Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.
In today’s world, most documents are in A4 format, but sometimes content rendered from HTML is a different size. This results in a lot of white space on the page, or the content just won’t fit on the page! In this article, we will consider how to use rendering options to resize document pages to the size of the content and vice versa.
The Aspose.Html.Rendering namespace provides a powerful set of tools such as low-level options classes, interfaces, structures, and enumerations for rendering HTML, MHTML, EPUB, and SVG documents to different output formats such as PDF, XPS, DOCX, and images. The PageSize class of provides a way to specify the width, height, and orientation of the pages when rendering HTML documents to output formats. But sometimes, you may need to crop documents to create a smaller page size that fits the page’s content size. This means the outer margins, borders, or empty space will be removed.
The PageSetup class provides a set of properties to manage the page setup settings for HTML documents when rendering them to different file formats. Let’s take a look at some of the more used ones:
You can easily use C# examples of converting HTML to Images with a custom page layout to convert HTML to PDF, XPS, and DOCX. The only differences are in specifying
To convert HTML to PNG with default rendering options, you should follow a few steps:
document instance. In the following examples, we load the local
rendering.html file.ImageFormat is PNG. Also, note that by default HorizontalResolution and VerticalResolution properties are 300 dpi. So, the rendered image will be stretched in height and width by about 3 times since the source content’s resolution is 96 dpi.options and output file path savePath as parameters.device object as a parameter.Further, the fragment of C# code shows an example of converting an HTML document to an image without any additional options, i.e. with default rendering options. As a result of the conversion, an A4 PNG document was obtained with a lot of empty space (see illustrations of conversion results (a).)
1// Render HTML to PDF with default RenderingOptions
2
3// Prepare path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "rendering.html");
5
6// Prepare path for converted file saving
7string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "a4.png");
8
9// Create an instance of the HTMLDocument class
10using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
11
12// Initialize an ImageRenderingOptions object with default options
13ImageRenderingOptions opt = new ImageRenderingOptions();
14
15// Create an output rendering device and convert HTML
16using ImageDevice device = new ImageDevice(opt, savePath);
17document.RenderTo(device);PageLayoutOptions enumeration of the Aspose.Html.Rendering namespace specifies flags that, together with other PageSetup options, determine sizes and layouts of pages. These flags can be combined together according to their descriptions.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| FitToContentWidth | This flag specifies that the width of pages is determined by the size of the content itself and not by the set page width. Instead, content width is calculated individually for each page. |
| UseWidestPage | When combined with FitToContentWidth, it specifies that the width of each page will be the same and equal to the widest content size of all pages. |
| FitToWidestContentWidth | This flag specifies that the width of each page will be the same and equal to the widest content size among all pages. |
| FitToContentHeight | This flag specifies that the page height is determined by the content’s size, not by the specified page height. If this flag is set, all document content will be placed on one page. |
| ScaleToPageWidth | This flag indicates that the document’s content will be scaled to fit the page. It collides with the FitToContentWidth flag, and if both flags are specified, only ScaleToPageWidth will take effect. |
| ScaleToPageHeight | This flag indicates that the document’s content will be scaled to fit the height of the first page. It collides with the FitToContentHeight flag, and if both flags are specified, only ScaleToPageHeight will take effect. All document content will be placed on a single page only. |
In order to fit page width of the output image to the width of the content, you need to use the FitToContentWidth flag, or the FitToWidestContentWidth flag, which will fit the width of the resulting document to the width of the widest page. Let’s look at the steps you should follow:
documentPath) constructor loads the HTML document from a local file system.FitToWidestContentWidth, which means that the output document’s page width will fit the widest content page’s width. 1// Render HTML to image with width fitting in C#
2
3// Prepare path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "rendering.html");
5
6// Prepare path for converted file saving
7string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "FitWidth.jpg");
8
9// Create an instance of HTMLDocument class
10using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
11
12// Initialize an ImageRenderingOptions object with custom options. Use the FitToWidestContentWidth flag
13ImageRenderingOptions opt = new ImageRenderingOptions(ImageFormat.Jpeg)
14{
15 PageSetup =
16 {
17 PageLayoutOptions = PageLayoutOptions.FitToWidestContentWidth
18 }
19};
20
21// Create an output rendering device and convert HTML
22using ImageDevice device = new ImageDevice(opt, savePath);
23document.RenderTo(device);The HTML to JPG conversion resulted in a JPG document with a page width that fits the width of the content, but with a page height that matches the height of the format A4 (see illustrations of conversion results (b)).
