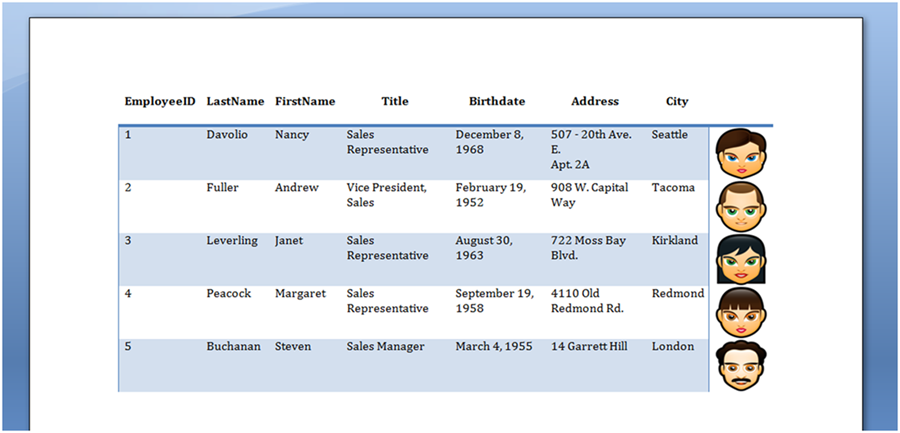
Construye una tabla a partir de DataTable
A menudo, su aplicación extraerá datos de una base de datos y los almacenará en forma de DataTable. Es posible que desee insertar fácilmente estos datos en su documento como una nueva tabla y aplicar formato rápidamente a toda la tabla.
Tenga en cuenta que la forma preferida de insertar datos de
DataTable en una tabla de documentos es mediante el uso de
Mail Merge con Regiones. La técnica presentada en este artículo solo se sugiere si no puede crear una plantilla adecuada de antemano para fusionar datos, en otras palabras, si requiere que todo suceda mediante programación.
Usando Aspose.Words, puede recuperar fácilmente datos de una base de datos y almacenarlos como una tabla:
- Cree un nuevo objeto DocumentBuilder en su Document.
- Inicie una nueva tabla usando DocumentBuilder.
- Si queremos insertar los nombres de cada una de las columnas de nuestro DataTable como fila de encabezado, itere a través de cada columna de datos y escriba los nombres de las columnas en una fila de la tabla.
- Iterar a través de cada DataRow en el DataTable:
- Iterar a través de cada objeto en el DataRow.
- Inserte el objeto en el documento usando DocumentBuilder. El método utilizado depende del tipo de objeto que se inserte, por ejemplo, DocumentBuilder.writeln() para texto y DocumentBuilder.insertImage() para una matriz de bytes que representa una imagen.
- Al final del procesamiento de la fila de datos, también finaliza la fila creada por DocumentBuilder usando DocumentBuilder.endRow().
- Una vez que se hayan procesado todas las filas de DataTable, finalice la tabla llamando a DocumentBuilder.endTable().
- Finalmente, podemos establecer el estilo de tabla deseado usando una de las propiedades de tabla apropiadas, como Table.getStyleIdentifier(), para aplicar formato automáticamente a toda la tabla.
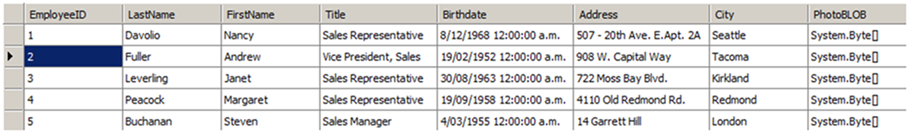
Los siguientes datos en nuestro DataTable se usan en este ejemplo:
El siguiente ejemplo de código muestra cómo ejecutar el algoritmo anterior en Aspose.Words:
Luego, se puede llamar fácilmente al método usando su DocumentBuilder y sus datos.
El siguiente ejemplo de código muestra cómo importar los datos de un DataTable e insertarlos en una nueva tabla del documento:
La tabla que se muestra en la imagen a continuación se produce ejecutando el código anterior.