Construir uma tabela a partir de um DataTable
Muitas vezes, seu aplicativo extrai dados de um banco de dados e os armazena na forma de DataTable. Poderá querer inserir facilmente estes dados no seu documento como uma nova tabela e aplicar rapidamente a formatação a toda a tabela.
Observe que a maneira preferida de inserir dados de um
DataTable em uma tabela de documentos é usando
Mail Merge com regi. A técnica apresentada neste artigo só é sugerida se não for possível criar previamente um modelo adequado para fundir os dados, ou seja, se exigir que tudo aconteça de forma programática.
Usando Aspose.Words, você pode facilmente recuperar dados de um banco de dados e armazená-los como uma tabela:
- Crie um novo objeto DocumentBuilder no seu Document.
- Inicie uma nova tabela usando DocumentBuilder.
- Se quisermos inserir os nomes de cada uma das colunas do nosso DataTable como uma linha de cabeçalho, em seguida, iterar através de cada coluna de dados e escrever os nomes das colunas em uma linha na tabela.
- Iterar através de cada DataRow no DataTable:
- Iterar através de cada objecto no DataRow.
- Insira o objecto no documento utilizando DocumentBuilder. O método utilizado depende do tipo do objecto que está a ser inserido, por exemplo, DocumentBuilder.writeln() para texto e DocumentBuilder.insertImage() para uma matriz de bytes que representa uma imagem.
- No final do processamento da linha de dados, também termina a linha que está sendo criada pelo DocumentBuilder Usando DocumentBuilder.endRow().
- Uma vez que todas as linhas do DataTable tenham sido processadas, termine a tabela chamando DocumentBuilder.endTable().
- Finalmente, podemos definir o estilo de tabela desejado usando uma das propriedades de tabela apropriadas, como Table.getStyleIdentifier(), para aplicar automaticamente a formatação a toda a tabela.
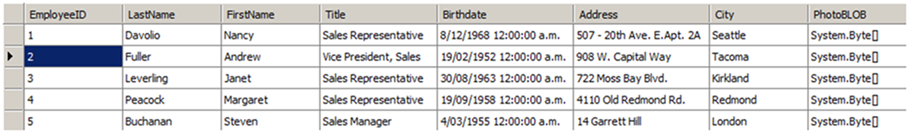
Os seguintes dados em nosso DataTable são usados neste exemplo:
O exemplo de código a seguir mostra como executar o algoritmo acima em Aspose.Words:
O método pode então ser facilmente chamado usando seu DocumentBuilder e dados.
O exemplo de código a seguir mostra como importar os dados de um DataTable e inseri - los em uma nova tabela no documento:
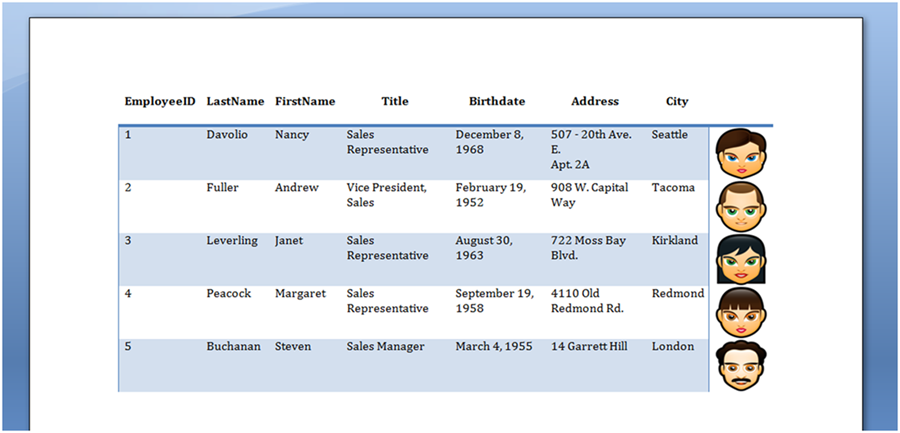
A tabela mostrada na figura abaixo é produzida executando o código acima.