 0, 1, 3), workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 0, 2, 5))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 1, 3, 10), workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 1, 4, 13))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 2, 3, 20), workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 2, 4, 15))
series.plot_on_second_axis = True
def add_second_series_to_chart(chart):
workbook = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
worksheet_index = 0
series = chart.chart_data.series.add(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 0, 5, "Series 4"), charts.ChartType.SCATTER_WITH_STRAIGHT_LINES_AND_MARKERS)
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 1, 3, 5), workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 1, 4, 2))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 1, 5, 10), workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 1, 6, 7))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 2, 5, 15), workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 2, 6, 12))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_scatter_series(workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 3, 5, 12), workbook.get_cell(worksheet_index, 3, 6, 9))
series.plot_on_second_axis = True
Updating Charts
- Instantiate a Presentation class that represents the presentation containing the chart.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Traverse through all shapes to find the desired chart.
- Access the chart data worksheet.
- Modify the chart data series data by changing series values.
- Add a new series and populate the data in it.
- Write the modified presentation as a PPTX file.
This Python code shows you how to update a chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
# Instantiate Presentation class that represents PPTX file
with slides.Presentation(path + "ExistingChart.pptx") as pres:
# Access first slideMarker
sld = pres.slides[0]
# Add chart with default data
chart = sld.shapes[0]
# Setting the index of chart data sheet
defaultWorksheetIndex = 0
# Getting the chart data worksheet
fact = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
# Changing chart Category Name
fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 1, 0, "Modified Category 1")
fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 0, "Modified Category 2")
# Take first chart series
series = chart.chart_data.series[0]
# Now updating series data
fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 0, 1, "New_Series1")# Modifying series name
series.data_points[0].value.data = 90
series.data_points[1].value.data = 123
series.data_points[2].value.data = 44
# Take Second chart series
series = chart.chart_data.series[1]
# Now updating series data
fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 0, 2, "New_Series2")# Modifying series name
series.data_points[0].value.data = 23
series.data_points[1].value.data = 67
series.data_points[2].value.data = 99
# Now, Adding a new series
chart.chart_data.series.add(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 0, 3, "Series 3"), chart.type)
# Take 3rd chart series
series = chart.chart_data.series[2]
# Now populating series data
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 1, 3, 20))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 2, 3, 50))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_bar_series(fact.get_cell(defaultWorksheetIndex, 3, 3, 30))
chart.type = charts.ChartType.CLUSTERED_CYLINDER
# Save presentation with chart
pres.save("AsposeChartModified_out-11.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Setting Data Range for Charts
- Instantiate a Presentation class that represents the presentation containing the chart.
- Get a slide’s reference through its index.
- Traverse through all shapes to find the desired chart.
- Access the chart data and set the range.
- Save the modified presentation as a PPTX file.
This Python code shows you how to set the data range for a chart:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
# Instantiate Presentation class that represents PPTX file
with slides.Presentation(path + "ExistingChart.pptx") as presentation:
# Access first slideMarker and add chart with default data
slide = presentation.slides[0]
chart = slide.shapes[0]
chart.chart_data.set_range("Sheet1!A1:B4")
presentation.save("SetDataRange_out-12.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)
Using Default Markers in Charts
When you use a default marker in charts, each chart series get different default marker symbols automatically.
This Python code shows you how to set a chart series market automatically:
import aspose.slides.charts as charts
import aspose.slides as slides
import aspose.pydrawing as draw
with slides.Presentation() as pres:
slide = pres.slides[0]
chart = slide.shapes.add_chart(charts.ChartType.LINE_WITH_MARKERS, 10, 10, 400, 400)
chart.chart_data.series.clear()
chart.chart_data.categories.clear()
fact = chart.chart_data.chart_data_workbook
chart.chart_data.series.add(fact.get_cell(0, 0, 1, "Series 1"), chart.type)
series = chart.chart_data.series[0]
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, 1, 0, "C1"))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_line_series(fact.get_cell(0, 1, 1, 24))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, 2, 0, "C2"))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_line_series(fact.get_cell(0, 2, 1, 23))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, 3, 0, "C3"))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_line_series(fact.get_cell(0, 3, 1, -10))
chart.chart_data.categories.add(fact.get_cell(0, 4, 0, "C4"))
series.data_points.add_data_point_for_line_series(fact.get_cell(0, 4, 1, None))
chart.chart_data.series.add(fact.get_cell(0, 0, 2, "Series 2"), chart.type)
#Take second chart series
series2 = chart.chart_data.series[1]
#Now populating series data
series2.data_points.add_data_point_for_line_series(fact.get_cell(0, 1, 2, 30))
series2.data_points.add_data_point_for_line_series(fact.get_cell(0, 2, 2, 10))
series2.data_points.add_data_point_for_line_series(fact.get_cell(0, 3, 2, 60))
series2.data_points.add_data_point_for_line_series(fact.get_cell(0, 4, 2, 40))
chart.has_legend = True
chart.legend.overlay = False
pres.save("DefaultMarkersInChart-13.pptx", slides.export.SaveFormat.PPTX)