To make the output page size match the height of the image in the source file, you must set the FitToContentHeight flag in the
PageLayoutOptions property. The following example shows a combination of two flags, FitToContentHeight and FitToContentWidth.
1// Fit HTML to content size when rendering to image in C#
2
3// Prepare path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "rendering.html");
5
6// Prepare path for converted file saving
7string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "FitPage.png");
8
9// Create an instance of the HTMLDocument class
10using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
11
12// Initialize an ImageRenderingOptions object with custom options. Use FitToContentWidth and FitToContentHeight flags
13ImageRenderingOptions opt = new ImageRenderingOptions()
14{
15 PageSetup =
16 {
17 PageLayoutOptions = PageLayoutOptions.FitToContentWidth | PageLayoutOptions.FitToContentHeight
18 },
19 HorizontalResolution=96,
20 VerticalResolution=96
21};
22
23// Create an output rendering device and convert HTML
24using ImageDevice device = new ImageDevice(opt, savePath);
25document.RenderTo(device);In the following example, the
AnyPage property sets the page size to 20x20 px, which is not large enough to fit the HTML document’s content when rendered to an image. Using PageLayoutOptions with the FitToWidestContentWidth and FitToContentHeight flags causes the page to grow in size to fit the content.
rendering.html file.ImageFormat as Jpeg.PageSetup object with the PageLayoutOptions property with the FitToWidestContentWidth and FitToContentHeight flags set. This ensures that the output image will fit the width and height of the content without any empty space.device object as a parameter. 1// Render HTML to image with small custom page size
2
3// Prepare path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "rendering.html");
5
6// Prepare path for converted file saving
7string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "FitSmallPage.jpg");
8
9// Initialize HTMLDocument
10using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
11
12// Initialize an ImageRenderingOptions object with custom options. Use FitToWidestContentWidth and FitToContentHeight flags
13ImageRenderingOptions opt = new ImageRenderingOptions(ImageFormat.Jpeg)
14{
15 PageSetup =
16 {
17 PageLayoutOptions = PageLayoutOptions.FitToWidestContentWidth | PageLayoutOptions.FitToContentHeight,
18 AnyPage = new Page(new Size(20,20))
19 }
20};
21
22// Create an output rendering device and convert HTML
23using ImageDevice device = new ImageDevice(opt, savePath);
24document.RenderTo(device);Despite setting the page size as 20x20 pixels, the FitToWidestContentWidth and FitToContentHeight flags allow us to fit the resulting JPG document would have a page size that fits the content size (see the
illustration of conversion results (d)).
By analogy with the FitTo* flags that control page sizes, there is a set of ScaleTo* flags that control content sizes and allow to scale it. If the content size exceeds the page size, the content is scaled with aspect ratio until it fits on the page in width and/or height, depending on the combination of flags. The following example shows how to set the width and height scaling of content:
1// Scale HTML content to fixed page size
2
3// Prepare path to a source HTML file
4string documentPath = Path.Combine(DataDir, "rendering.html");
5
6// Prepare path for converted file saving
7string savePath = Path.Combine(OutputDir, "ScaleSmallPage.png");
8
9// Initialize an HTMLDocument object
10using HTMLDocument document = new HTMLDocument(documentPath);
11
12// Initialize an ImageRenderingOptions object and use ScaleToPageWidth and ScaleToPageHeight flags
13ImageRenderingOptions opt = new ImageRenderingOptions()
14{
15 PageSetup =
16 {
17 PageLayoutOptions = PageLayoutOptions.ScaleToPageWidth | PageLayoutOptions.ScaleToPageHeight,
18 AnyPage = new Page(new Size(200,200))
19 }
20};
21
22// Create an output rendering device and convert HTML
23using ImageDevice device = new ImageDevice(opt, savePath);
24document.RenderTo(device);In the example, the
AnyPage property of the PageSetup sets a new
Page object with a Size of 200x200 pixels. This sets the page size to 200x200 pixels.
