Hello, world!
In this article, you will learn how to build a bare minimum console application for extracting text from an image with with Aspose.OCR for C++.
You will need
- A compatible system with Microsoft Visual Studio installed. As an individual developer, you can use a free Visual Studio Community Edition.
- Some image containing a text. You can simply download the one from the article.
- 5 minutes of spare time.
Preparing
-
Create a new C++ project in Visual Studio. You can use a very basic project template, such as Console App.
-
Install Aspose.OCR.Cpp (CPU-based) NuGet package to the project. This may take up to several minutes depending on your internet connection.
-
Download this sample image somewhere to your computer under the name
source.png:
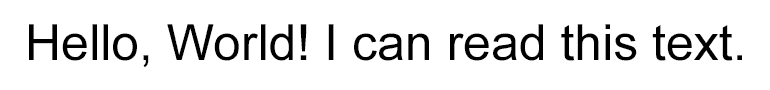
For simplicity, this example assumes that the recognized image is located in the application’s working directory. It depends on how you run the application:
- Project directory, if you run the application directly from Visual Studio (Local Windows Debugger).
- x64\Debug subfolder in the project directory if you plan to run the compiled application. If this folder does not exist, run the application first.
Coding
-
Include the required header files to the project:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <aspose_ocr.h> -
Declare the following statement to use names for objects and variables from the standard library without mentioning
std::every time:using namespace std;The statement
using namespace stdis generally considered bad practice. In this basic example, it is only used to improve the readability of the code.When developing production applications, specify the namespace to which the identifier belongs using the scope operator(::) each time you declare a type.
-
Provide the recognized image by file path:
string file = "source.png"; AsposeOCRInput source; source.url = file.c_str(); vector<AsposeOCRInput> content = {source};The image file will be searched in the application’s working directory (see the note in Preparing section).
Alternatively, you can specify the full image path (for example,
string file = "C:\\source.png";) or calculate it in the runtime. -
Specify the recognition language
RecognitionSettings settings; settings.language_alphabet = language::eng; -
Extract text from the image:
AsposeOCRRecognitionResult result = asposeocr_recognize(content.data(), content.size(), settings); -
Output the recognized text:
size_t size = 0; wchar_t* buffer = asposeocr_serialize_result(result, size); wcout << wstring(buffer) << endl; -
Release the resources
asposeocr_free_result(result);
Full code
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <aspose_ocr.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Provide the image for recognition
string file = "source.png";
AsposeOCRInput source;
source.url = file.c_str();
vector<AsposeOCRInput> content = {source};
// Set recognition language
RecognitionSettings settings;
settings.language_alphabet = language::eng;
// Extract text from the image
AsposeOCRRecognitionResult result = asposeocr_recognize(content.data(), content.size(), settings);
// Output the recognized text
size_t size = 0;
wchar_t* buffer = asposeocr_serialize_result(result, size);
wcout << wstring(buffer) << endl;
// Release the resources
asposeocr_free_result(result);
}
Running
Run the program. You will see extracted text in the console output:
Hello. World! I can read this text
What’s next
Congratulations! You have performed OCR on an image and extracted the machine-readable text from it. Read the Developer reference and API reference for details on developing advanced applications with Aspose.OCR for C++.