Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
Aspose.SVG for .NET allows you to create various lighting effects to enhance the visual appeal of graphics and illustrations. Lighting effects can add depth, realism, and a sense of lighting to flat images. The lighting effect is created in SVG using a set of filters. Consider some of them: <feSpecularLighting>, and <fePointLight>. You can combine several filters, create and control the details for a lighting effect.
In this article, you will learn how to write SVG code to create SVG lighting effects and consider detailed C# examples of using the Aspose.Svg.Filters namespace to apply the lighting effects to SVG elements or bitmaps.
The <fePointLight> filter defines a light source that sets a point light effect. It can be used within the <feDiffuseLighting> or <feSpecularLighting> primitive as a child. Specific attributes x, y, and z indicate the position of the point light source. The <feSpecularLighting> filter lights an image using its alpha channel as a bump map. Consider an SVG example of a light effect:
1<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
2 <rect x="40" y="40" width="150" height="150" fill="Teal" filter="url(#light)"/>
3 <defs>
4 <filter id="light">
5 <feGaussianBlur in="SourceAlpha" stdDeviation="5" result="blur"/>
6 <feSpecularLighting in="blur" result="light" specularExponent="30" lighting-color="#ddd">
7 <fePointLight x="70" y="70" z="150"/>
8 </feSpecularLighting>
9 <feComposite in="SourceGraphic" in2="light" operator="arithmetic" k1="0" k2="1" k3="1" k4="0"/>
10 </filter>
11 </defs>
12</svg>In this example, four SVG filters are applied to create the light effect (figure b):
<feGaussianBlur> takes input SourceAlpha, which is the alpha channel of the source image. The result is stored in a temporary buffer named "blur".<feSpecularLighting> and <fePointLighting> filter primitives. The <feSpecularLighting> uses buffer "blur" as a model of a surface elevation and generates a lighting effect from a point source that sets in the <fePointLighting> filter. The result is stored in buffer "light".<feComposite> filter takes two inputs in ="SourceGraphic" and in2 ="light" and combines them using the arithmetic composition operation. The output from the arithmetic operator for each result pixel is computed as k1·in1·in2 + k2·in1 + k3·in2 + k4If we remove the Gaussian blur filter in the code for the “light” filter (figure b), we get the following “flat-light” filter, which gives a flatter light (figure c):
1<filter id="flat-light">
2 <feSpecularLighting result="light" specularExponent="30" lighting-color="#ddd">
3 <fePointLight x="70" y="70" z="150"/>
4 </feSpecularLighting>
5 <feComposite in="SourceGraphic" in2="light" operator="arithmetic" k1="0" k2="1" k3="1" k4="0"/>
6</filter>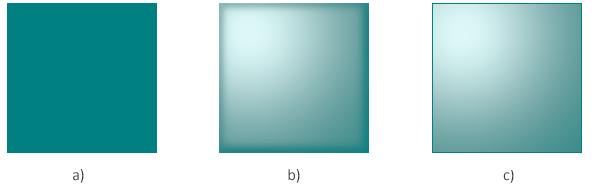
The following C# code snippet shows how to create the same SVG lighting effect (“light” filter) as in the above SVG code. Let’s consider the C# code step by step:
RootElement property of the SVGDocument class points to the document’s root <svg> element.<defs> element and add it to the <svg> element:namespaceURI, qualifiedName) method to create an instance of the
SVGDefsElement class.<defs> element to the <svg> element.<filter> element, set an id attribute, and add <filter> to the <defs> element:filterElement.Id for the <filter> element. Use the
Id property of the SVGElement class.<filter> to the <defs> element.<feGaussianBlur> element and set in, result, and stdDeviation attributes. Then add it to the <filter> element.name, value) method to set in1 and result attributes.<feGaussianBlur> to the <filter> element.<feSpecularLighting>, <fePointLight>, and <feComposite> elements in the same way. Specify their required attributes and add these elements in the correct order to the filter.<rect> element with attributes and add it to the <svg> element:filter attribute referring to the url name of an id attribute in filterElement allows applying the SVG lighting effect to the rectangle.rectElement to svgElement, you can use the AppendChild() method.1using Aspose.Svg;