Then we set the
PageLayoutOptions property of the PageSetup object to include the ScaleToPageWidth and ScaleToPageHeight flags. This means that the output document content will be scaled to fit within the page’s width and/or height (see the
illustration of conversion results (e).)
The figure shows the results of converting the rendering.html file to PNG, JPG, and PDF formats using the RenderTo() method and various rendering options that control the page size of the output document.
Note: The source image size in rendering.html file is 404x303, with a resolution of 96 dpi.
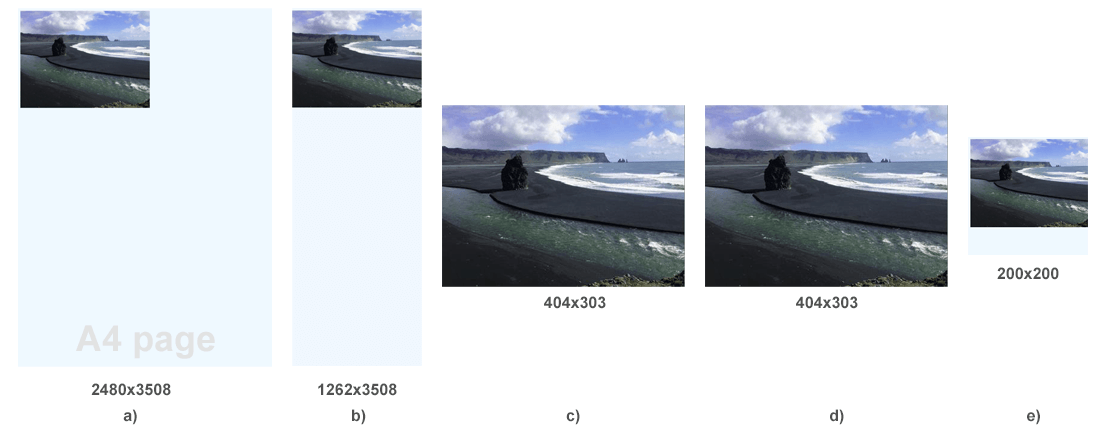
a) The result of HTML to PNG conversion with default rendering options is an A4 page size PNG document with a lot of empty space on it. The rendered image on the A4 page is stretched in height and width by about 3 times since the default resolution is 300 dpi.
b) The HTML to JPG conversion resulted in a JPG document with a page width that fits the width of the content, but with a page height that matches the height of the format A4. The rendered image on the A4 page is stretched in height and width by about 3 times since the default resolution is 300 dpi.
c) The result of converting HTML to PNG with cropping the output document to fit the page size to the size of the content.
d) Even though the page size was set as 20x20 px, using the FitToWidestContentWidth and FitToContentHeight flags made it possible to get the resulting JPG document with a page size that fits the size of the content.
e) The result of rendering HTML to image when the content size is larger than the page size. We scaled down the content to fit the page size of 200x200 px.
You can download the complete C# examples and data files from GitHub.
Aspose.HTML offers free online Converters for converting HTML, XHTML, MHTML, EPUB, XML, and Markdown files to various popular formats. For example, you can easily convert HTML to PDF, HTML to JPG, HTML to XHTML, SVG to PDF, MHTML to PDF, MD to HTML, etc. Just select a file, choose the format to convert, and you’re done. It’s fast and completely free!
Analyzing your prompt, please hold on...
An error occurred while retrieving the results. Please refresh the page and try again.