2using System.IO;
3using Aspose.Svg.Filters; 1// Create an SVG <rect> with specular lighting effect using filters in C#
2
3// Set SVG Namespace Url
4string SvgNamespace = "http://www.w3.org/2000/svg";
5
6// Initialize an SVG document
7using (SVGDocument document = new SVGDocument())
8{
9 SVGSVGElement svgElement = document.RootElement;
10
11 // Create a <defs> element and add to the svgElement
12 SVGDefsElement defsElement = (SVGDefsElement)document.CreateElementNS(SvgNamespace, "defs");
13 svgElement.AppendChild(defsElement);
14
15 // Create a <filter> element and add to the defsElement
16 SVGFilterElement filterElement = (SVGFilterElement)document.CreateElementNS(SvgNamespace, "filter");
17 filterElement.Id = "light";
18 defsElement.AppendChild(filterElement);
19
20 // Create a <feGaussianBlur> element and add to the filterElement
21 SVGFEGaussianBlurElement feGaussianBlurElement = (SVGFEGaussianBlurElement)document.CreateElementNS(SvgNamespace, "feGaussianBlur");
22 feGaussianBlurElement.StdDeviationX.BaseVal = 5;
23 feGaussianBlurElement.StdDeviationY.BaseVal = 5;
24 feGaussianBlurElement.SetAttribute("in1", "SourceAlpha");
25 feGaussianBlurElement.SetAttribute("result", "blur");
26 filterElement.AppendChild(feGaussianBlurElement);
27
28 // Create a feSpecularLighting filter primitive and add it to the filterElement
29 SVGFESpecularLightingElement feSpecularLightingElement = (SVGFESpecularLightingElement)document.CreateElementNS(SvgNamespace, "feSpecularLighting");
30 feSpecularLightingElement.In1.BaseVal = "blur";
31 feSpecularLightingElement.SetAttribute("result", "light");
32 feSpecularLightingElement.SetAttribute("specularExponent", "30");
33 feSpecularLightingElement.SetAttribute("lighting-color", "#ddd");
34 filterElement.AppendChild(feSpecularLightingElement);
35
36 // Create a fePointLight filter primitive and add it to the feSpecularLighting element
37 SVGFEPointLightElement fePointLightElement = (SVGFEPointLightElement)document.CreateElementNS(SvgNamespace, "fePointLight");
38 fePointLightElement.SetAttribute("x", "70");
39 fePointLightElement.SetAttribute("y", "70");
40 fePointLightElement.SetAttribute("z", "150");
41 feSpecularLightingElement.AppendChild(fePointLightElement);
42
43 // Create a feComposite filter primitive and add it to the filterElement
44 SVGFECompositeElement feCompositeElement = (SVGFECompositeElement)document.CreateElementNS(SvgNamespace, "feComposite");
45 feCompositeElement.In1.BaseVal = "SourceGraphic";
46 feCompositeElement.In2.BaseVal = "light";
47 feCompositeElement.SetAttribute("operator", "arithmetic");
48 feCompositeElement.SetAttribute("k1", "0");
49 feCompositeElement.SetAttribute("k2", "1");
50 feCompositeElement.SetAttribute("k3", "1");
51 feCompositeElement.SetAttribute("k4", "0");
52 filterElement.AppendChild(feCompositeElement);
53
54 // Create a <rect> element and set the "fill" and "filter" attributes
55 SVGRectElement rectElement = (SVGRectElement)document.CreateElementNS(SvgNamespace, "rect");
56 rectElement.X.BaseVal.Value = 40;
57 rectElement.Y.BaseVal.Value = 40;
58 rectElement.Width.BaseVal.Value = 150;
59 rectElement.Height.BaseVal.Value = 150;
60 rectElement.SetAttribute("fill", "Teal");
61 rectElement.SetAttribute("filter", "url(#light)");
62 svgElement.InsertBefore(rectElement, svgElement.FirstChild);
63
64 // Save the document
65 document.Save(Path.Combine(OutputDir, "svg-lighting-effect.svg"));
66}The resulting image, lighting-effect.svg, looks exactly like the figure b above.
See also
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.